Fortinet NSE 5 - FortiSIEM 6.3 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년11월17일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 Fortinet NSE5_FSM-6.3 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 NSE5_FSM-6.3 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 42개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
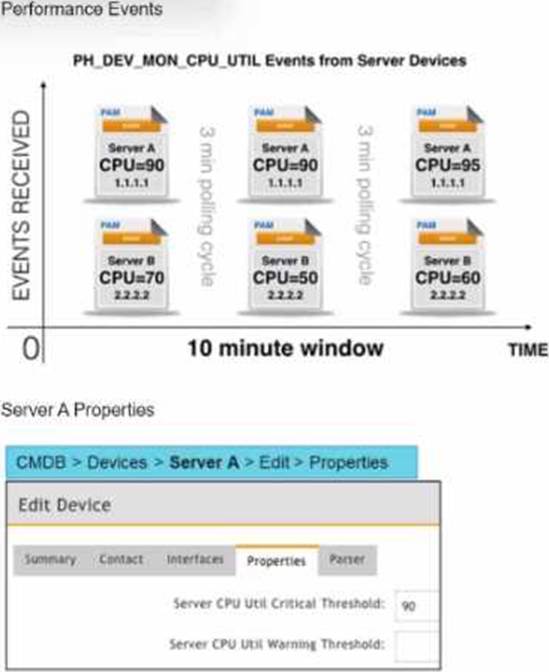
Event Collection Overview: The exhibits show three events collected over a 10-minute period from two servers, Server A and Server B.
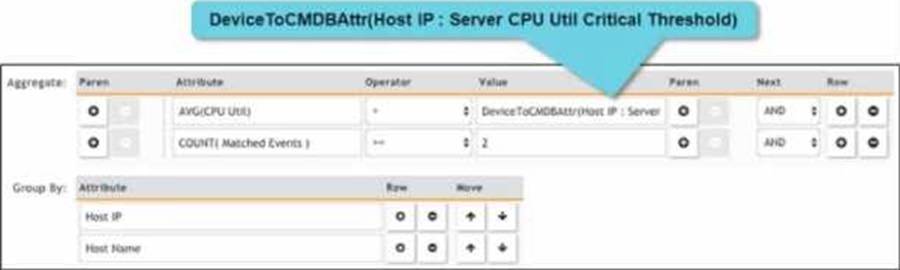
Rule Subpattern Settings: The rule subpattern specifies two conditions:
AVG (CPU Util) > DeviceToCMDBAttr(Host IP: Server CPU Util Critical Threshold): This checks if the average CPU utilization exceeds the critical threshold defined for each server.
COUNT (Matched Events) >= 2: This requires at least two matching events within the specified period.
Server A Analysis:
Events: Three events (CPU=90, CPU=90, CPU=95).
Average CPU Utilization: (90+90+95)/3 = 91.67, which exceeds the critical threshold of 90.
Matched Events Count: 3, which meets the condition of being greater than or equal to 2.
Incident Generation: Server A meets both conditions, so it generates one incident.
Server B Analysis:
Events: Three events (CPU=70, CPU=50, CPU=60).
Average CPU Utilization: (70+50+60)/3 = 60, which does not exceed the critical threshold of 90. Matched Events Count: 3, but since the average CPU utilization condition is not met, no incident is generated.
Conclusion: Based on the rule subpattern, Server A will generate one incident, and Server B will not generate any incidents.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Event Correlation Rules and Incident Management sections, which explain how incidents are generated based on rule subpatterns and event conditions.
정답:
Explanation:
Raw Log Data: When devices send logs to FortiSIEM, the data arrives in a raw, unstructured format.
Data Parsing Process: The process that converts this raw log data into a structured format is known as data parsing.
Data Parsing: This involves extracting relevant fields from the raw log entries and organizing them into a structured format, making the data usable for analysis, reporting, and correlation.
