WGU Integrated Physical Sciences (MTC1) 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년11월17일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 WGU Integrated Physical Sciences 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 Integrated Physical Sciences 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 70개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
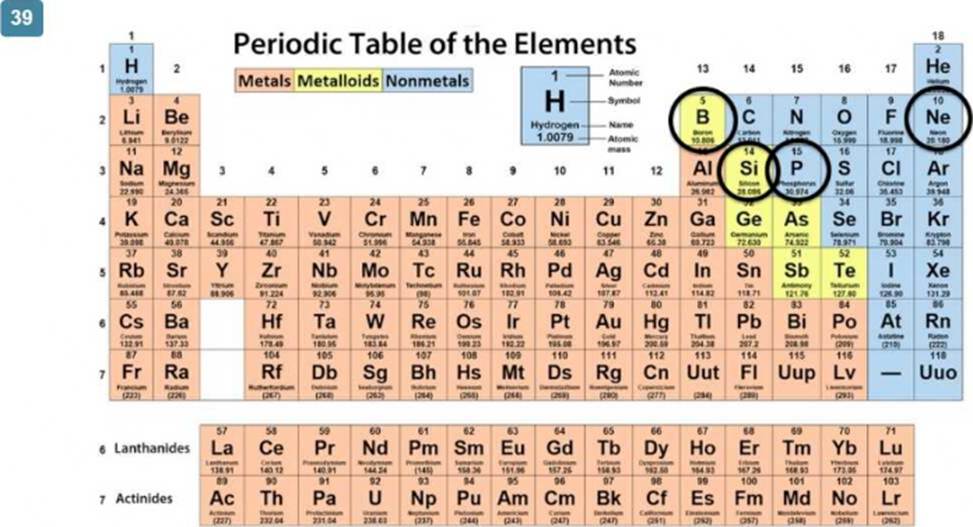
정답:
Explanation:
Elements in the same group (column) of the periodic table have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of valence electrons. Phosphorus (P) is in the same group as nitrogen (N), Group 15, and thus has similar chemical properties.
In comparison:
Neon (Ne) is a noble gas in Group 18.
Silicon (Si) is in Group 14.
Boron (B) is in Group 13.
References: Integrated Physical Sciences Learning Resources, Chapter on the Periodic Table
정답:
Explanation:
In the solid state of matter, particles are closest together. This is due to the fact that solids have a definite shape and volume, meaning the particles are tightly packed in a fixed, orderly arrangement.
In comparison:
Liquids have particles that are close together but not in a fixed position, allowing them to flow.
Gases have particles that are far apart and move freely.
Plasma consists of ionized particles and is not typically considered in the context of ordinary matter states at standard conditions.
References: Integrated Physical Sciences Learning Resources, Chapter on States of Matter
정답:
Explanation:
A physical change is a change in the state or properties of matter without any accompanying change in its chemical composition. Chopping wood is an example of a physical change because the wood is merely being broken into smaller pieces, and its chemical composition remains unchanged.
In comparison:
Baking cookies involves chemical reactions, changing the ingredients' composition.
Iron rusting is a chemical change where iron reacts with oxygen to form iron oxide.
Milk becoming sour is a chemical change due to the fermentation process.
References: Integrated Physical Sciences Learning Resources, Chapter on Physical and Chemical Changes
정답:
Explanation:
정답:
Explanation:
The scientist is determining how the speed of flowing water affects the size of sediment particles it can carry by varying the water speed and measuring the sediment sizes. This involves manipulating one variable (water speed) and observing the effect on another variable (sediment size), which is the essence of a controlled experiment. The setting and control of conditions ensure that the experimenter can establish a cause-and-effect relationship.
References: Integrated Physical Sciences, Chapter 2: Methods of Scientific Investigation
정답:
Explanation:
정답:
Explanation:
Kepler’s discovery that planets move in elliptical paths around the sun is an example of a scientific law. A scientific law describes a relationship in nature that has been consistently observed to be true. Kepler’s laws of planetary motion describe the predictable patterns of planetary orbits, which have been repeatedly confirmed through observation.
