CompTIA Linux+ Exam 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년11월17일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 CompTIA XK0-005 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 XK0-005 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 136개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
The ip link show eth1 command can be used to check the link status of a network interface named eth1 in a Linux server. It will display information such as the MAC address, MTU, state, and flags of the interface. The ifconfig hw eth1 command is invalid, as hw is not a valid option for ifconfig. The netstat -r eth1 command would display the routing table for eth1, not the link status. The ss -ti eth1 command would display TCP information for sockets associated with eth1, not the link status. CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 13: Networking Fundamentals, page 436.
정답:
Explanation:
The systemct1 reload sshd command can be used to apply the configuration changes of the SSH server daemon without restarting it. This is useful to avoid interrupting existing connections. The systemct1 stop sshd command would stop the SSH server daemon, not apply the changes. The systemct1 mask sshd command would prevent the SSH server daemon from being started, not apply the changes. The systemct1 start sshd command would start the SSH server daemon if it is not running, but it would not apply the changes if it is already running. CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 12: Secure Shell (SSH), page 415.
정답:
Explanation:
The ~/.ssh/config file can be used to set various options for SSH connections, including the port number, for specific hosts or groups of hosts. This file is located in the user’s home directory and affects only the current user. The /etc/ssh/sshd_config file is used to configure the SSH server daemon, not the client. The /etc/ssh/moduli file contains parameters for Diffie-Hellman key exchange, not port settings. The ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file contains public keys for authentication, not port settings. CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 12: Secure Shell (SSH), page 414.
정답:
Explanation:
The file that will need to be modified for the server to be able to boot again is /etc/fstab. The /etc/fstab file is a file that contains the information about the file systems that are mounted at boot time on Linux systems. The file specifies the device name, mount point, file system type, mount options, dump frequency, and pass number for each file system. The error message indicates that the dependency failed for /data, which is a mount point for a file system. This means that the system could not mount the /data file system at boot time, which caused the system to enter the emergency mode. The emergency mode is a mode that allows the administrator to log in as the root user and perform basic tasks such as repairing the system. The administrator should modify the /etc/fstab file and check the entry for the /data file system. The administrator should look for any errors or inconsistencies in the device name, file system type, or mount options, and correct them. The administrator should also verify that the device and the file system are intact and functional by using commands such as blkid, fdisk, fsck, or mount. The administrator should then reboot the system and see if the issue is resolved. The file that will need to be modified for the server to be able to boot again is /etc/fstab. This is the correct answer to the question. The other options are incorrect because they are not related to the file systems that are mounted at boot time (/etc/mtab, /dev/sda, or /etc/grub.conf). CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 10: Managing Storage, page 321.
정답:
Explanation:
The process that will accomplish the task of creating a custom script to run at boot as part of the system services is:
Create a unit file in the /etc/systemd/system/ directory. A unit file is a configuration file that defines the properties and behavior of a systemd service. The systemd is a system and service manager that controls the startup and operation of Linux systems. The /etc/systemd/system/ directory is the location where the administrator can create and store custom unit files. The unit file should have a name that matches the name of the script, such as cleanup.service, and should contain the following sections and options:
[Unit]: This section provides the general information about the service, such as the description, dependencies, and conditions. The administrator should specify the following options in this section: Description: A brief description of the service, such as “Custom cleanup script”.
After: The name of another unit that this service should start after, such as “network.target”.
ConditionPathExists: The path of the file or directory that must exist for the service to start, such as
“/opt/scripts/cleanup.sh”.
[Service]: This section defines how the service should be started and stopped, and what commands should be executed. The administrator should specify the following options in this section:
Type: The type of the service, such as “oneshot”, which means that the service will run once and then exit.
ExecStart: The command that will start the service, such as “/bin/bash /opt/scripts/cleanup.sh”. RemainAfterExit: A boolean value that indicates whether the service should remain active after the command exits, such as “yes”.
[Install]: This section defines how the service should be enabled and under what circumstances it should be started. The administrator should specify the following option in this section: WantedBy: The name of another unit that wants this service to be started, such as “multi-user.target”, which means that the service will be started when the system reaches the multi-user mode.
Run the command systemct1 enable cleanup. This command will enable the service and create the necessary symbolic links to start the service at boot.
Run the command systemct1 is-enabled cleanup. This command will check the status of the service and confirm that it is enabled.
