CompTIA PenTest+ Exam 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년11월17일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 CompTIA PT0-003 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 PT0-003 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 131개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
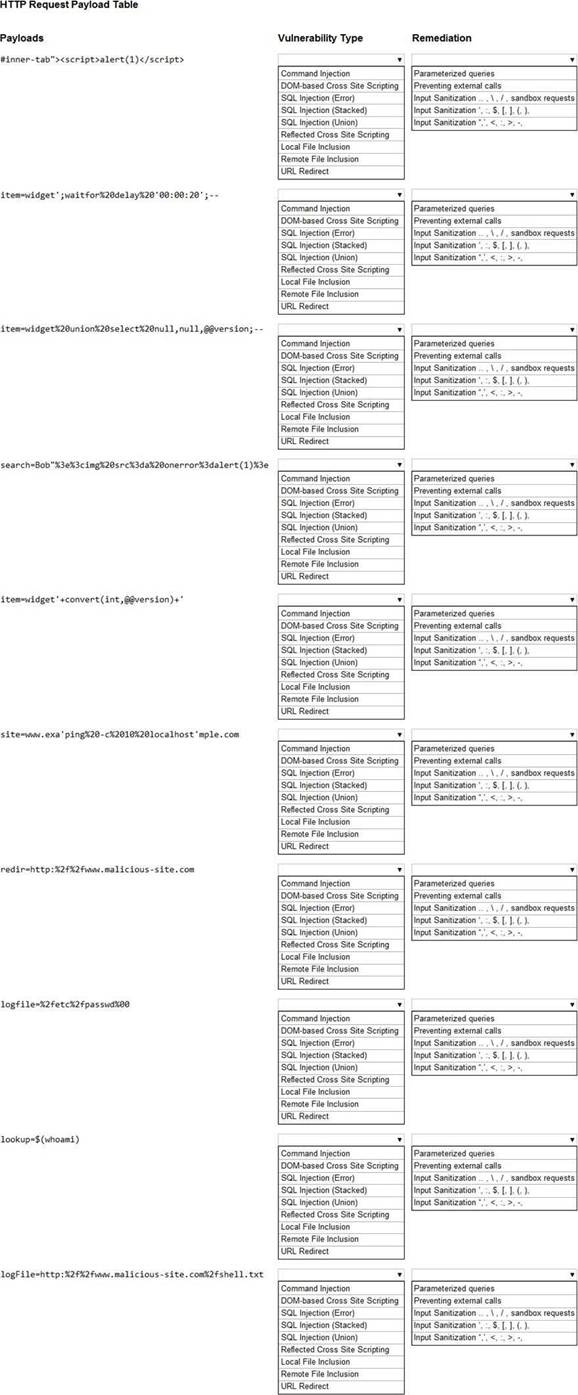
정답:
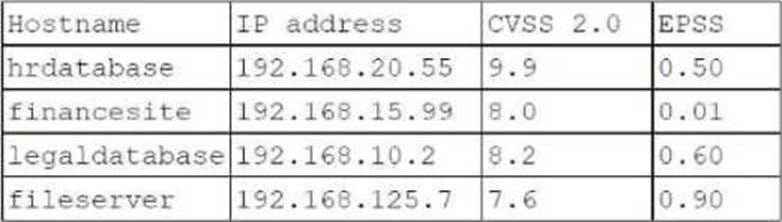
정답:
Explanation:
Evaluation Criteria:
CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System): Indicates the severity of vulnerabilities, with higher scores representing more critical vulnerabilities.
EPSS (Exploit Prediction Scoring System): Estimates the likelihood of a vulnerability being exploited in the wild.
Analysis:
hrdatabase: CVSS = 9.9, EPSS = 0.50
financesite: CVSS = 8.0, EPSS = 0.01
legaldatabase: CVSS = 8.2, EPSS = 0.60
fileserver: CVSS = 7.6, EPSS = 0.90
Selection Justification:
fileserver has the highest EPSS score of 0.90, indicating a high likelihood of exploitation despite having a slightly lower CVSS score compared to other targets.