Significance of Structured Data: Structured data is essential for effective event correlation, alerting, and generating meaningful reports.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Data Parsing section, which details how raw log data is transformed into structured data through parsing.
정답:
Explanation:
Incident Management in FortiSIEM: FortiSIEM tracks incidents and their occurrences to help administrators manage and respond to recurring issues.
Performance Rule Triggering: When a performance rule, such as one for high CPU usage, is repeatedly triggered, FortiSIEM updates the corresponding incident rather than creating a new one each time.
Incident Table Updates:
Incident Count: The Incident Count value increases each time the rule is triggered, indicating how many times the incident has occurred.
First Seen and Last Seen Times: These timestamps are updated to reflect the first occurrence and the most recent occurrence of the incident.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Incident Management section, explains how FortiSIEM handles recurring incidents and updates the incident table accordingly.
정답:
Explanation:
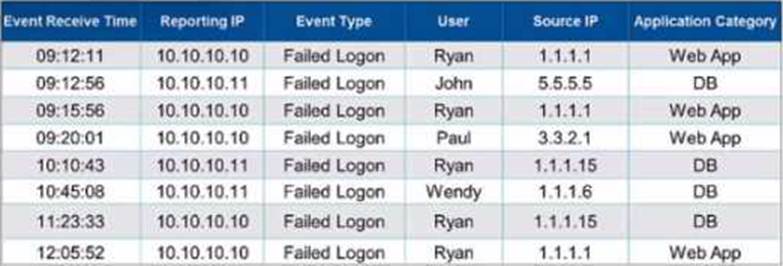
Grouping Events in FortiSIEM: Grouping events by specific attributes allows for the aggregation of similar events, providing clearer insights and reducing clutter.
Grouping Criteria: For this question, events are grouped by "User," "Source IP," and "Application Category."
Unique Combinations Analysis:
Ryan, 1.1.1.1, Web App (appears multiple times but is one unique combination)
John, 5.5.5.5, DB
Paul, 3.3.2.1, Web App
Ryan, 1.1.1.15, DB
Wendy, 1.1.1.6, DB
Result Calculation: There are five unique combinations in the provided data based on the specified grouping attributes.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Event Management and Reporting sections, which explain how to group events by various attributes for analysis and reporting purposes.
정답:
Explanation:
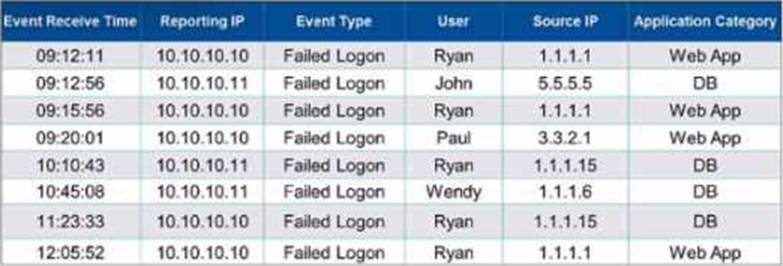
Grouping Events in FortiSIEM: Grouping events by specific attributes allows administrators to aggregate and analyze data more efficiently.
Grouping Criteria: In this case, the events are grouped by "Event Type" and "User" attributes.
Unique Combinations: To determine the number of results displayed, identify the unique combinations of the "Event Type" and "User" attributes in the provided data.
Failed Logon by Ryan (appears multiple times but is one unique combination) Failed Logon by John
Failed Logon by Paul Failed Logon by Wendy
Unique Groupings: There are four unique groupings based on the given data: "Failed Logon" by "Ryan", "John", "Paul", and "Wendy".
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Event Management and Reporting sections, which explain how events are grouped and reported based on selected attributes.
정답:
Explanation:
Syslog Configuration in FortiSIEM: For FortiSIEM to receive syslog messages from network devices, those devices need to be properly configured to send syslog data to FortiSIEM.