This process will create a custom script, cleanup.sh, to run at boot as part of the system services. This is the correct process to use to accomplish the task. The other options are incorrect because they either use the wrong directory for the unit file (/etc/default/, /etc/skel/, or /etc/sysctl.d/) or do not create a unit file at all.
Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 15: Managing System Services, pages 457-459.

정답:
Explanation:
The command setfacl -m g:finance:rw file will permanently fix the access issue while limiting access to IT and finance department employees. The setfacl command is a tool for modifying the access control lists (ACLs) of files and directories on Linux systems. The ACLs are a mechanism that allows more fine-grained control over the permissions of files and directories than the traditional owner-group-others model. The -m option specifies the modification to the ACL. The g:finance:rw means that the group named finance will have read and write permissions on the file. The file is the name of the file to modify, in this case /opt/work/file. The command setfacl -m g:finance:rw file will add an entry to the ACL of the file that will grant read and write access to the finance group. This will fix the access issue and allow the finance employees to access the file. The command will also preserve the existing permissions of the file, which means that the IT employees will still have read and write access to the file. This will limit the access to IT and finance department employees and prevent unauthorized access from other users. This is the correct command to use to accomplish the task. The other options are incorrect because they either do not fix the access issue (chattr +i file or chown it:finance file) or do not limit the access to IT and finance department employees (chmod 666
file).
Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 11: Managing File Permissions and Ownership, page 352.
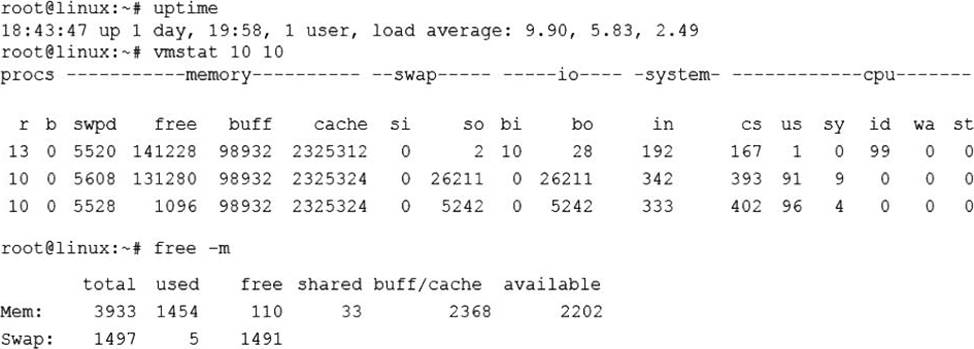
정답:
Explanation:
The slowness is caused by the CPU being overloaded. The iostat command shows that the CPU utilization is 100%, which means that there are more processes competing for CPU time than the CPU can handle.
The other options are incorrect because:
The system is not running out of swap space, as shown by the iostat command, which shows that there is no swap activity (si and so columns are zero).
The memory is not exhausted, as shown by the free -m command, which shows that there is still available memory (avail column) and free buffer/cache memory (buff/cache column).
The processes are not paging, as shown by the vmstat command, which shows that there are no major page faults (majflt column) and no swap activity (si and so columns).
Reference: CompTIA Linux+ Study Guide, Fourth Edition, page 417-419, 424-425.
정답:
Explanation:
The command that will allow the technician to execute the services and continue deploying other microservices within the same terminal session is bg %1 job name. This command will send the job with ID 1 and name job name to the background, where it will run without occupying the terminal.
The other options are incorrect because:
gedit & disown will launch a graphical text editor in the background and detach it from the terminal, but it will not execute any service.
kill 9 %1 will terminate the job with ID 1 using a SIGKILL signal, which cannot be ignored or handled by the process.
fg %1 will bring the job with ID 1 to the foreground, where it will occupy the terminal until it finishes or is stopped. CompTIA Linux+ Study Guide, Fourth Edition, page 181-182.