This makes it a critical target for immediate testing to mitigate potential exploitation risks.
Pentest
Reference: Risk Prioritization: Balancing between severity (CVSS) and exploitability (EPSS) is crucial for effective vulnerability management.
Risk Assessment: Evaluating both the impact and the likelihood of exploitation helps in making informed decisions about testing priorities.
By selecting the fileserver, the penetration tester focuses on a target that is highly likely to be exploited, addressing the most immediate risk based on the given scores. Top of Form
Bottom of Form
정답:
Explanation:
To break the key for a Wi-Fi network that uses WPA2 encryption, the penetration tester should use the KRACK (Key Reinstallation Attack) attack.
KRACK (Key Reinstallation Attack):
Definition: KRACK is a vulnerability in the WPA2 protocol that allows attackers to decrypt and potentially inject packets into a Wi-Fi network by manipulating and replaying cryptographic handshake messages.
Impact: This attack exploits flaws in the WPA2 handshake process, allowing an attacker to break the
encryption and gain access to the network.
Other Attacks:
ChopChop: Targets WEP encryption, not WPA2.
Replay: Involves capturing and replaying packets to create effects such as duplicating transactions; it does not break WPA2 encryption.
Initialization Vector (IV): Related to weaknesses in WEP, not WPA2.
Pentest Reference: Wireless Security: Understanding vulnerabilities in Wi-Fi encryption protocols, such as WPA2, and how they can be exploited.
KRACK Attack: A significant vulnerability in WPA2 that requires specific techniques to exploit.
By using the KRACK attack, the penetration tester can break WPA2 encryption and gain unauthorized access to the Wi-Fi network.
Top of Form
Bottom of Form
정답:
Explanation:
In a cloud environment, the information used to configure virtual machines during their initialization could have been accessed through metadata services.
Metadata Services:
Definition: Cloud service providers offer metadata services that provide information about the running instance, such as instance ID, hostname, network configurations, and user data.
Access: These services are accessible from within the virtual machine and often include sensitive information used during the initialization and configuration of the VM.
Other Features:
IAM (Identity and Access Management): Manages permissions and access to resources but does not directly expose initialization data.
Block Storage: Provides persistent storage but does not directly expose initialization data.
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): Provides network isolation for cloud resources but does not directly expose initialization data.
Pentest
Reference: Cloud Security: Understanding how metadata services work and the potential risks associated with them is crucial for securing cloud environments.
Exploitation: Metadata services can be exploited to retrieve sensitive data if not properly secured. By accessing metadata services, an attacker can retrieve sensitive configuration information used during VM initialization, which can lead to further exploitation.
정답:
Explanation:
Enabling monitoring mode on the wireless adapter is the essential step before capturing WPA2 handshakes. Monitoring mode allows the adapter to capture all wireless traffic in its vicinity, which is necessary for capturing handshakes.
Preparation:
Wireless USB Dongle: Ensure the wireless USB dongle is compatible with monitoring mode and packet injection.
Aircrack-ng Suite: Use the Aircrack-ng suite, a popular set of tools for wireless network auditing.
Enable Monitoring Mode:
Command: Use the airmon-ng tool to enable monitoring mode on the wireless interface.
Step-by-Step Explanationairmon-ng start wlan0
Verify: Check if the interface is in monitoring mode.
iwconfig
Capture WPA2 Handshakes:
Airodump-ng: Use airodump-ng to start capturing traffic and handshakes.
airodump-ng wlan0mon
Reference from Pentesting Literature:
Enabling monitoring mode is a fundamental step in wireless penetration testing, discussed in guides like "Penetration Testing - A Hands-on Introduction to Hacking".
HTB write-ups often start with enabling monitoring mode before proceeding with capturing WPA2
handshakes.
Reference: Penetration Testing - A Hands-on Introduction to Hacking HTB Official Writeups
정답:
Explanation:
Client Concern:
Availability: The client is specifically concerned about the availability of their consumer-facing production application. Ensuring this application is secure and available is crucial to the business.
