Splunk SOAR Certified Automation Developer Exam 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년10월10일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 Splunk SPLK-2003 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 SPLK-2003 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 58개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
Splunk Phantom supports different types of backups to safeguard data. Full backups create a complete copy of the current state of the system, while incremental backups only save the changes made since the last backup. This approach allows for efficient use of storage space and faster backups after the initial full backup. Delta backups, which would save changes since the last full or incremental backup, are not a standard part of Phantom's backup capabilities according to available documentation. Therefore, the complete list of backups supported by Phantom would be Full and Incremental backups.
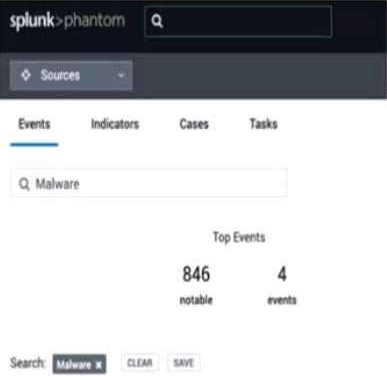
정답:
Explanation:
The image shows a user interface of “splunk>phantom” with a search bar at the top, where a search for “Malware” has been initiated. The tabs labeled “Events,” “Indicators,” “Cases,” and “Tasks” suggest that the search functionality could span across various container fields within the Splunk SOAR environment. Typically, the search would include fields that are most relevant to the user’s query, which in this case, are likely to be the Event Name and Artifact Names. These fields are central to identifying and categorizing events and artifacts within Splunk SOAR, making them primary targets for a search term like “Malware” which is commonly associated with security events and indicators17.
Reference: Understanding containers - Splunk Documentation
정답:
Explanation:
The global block within a Splunk SOAR playbook is primarily used to import external packages or define global variables that will be utilized across various parts of the playbook. This block sets the stage for the playbook by ensuring that all necessary libraries, modules, or predefined variables are available for use in subsequent actions, decision blocks, or custom code segments within the playbook. This practice promotes code reuse and efficiency, enabling more sophisticated and powerful playbook designs by leveraging external functionalities.
정답:
Explanation:
When working with complex data paths in Splunk SOAR, particularly within playbooks, the dot (.) operator is used to access sub-elements within a larger data structure. This operator allows for the navigation through nested data, such as dictionaries or objects within JSON responses, enabling playbook actions and decision blocks to reference specific pieces of data within the artifacts or action results. This capability is crucial for extracting and manipulating relevant information from complex data sets during incident analysis and response automation.
정답:
Explanation:
In Splunk SOAR, when working on a case and analyzing events, items marked as significant evidence are aggregated for review. These evidence items can be collectively viewed on the Investigation page under the Evidence tab. This centralized view allows analysts to easily access and review all marked evidence related to a case, facilitating a streamlined analysis process and ensuring that key information is readily available for investigation and decision-making.
정답:
Explanation:
The format block in Splunk SOAR is utilized to construct text strings by merging static text with dynamic values, which can then be used for both input to other playbook blocks and output for reports, emails, or other forms of communication. This capability is essential for customizing messages, commands, or data processing tasks within a playbook, allowing for the dynamic insertion of variable data into predefined text templates. This feature enhances the playbook's ability to present information clearly and to execute actions that require specific parameter formats.
정답:
Explanation:
Splunk SOAR (formerly Phantom) does not natively run on Windows servers as it is primarily designed for Linux environments. However, it can be deployed on a Windows server through virtualization. By running the Phantom OVA (Open Virtualization Appliance) as a virtual machine, users can utilize virtualization platforms like VMware or VirtualBox on a Windows server to host the Phantom environment. This approach allows for the deployment of Phantom in a Windows-centric infrastructure by leveraging virtualization technology to encapsulate the Phantom application within a supported Linux environment provided by the OVA.
정답:
Explanation:
The phantom.debug() function is used within Splunk SOAR playbooks to output debug information to the debug window in the Visual Playbook Editor. This function is instrumental in troubleshooting and developing playbooks, as it allows developers to print out variables, messages, or any relevant information that can help in understanding the flow of the playbook, the data being processed, and any issues that might arise during execution. This debugging tool is essential for ensuring that playbooks are functioning as intended and for diagnosing any problems that may occur.