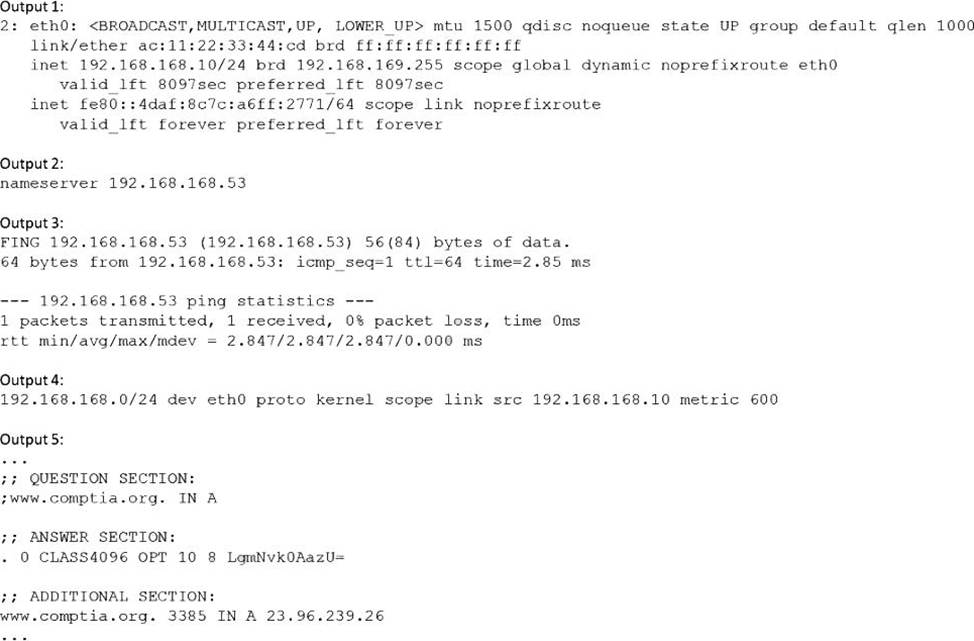
정답:
Explanation:
The issue is caused by the server 192.168.168.53 being unreachable. This server is the DNS server configured in the /etc/resolv.conf file, which is used to resolve domain names to IP addresses. The ping command shows that the server cannot be reached, and the nslookup command shows that the name www.comptia.org cannot be resolved using this server.
The other options are incorrect because:
The name www.comptia.org does point to a valid IP address, as shown by the nslookup command using another DNS server (8.8.8.8).
The default route is set on the server, as shown by the ip route command, which shows a default gateway of 192.168.168.1.
The network interface eth0 is connected, as shown by the ip link command, which shows a state of UP for eth0.
Reference: CompTIA Linux+ Study Guide, Fourth Edition, page 457-458, 461-462.
정답:
Explanation:
The administrator should modify the /etc/hosts file and change the db.example.com entry to 192.168.20.88 to address the issue. The /etc/hosts file is a file that maps hostnames to IP addresses on Linux systems. The file can be used to override the DNS resolution and provide a local lookup for hostnames. The dig output shows that the DNS returns the IP address 192.168.20.88 for the hostname db.example.com, which is the correct IP address of the system. The grep output shows that the /etc/hosts file contains an entry for db.example.com with the IP address 192.168.20.89, which is the wrong IP address of the system. This can cause a conflict and prevent the system from being accessed by the hostname. The administrator should modify the /etc/hosts file and change the db.example.com entry to 192.168.20.88, which is the correct IP address of the system. This will align the /etc/hosts file with the DNS and allow the system to be accessed by the hostname. The administrator should modify the /etc/hosts file and change the db.example.com entry to 192.168.20.88 to address the issue. This is the correct answer to the question. The other options are incorrect because they either do not modify the /etc/hosts file (modify the /etc/network file and change the db.example.com entry to 192.168.20.88 or modify the /etc/network file and change the db.example.com entry to 192.168.20.89) or do not change the IP address to the correct one (modify the /etc/hosts file and change the db.example.com entry to 192.168.20.89).
Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 12: Managing Network Connections, page 378.
정답:
Explanation:
The server is in a "Listen" state on port 9943 using its loopback address. The "1234" is a process-id
The cause of the issue is that the application is listening on the loopback interface. The loopback interface is a virtual network interface that is used for internal communication within the system. The loopback interface has the IP address 127.0.0.1, which is also known as localhost. The netstat output shows that the application is listening on port 9443 using the IP address 127.0.0.1. This means that the application can only accept connections from the same system, not from other systems on the network. This can prevent the users from reaching the application and cause the issue. The administrator should configure the application to listen on the IP address 0.0.0.0, which means all available interfaces, or on the specific IP address of the system that is reachable from the network. This will allow the application to accept connections from other systems and resolve the issue. The cause of the issue is that the application is listening on the loopback interface. This is the correct answer to the question. The other options are incorrect because they are not supported by the outputs. The IP address 0.0.0.0 is valid and means all interfaces, the application is not listening on port 1234, and the application is running as shown by the process ID 1234. CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 12: Managing Network Connections, page 383.