Server Analysis:
Server 1 (Development sandbox server): Typically not a production server; vulnerabilities here are less likely to impact the consumer-facing application.
Server 2 (Back office file transfer server): Important but generally more internal-facing and less likely to directly affect the consumer-facing application.
Server 3 (Perimeter network web server): Likely hosts the consumer-facing application or critical services related to it. High-severity vulnerabilities here could directly impact availability.
Server 4 (Developer QA server): Similar to Server 1, more likely to be used for testing rather than production, making it less critical for immediate manual testing.
Pentest Reference: Risk Prioritization: Focus on assets that have the most significant impact on business operations, especially those directly facing consumers.
Critical Infrastructure: Ensuring the security and availability of web servers exposed to the internet as they are prime targets for attacks.
By selecting Server 3 (the perimeter network web server) for additional manual testing, the penetration tester addresses the client's primary concern about the availability and security of the consumer-facing production application.
정답:
Explanation:
To avoid locking out accounts while attempting access, the penetration tester should use credential stuffing.
Credential Stuffing:
Definition: An attack method where attackers use a list of known username and password pairs, typically obtained from previous data breaches, to gain unauthorized access to accounts. Advantages: Unlike brute-force attacks, credential stuffing uses already known credentials, which reduces the number of attempts per account and minimizes the risk of triggering account lockout mechanisms.
Tool: Tools like Sentry MBA, Snipr, and others are commonly used for credential stuffing attacks.
Other Techniques:
MFA Fatigue: A social engineering tactic to exhaust users into accepting multi-factor authentication requests, not applicable for avoiding lockouts in this context.
Dictionary Attack: Similar to brute-force but uses a list of likely passwords; still risks lockout due to multiple attempts.
Brute-force Attack: Systematically attempts all possible password combinations, likely to trigger account lockouts due to high number of failed attempts. Pentest
Reference: Password Attacks: Understanding different types of password attacks and their implications on account security.
Account Lockout Policies: Awareness of how lockout mechanisms work and strategies to avoid triggering them during penetration tests.
By using credential stuffing, the penetration tester can attempt to gain access using known credentials without triggering account lockout policies, ensuring a stealthier approach to password attacks.
정답:
Explanation:
Identified Weaknesses:
Weaker password settings than the company standard: Indicates inconsistency in password policies across systems.
Systems without the company's endpoint security software installed: Suggests lack of uniformity in security software deployment.
Operating systems not updated by the patch management system: Points to gaps in patch management processes.
Configuration Management System:
Definition: A configuration management system automates the deployment, maintenance, and enforcement of configurations across all systems in an organization.
Benefits: Ensures consistency in security settings, software installations, and patch management across the entire environment.
Examples: Tools like Ansible, Puppet, and Chef can help automate and manage configurations, ensuring compliance with organizational standards.
Other Recommendations:
Vulnerability Management System: While adding systems to this system helps track vulnerabilities, it does not address the root cause of configuration inconsistencies.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Useful for detecting and responding to threats, but not for enforcing consistent configurations.
Patch Management: Patching systems addresses specific vulnerabilities but does not solve broader
configuration management issues.
Pentest
Reference: System Hardening: Ensuring all systems adhere to security baselines and configurations to reduce attack surfaces.
Automation in Security: Using configuration management tools to automate security practices, ensuring compliance and reducing manual errors.
Implementing a configuration management system addresses the root issue by ensuring consistent security configurations, software deployments, and patch management across the entire environment.
정답:
Explanation:
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST):
Definition: DAST involves testing the application in its running state to identify vulnerabilities that could be exploited by an attacker.
Purpose: Simulates attacks on a live application, examining how it behaves and identifying security weaknesses.
ZAP (Zed Attack Proxy):
Description: An open-source DAST tool developed by OWASP.
Features: Capable of scanning web applications for vulnerabilities, including SQL injection, XSS, CSRF, and other common web application vulnerabilities.
Usage: Ideal for dynamic testing as it interacts with the live application and identifies vulnerabilities
that may not be visible in static code analysis.