References:
Integrated Physical Sciences, Chapter 4: Scientific Laws and Theories
정답:
Explanation:
A low pressure system is typically associated with cloudy and rainy weather. Low pressure areas are regions where the atmospheric pressure is lower than the surrounding areas. Air rises in low pressure systems, leading to cloud formation and precipitation. Therefore, when a low pressure system is settling over an area, it is advisable to prepare for rain by bringing an umbrella and wearing waterproof shoes.
References:
Integrated Physical Sciences documents on weather systems and pressure systems.
Meteorological resources on the effects of low pressure systems.
정답:
Explanation:
정답:
Explanation:
The grocery store manager's assumption that visibility of items increases how often they are purchased is a hypothesis. A hypothesis is a testable prediction or explanation that can be investigated through experiments or observations. In this case, the manager’s idea can be tested by placing items in different locations and measuring their sales.
References:
Integrated Physical Sciences, Chapter 1: The Nature of Scientific Inquiry
정답:
Explanation:
Commercial airline pilots primarily fly in the lower stratosphere and upper troposphere to avoid turbulence and ensure smooth flight conditions.
The troposphere is where weather phenomena and turbulence are common, so pilots seek stable conditions typically found at the boundary with the stratosphere.
The stratosphere offers stable atmospheric conditions, ideal for cruising altitudes.
References:
Integrated Physical Sciences materials on atmospheric layers and aviation.
정답:
Explanation:
The weather change from cool and clear in the morning to light rain and fog in the afternoon, followed by warmer and clear conditions the next morning, is indicative of a warm front passing through the area. A warm front occurs when a warm air mass moves over a cold air mass, causing the warm air to rise and condense, leading to precipitation. After the front passes, the area experiences warmer temperatures and clearing skies.
References:
Integrated Physical Sciences resources on weather fronts and their effects.
Meteorological studies on the impact of warm fronts on local weather patterns.
정답:
Explanation:
Atomic Nucleus Composition: The nucleus of an atom contains protons and neutrons.
Protons (C): Positively charged particles.
Neutrons (A): Neutral particles with no charge.
Electron Positioning:
Electrons (B): Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus, not located within it.