Manual Configuration Requirement: FortiSIEM does not automatically configure network devices to send syslog messages. Instead, this configuration must be performed manually by the network administrator.
Process Overview: The network administrator must access each device and set up the syslog parameters to direct log data to the FortiSIEM collector's IP address.
Discovery Process: While FortiSIEM can discover network devices using SNMP, WMI, and other protocols, the configuration of syslog on these devices is beyond its scope and requires manual intervention.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Device Configuration and Syslog Integration sections, which explain the requirements and steps for setting up syslog forwarding on network devices.
정답:
Explanation:
Device Status in FortiSIEM: FortiSIEM assigns different statuses to devices based on their operational state and performance metrics.
Packet Loss Impact: The reported packet loss percentage directly influences the status assigned to a device. Packet loss between 50% and 98% indicates significant network issues that affect the device's performance.
Degraded Status: When packet loss is between 50% and 98%, FortiSIEM assigns a "Degraded" status to the device. This status indicates that the device is experiencing substantial packet loss, which impairs its performance but does not render it completely non-functional.
Reasoning: The "Degraded" status helps administrators identify devices with serious performance issues that need attention but are not entirely down.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Device Availability and Status section, explains the criteria for assigning different statuses based on performance metrics such as packet loss.
정답:
Explanation:
Disaster Recovery Mode: FortiSIEM's disaster recovery (DR) mode ensures that there is a backup system ready to take over in case the primary system fails.
Manual Tasks for DR Operation: In the event of a disaster, certain tasks must be performed manually to ensure a smooth transition to the secondary system.
Promoting the Secondary Supervisor:
Use the command phSecondary2primary to promote the secondary supervisor to the primary role. This command reconfigures the secondary supervisor to take over as the primary supervisor, ensuring continuity in management and coordination.
Changing DNS Configuration:
Update the DNS configuration to direct all users, devices, and collectors to the secondary FortiSIEM instance. This ensures that all components in the environment can communicate with the newly promoted primary supervisor without manual reconfiguration of individual devices.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 Administration Guide, Disaster Recovery section, provides detailed steps on promoting the secondary supervisor and updating DNS configurations during a disaster recovery operation.
정답:
Explanation:
FortiSIEM Architecture: The FortiSIEM architecture includes several components such as Supervisors, Workers, Collectors, and Agents, each playing a distinct role in the SIEM ecosystem.
Real-Time Event Correlation: Real-time event correlation is a critical function that involves analyzing and correlating incoming events to detect patterns indicative of security incidents or operational issues.
Role of Supervisor and Worker:
Supervisor: The Supervisor oversees the entire FortiSIEM system, coordinating the processing and analysis of events.
Worker: Workers are responsible for processing and correlating the events received from Collectors
and Agents.
Collaboration for Correlation: Together, the Supervisor and Worker components perform real-time event correlation by distributing the load and ensuring efficient processing of events to identify incidents in real-time.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Event Correlation and Processing section, details how the Supervisor and Worker components collaborate for real-time event correlation.
정답:
Explanation:
Enterprise Licensing Mode: In FortiSIEM enterprise licensing mode, collectors are deployed in remote sites to gather and forward data to the central FortiSIEM cluster located in the data center. Collector Functionality: Collectors are responsible for receiving logs, events (e.g., syslog), and performance metrics from devices.
Link Down Scenario: When the link between the collector and the FortiSIEM cluster is down, the collector needs a mechanism to ensure no data is lost during the disconnection.
Event Buffering: The collector buffers the events locally until the connection is restored, ensuring that no incoming events are lost. This buffered data is then forwarded to the FortiSIEM cluster once the link is re-established.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Data Collection and Buffering section, explains the behavior of collectors during network disruptions.
정답:
Explanation:
Threshold Management: FortiSIEM uses thresholds to generate alerts and incidents based on performance and security metrics.
Global Thresholds: These are default thresholds applied to all devices and metrics across the system, providing a baseline for alerts.