Other Tools:
Mimikatz: Used for post-exploitation activities, specifically credential dumping on Windows systems. OllyDbg: A debugger used for reverse engineering and static analysis of binary files, not suitable for dynamic testing.
SonarQube: A static code analysis tool used for SAST (Static Application Security Testing), not for dynamic testing.
Pentest
Reference: Web Application Security Testing: Utilizing DAST tools like ZAP to dynamically test and find vulnerabilities in running web applications.
OWASP Tools: Leveraging open-source tools recommended by OWASP for comprehensive security testing.
By using ZAP, the penetration tester can perform dynamic testing to identify runtime vulnerabilities in web applications, extending the scope of the vulnerability search.
정답:
Explanation:
By running the command findstr /SIM /C:"pass" *.txt *.cfg *.xml, the penetration tester is trying to enumerate secrets.
Command Analysis:
findstr: A command-line utility in Windows used to search for specific strings in files.
/SIM: Combination of options; /S searches for matching files in the current directory and all subdirectories, /I specifies a case-insensitive search, and /M prints only the filenames with matching content.
/C:"pass": Searches for the literal string "pass".
***.txt .cfg .xml: Specifies the file types to search within.
Objective:
The command is searching for the string "pass" within .txt, .cfg, and .xml files, which is indicative of searching for passwords or other sensitive information (secrets).
These file types commonly contain configuration details, credentials, and other sensitive data that might include passwords or secrets.
Other Options:
Configuration files: While .cfg and .xml files can be configuration files, the specific search for "pass" indicates looking for secrets like passwords.
Permissions: This command does not check or enumerate file permissions.
Virtual hosts: This command is not related to enumerating virtual hosts.
Pentest
Reference: Post-Exploitation: Enumerating sensitive information like passwords is a common post-exploitation
activity after gaining initial access.
Credential Discovery: Searching for stored credentials within configuration files and documents to escalate privileges or move laterally within the network.
By running this command, the penetration tester aims to find stored passwords or other secrets that could help in further exploitation of the target system.
정답:
Explanation:
Kerberoasting is an attack that involves requesting service tickets for service accounts from a Kerberos service, extracting the service tickets, and attempting to crack them offline to retrieve the plaintext passwords.
Understanding Kerberoasting:
Purpose: To obtain service account passwords by cracking the encrypted service tickets (TGS tickets) offline.
Service Principal Names (SPNs): SPNs are used in Kerberos authentication to uniquely identify a service instance.
Command Breakdown:
setspn.exe -Q /: This command queries all SPNs in the domain.
Use Case: Identifying accounts with SPNs that can be targeted for Kerberoasting.
Kerberoasting Steps:
Identify SPNs: Use setspn.exe to list service accounts with SPNs.
Request TGS Tickets: Request TGS tickets for the identified SPNs.
Extract Tickets: Use tools like Mimikatz to extract the service tickets.
Crack Tickets: Use password cracking tools like Hashcat to crack the extracted tickets offline.
Reference from Pentesting Literature:
Kerberoasting is a well-documented attack method in penetration testing guides, specifically targeting service accounts in Active Directory environments.
HTB write-ups often detail the use of Kerberoasting for gaining credentials from service accounts.
Step-by-Step ExplanationReference: Penetration Testing - A Hands-on Introduction to Hacking HTB Official Writeups
정답:
Explanation:
Port 445 is used for SMB (Server Message Block) services, which are commonly targeted for hash-based relay attacks like NTLM relay attacks.
Understanding Hash-Based Relays:
NTLM Relay Attack: An attacker intercepts and relays NTLM authentication requests to another service, effectively performing authentication on behalf of the victim.
SMB Protocol: Port 445 is used for SMB/CIFS traffic, which supports NTLM authentication.
Prioritizing Port 445:
Vulnerability: SMB is often targeted because it frequently supports NTLM authentication, making it susceptible to relay attacks.
Tools: Tools like Responder and NTLMRelayX are commonly used to capture and relay NTLM hashes over SMB.
Execution:
Capture Hash: Use a tool like Responder to capture NTLM hashes.