정답:
Explanation:
The command sed -i 's/auto/persistent/g' /etc/systemd/journald.conf && sed -i 'persistent/s/ˆ#//q' /etc/systemd/journald.conf will accomplish the task of guaranteeing the persistency of journal log files across system reboots. The sed command is a tool for editing text files on Linux systems. The - i option modifies the file in place. The s command substitutes one string for another. The g flag replaces all occurrences of the string. The && operator executes the second command only if the first command succeeds. The q command quits after the first match. The /etc/systemd/journald.conf file is a configuration file for the systemd-journald service, which is responsible for collecting and storing log messages. The command sed -i 's/auto/persistent/g' /etc/systemd/journald.conf will replace the word auto with the word persistent in the file. This will change the value of the Storage option, which controls where the journal log files are stored. The value auto means that the journal log files are stored in the volatile memory and are lost after reboot, while the value persistent means that the journal log files are stored in the persistent storage and are preserved across reboots. The command sed -i 'persistent/s/ˆ#//q' /etc/systemd/journald.conf will remove the # character at the beginning of the line that contains the word persistent. This will uncomment the Storage option and enable it. The command sed -i 's/auto/persistent/g' /etc/systemd/journald.conf && sed -i 'persistent/s/ˆ#//q' /etc/systemd/journald.conf will guarantee the persistency of journal log files across system reboots by changing and enabling the Storage option to persistent. This is the correct command to use to accomplish the task. The other options are incorrect because they either do not change the value of the Storage option (grep -i auto /etc/systemd/journald.conf && systemct1 restart systemd-journald.service or cat /etc/systemd/journald.conf | awk '(print $1,$3)') or do not enable the Storage option (journalctl --list-boots && systemct1 restart systemd-journald.service).
Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 16: Managing Logging and Monitoring, page 489.
정답:
Explanation:
"A service mesh controls the delivery of service requests in an application. Common features provided by a service mesh include service discovery, load balancing, encryption and failure recovery."
The technology that provides load balancing, encryption, and observability in containerized environments is service mesh. A service mesh is a dedicated infrastructure layer that manages the communication and security between microservices in a distributed system. A service mesh consists of two components: a data plane and a control plane. The data plane is composed of proxies that are deployed alongside the microservices as sidecar pods. The proxies handle the network traffic between the microservices and provide features such as load balancing, encryption, authentication, authorization, routing, and observability. The control plane is responsible for configuring and managing the data plane and providing a unified interface for the administrators and developers. A service mesh can help improve the performance, reliability, and security of containerized applications and simplify the development and deployment process. A service mesh is the technology that provides load balancing, encryption, and observability in containerized environments. This is the correct answer to the question. The other options are incorrect because they either do not provide all the features of a service mesh (virtual private network or overlay network) or are not a technology but a component of a service mesh (sidecar pod).
Reference: CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 19: Managing Cloud and Virtualization Technologies, page 574.
https://www.techtarget.com/searchitoperations/definition/service-mesh
정답:
Explanation:
The command vmstat will most likely be run next by the administrator to troubleshoot the system performance. The vmstat command is a tool for reporting virtual memory statistics on Linux systems. The command shows information about processes, memory, paging, block IO, interrupts, and CPU activity. The command can help the administrator identify the source of the performance issue, such as high CPU usage, low free memory, excessive swapping, or disk IO bottlenecks. The command can also be used with an interval and a count to display the statistics repeatedly over time and observe the changes. The command vmstat will provide useful information for diagnosing the system performance and finding the root cause of the issue. This is the most likely command to run next after the top command. The other options are incorrect because they either do not show the virtual memory statistics (strace or lsof) or do not provide more information than the top command (htop). CompTIA Linux+ (XK0-005) Certification Study Guide, Chapter 14: Managing Processes and Scheduling Tasks, page 425.
정답:
Explanation:
Ctrl+Z suspended the process, and "fg" will bring it back into the foreground of the shell
A Comprehensive and To go back to a program that was suspended by pressing Ctrl+Z in the command line, the command that can be used is fg. The fg command stands for foreground, and it resumes the job that is next in the queue and brings it to the foreground. Alternatively, if there are more than one suspended jobs, fg can be followed by a job number to resume a specific job. The other commands are incorrect because they either do not resume a suspended job, or they have different functions such as switching user (su), pushing a job to the background (bg), or editing a file (ed). CompTIA Linux+ Study Guide, Fourth Edition, page 181-182.