Per Device Thresholds: These thresholds can be customized for individual devices, allowing for more granular control and tailored monitoring based on specific device characteristics and requirements.
Usage in Performance Metrics: Both global and per device thresholds are used for performance metrics to ensure comprehensive and precise monitoring.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Thresholds and Alerts section, details the application of global and per device thresholds for performance and security metrics.
정답:
Explanation:
Feature Overview: FortiSIEM provides several tools for querying and reporting on device information within an environment.
Inventory Tab: The Inventory tab is specifically designed to display detailed information about devices, including their firmware versions.
Query Functionality: Within the Inventory tab, you can run queries to filter and display devices based on specific attributes, such as the firmware version for FortiGate devices.
Report Generation: By running a query in the Inventory tab, you can produce a report that lists the FortiGate devices and their corresponding firmware versions.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Inventory Management section, explains how to use the Inventory tab to query and report on device attributes.

정답:
Explanation:
Offline Licensing in FortiSIEM: FortiSIEM provides mechanisms for offline licensing to accommodate environments without direct internet access.
License Tool Command: The command ./phLicenseTool --collect license_req.dat is used to collect license information necessary for offline registration.
Procedure Analysis: The exhibit shows the output of this command, which indicates the collection of license information to a file named license_req.dat.
Offline License Registration: This collected data file is then typically uploaded to the FortiSIEM support portal or provided to the FortiSIEM support team for processing and generating a license file.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 Administration Guide, Licensing section, details the procedures for both online and offline license registration, including the use of the phLicenseTool for offline scenarios.
정답:
Explanation:
Process Monitoring in FortiSIEM: FortiSIEM can monitor critical processes on managed devices, such as an SMTP process on a Linux server.
Event Generation: When a critical process stops, FortiSIEM generates an event to alert administrators.
Event Types: Specific event types correspond to different monitored conditions. For a stopped process, the event type PH_DEV_MON_PROC_STOP is used.
Reasoning: The name PH_DEV_MON_PROC_STOP (Device Monitoring Process Stop) is a generic event type used by FortiSIEM to indicate that any monitored process, including SMTP, has stopped.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Event Types section, explains the predefined event types and their usage in different monitoring scenarios.
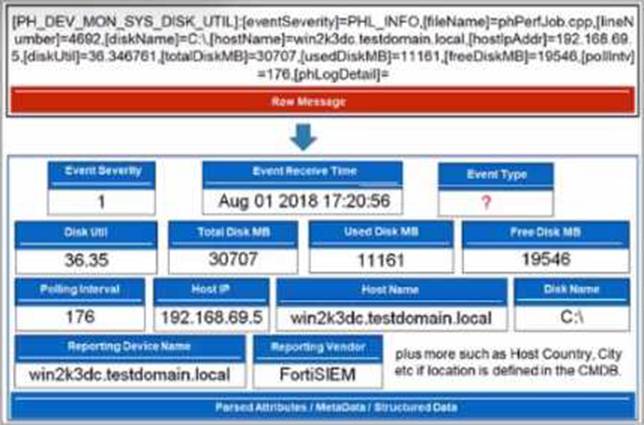
정답:
Explanation:
Event Type Population: In FortiSIEM, the Event Type field is populated based on specific identifiers within the raw message or event log.
Raw Message Analysis: The exhibit shows a raw message with various components, including PH_DEV_MON_SYS_DISK_UTIL, PHL_INFO, phPerfJob, and diskUtil.
Primary Event Identifier: The PH_DEV_MON_SYS_DISK_UTIL at the beginning of the raw message is the primary identifier for the event type. It categorizes the type of event, in this case, a system disk utilization monitoring event.
Event Type Field: FortiSIEM uses this primary identifier to populate the Event Type field, providing a clear categorization of the event.
Reference: FortiSIEM 6.3 User Guide, Event Processing and Event Types section, details how event types are identified and populated in the system.