Relay Hash: Use a tool like NTLMRelayX to relay the captured hash to another service on port 445.
Reference from Pentesting Literature:
Penetration testing guides frequently discuss targeting SMB (port 445) for hash-based relay attacks.
HTB write-ups often include examples of NTLM relay attacks using port 445.
Step-by-Step ExplanationReference: Penetration Testing - A Hands-on Introduction to Hacking HTB Official Writeups
정답:
Explanation:
Debugging Mode:
Purpose: Debugging mode provides detailed error messages and debugging information, useful during development.
Risk: In a production environment, it exposes sensitive information and vulnerabilities, making the system more susceptible to attacks.
Common Causes:
Configuration Changes: During testing or penetration testing, configurations might be altered to facilitate debugging. If not reverted, these changes can leave the system in a vulnerable state.
Oversight: Configuration changes might be overlooked during deployment.
Best Practices:
Deployment Checklist: Ensure a checklist is followed that includes reverting any debug configurations before moving to production.
Configuration Management: Use configuration management tools to track and manage changes.
Reference from Pentesting Literature:
The importance of reverting configuration changes is highlighted in penetration testing guides to prevent leaving systems in a vulnerable state post-testing.
HTB write-ups often mention checking and ensuring debugging modes are disabled in production environments.
Reference: Penetration Testing - A Hands-on Introduction to Hacking HTB Official Writeups
정답:
Explanation:
Banner grabbing is a technique used to obtain information about a network service, including its version number, by connecting to the service and reading the response.
Understanding Banner Grabbing:
Purpose: Identify the software version running on a service by reading the initial response banner.
Methods: Can be performed manually using tools like Telnet or automatically using tools like Nmap.
Manual Banner Grabbing:
Step-by-Step Explanationtelnet target_ip 80
Netcat: Another tool for banner grabbing.
nc target_ip 80
Automated Banner Grabbing:
Nmap: Use Nmap’s version detection feature to grab banners.
nmap -sV target_ip
Benefits:
Information Disclosure: Quickly identify the version and sometimes configuration details of the service.
Targeted Exploits: Helps in selecting appropriate exploits based on the identified version.
Reference from Pentesting Literature:
Banner grabbing is a fundamental technique in reconnaissance, discussed in various penetration testing guides.
HTB write-ups often include banner grabbing as a step in identifying the version of services.
Reference: Penetration Testing - A Hands-on Introduction to Hacking HTB Official Writeups
정답:
Explanation:
ProxyChains is a tool that allows you to route your traffic through a chain of proxy servers, which can be used to anonymize your network activity. In this context, it is being used to route Nmap scan traffic through the compromised host, allowing the penetration tester to pivot and enumerate other targets within the network.
Understanding ProxyChains:
Purpose: ProxyChains allows you to force any TCP connection made by any given application to follow through proxies like TOR, SOCKS4, SOCKS5, and HTTP(S).
Usage: It’s commonly used to anonymize network traffic and perform actions through an intermediate proxy.
Command Breakdown:
proxychains nmap -sT <target_cidr>: This command uses ProxyChains to route the Nmap scan traffic through the configured proxies.
Nmap Scan (-sT): This option specifies a TCP connect scan.
Setting Up ProxyChains:
Configuration File: ProxyChains configuration is typically found at /etc/proxychains.conf.
Adding Proxy: Add the compromised host as a SOCKS proxy.
Step-by-Step Explanationplaintext
Copy code
socks4 127.0.0.1 1080
Execution:
Start Proxy Server: On the compromised host, run a SOCKS proxy (e.g., using ssh -D 1080 user@compromised_host).
Run ProxyChains with Nmap: Execute the command on the attacker's host.
proxychains nmap -sT <target_cidr>
Reference from Pentesting Literature:
ProxyChains is commonly discussed in penetration testing guides for scenarios involving pivoting through a compromised host.
HTB write-ups frequently illustrate the use of ProxyChains for routing traffic through intermediate systems.
Reference: Penetration Testing - A Hands-on Introduction to Hacking HTB Official Writeups