Positron Clarification:
Positrons (D): Positively charged particles similar to electrons, but they are not typically found in the nucleus of an atom in stable matter.
Conclusion: The particles located in the nucleus are protons and neutrons.
References:
Atomic Nucleus: Composition and characteristics of atomic particles.
정답:
Explanation:
Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system, has played a crucial role in protecting Earth from comets. Its massive gravitational field acts as a shield, deflecting or capturing many comets and asteroids that might otherwise collide with Earth. This gravitational influence reduces the frequency of potentially catastrophic impacts on our planet.
References:
NASA's Planetary Science Division
"The Role of Jupiter in the Formation and Evolution of the Solar System" - Research Publications
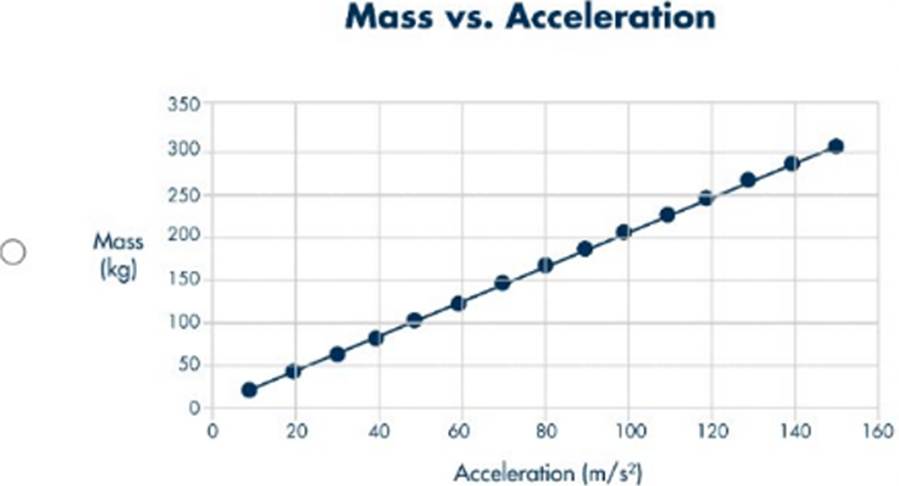
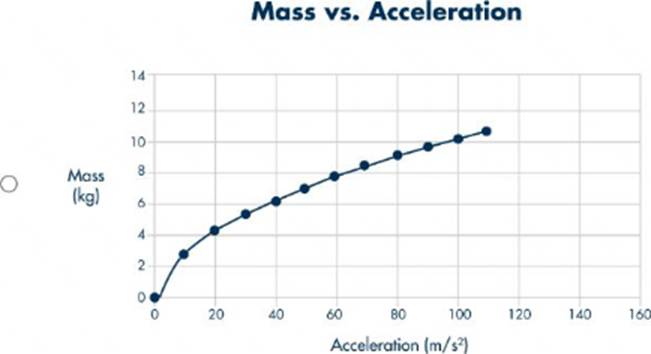
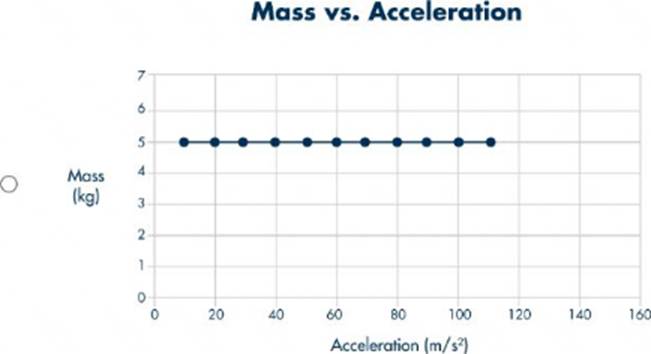
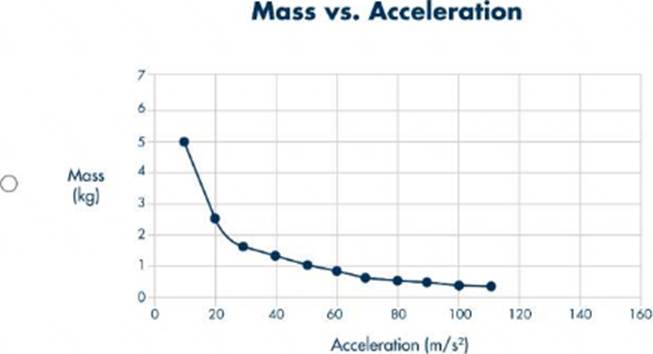
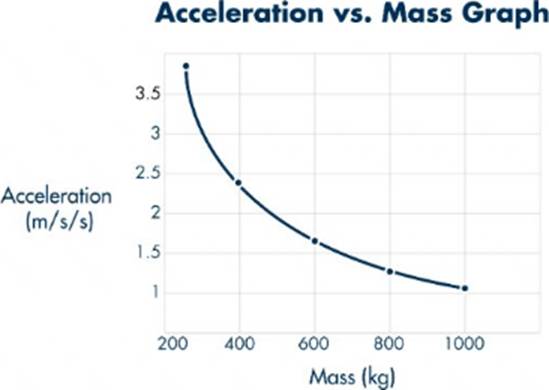
정답:
Explanation:
To determine which graph correctly represents the mass versus acceleration of objects with different masses pulled by the same net force, we must apply Newton's Second Law of Motion. Newton's Second Law states: \[ F = m \cdot a \] where \(F \) is the net force, \(m \) is the mass, and \(a \) is the acceleration. If we rearrange this equation to solve for acceleration, we get: \[ a = \frac{F}{m} \] This shows that acceleration is inversely
proportional to mass when the net force is constant. Therefore, as mass increases, acceleration decreases, and this relationship is not linear but rather a hyperbolic curve. Let's analyze each graph:
- Graph A: Shows a linear relationship between mass and acceleration, which contradicts the inverse relationship dictated by Newton's Second Law.
- Graph B: Shows a curve where acceleration increases with mass, which again contradicts the expected inverse relationship.
- Graph C: Shows a constant mass for all acceleration values, which is not applicable in this context.
- Graph D: Shows a hyperbolic relationship, where acceleration decreases as mass increases, which is consistent with the equation \(a = \frac{F}{m} \). Thus, **Graph D** correctly represents the mass versus acceleration for objects pulled by the same net force, demonstrating the inverse relationship between mass and acceleration.
References: - Newton's Second Law of Motion, Integrated Physical Sciences Learning Resources