정답:
Explanation:
The ROI (Return on Investment) Settings within Splunk SOAR are designed to help organizations
assess the value derived from their use of the platform, particularly in terms of resource allocation and efficiency gains. The setting mentioned in the question, "Number of full time employees (FTEs)," relates directly to measuring this efficiency.
Answer "C" is correct because configuring the number of full-time employees (FTEs) in the ROI settings allows an organization to input and monitor how many personnel are dedicated to security operations managed through SOAR. This setting is crucial for calculating the labor cost associated with incident response and routine security tasks. By understanding the number of FTEs involved, organizations can better assess the labor cost savings provided by automation and orchestration in SOAR. This data helps in quantifying the operational efficiency and the overall impact of SOAR on resource optimization.
In contrast, other options like "Analyst hours per month," "Time lost," and "Annual analyst salary" might seem relevant but are not directly configurable within the ROI settings of Splunk SOAR. These aspects could be indirectly calculated or estimated based on the number of FTEs and other operational metrics but are not directly input as settings in the system.
This use of FTEs in ROI calculations is often discussed in materials related to cybersecurity efficiency metrics and SOAR platform utilization. Official Splunk documentation and best practices guides typically provide insights into how to set up and interpret ROI settings, highlighting the importance of accurate configuration for meaningful analytics.
정답:
Explanation:
The correct answer is A because the _filter parameter is used to filter the results based on a field value, and the icontain operator is used to perform a case-insensitive substring match.
The filePath field is part of the Common Event Format (CEF) standard, and the cef_ prefix is used to access CEF fields in the REST API. The answer B is incorrect because it uses the wrong syntax for the REST API. The answer C is incorrect because it uses the wrong endpoint (result instead of artifact) and the wrong syntax for the REST API. The answer D is incorrect because it uses the wrong syntax for the REST API and the wrong spelling for the icontains operator.
Reference: Splunk SOAR REST API Guide, page 18.
To query and display all artifacts that contain the term "results" in a filePath CEF (Common Event Format) value, using the REST API endpoint with a filter parameter is effective. The filter _filter_cef_filePath_icontain="results" is applied to search within the artifact data for filePath fields that contain the term "results", disregarding case sensitivity. This method allows users to precisely locate and work with artifacts that meet specific criteria, aiding in the investigation and analysis processes within Splunk SOAR.
정답:
Explanation:
The primary system requirement that should be increased with heavy usage of the file vault is the amount of storage. The file vault is a secure repository for storing files on Phantom. The more files are stored, the more storage space is needed. The other options are not directly related to the file vault usage. See [File vault] for more information.
Heavy usage of the file vault in Splunk SOAR necessitates an increase in the amount of storage available. The file vault is used to securely store files associated with cases, such as malware samples, logs, and other artifacts relevant to an investigation. As the volume of files and the size of stored data grow, ensuring sufficient storage capacity becomes critical to maintain performance and ensure that all necessary data is retained for analysis and evidence.
정답:
Explanation:
A step when configuring event forwarding from Splunk to Phantom is to create a Splunk alert that uses the event_forward.py script to send events to Phantom. This script will convert the Splunk events to CEF format and send them to Phantom as containers. The other options are not valid steps for event forwarding. See Forwarding events from Splunk to Phantom for more details.
Configuring event forwarding from Splunk to Phantom typically involves creating a Splunk alert that leverages a script (like event_forward.py) to automatically send triggered event data to Phantom. This setup enables Splunk to act as a detection mechanism that, upon identifying notable events based on predefined criteria, forwards these events to Phantom for further orchestration, automation, and response actions. This integration streamlines the process of incident management by connecting Splunk's powerful data analysis capabilities with Phantom's orchestration and automation framework.
정답:
Explanation:
The main purpose of using a customized workbook is to guide user activity and coordination during event analysis and case operations. Workbooks can be customized to include different phases, tasks, and instructions for the users. The other options are not valid purposes of using a customized workbook. See Workbooks for more information.
Customized workbooks in Splunk SOAR are designed to guide users through the process of analyzing events and managing cases. They provide a structured framework for documenting investigations, tracking progress, and ensuring that all necessary steps are followed during incident response and case management. This helps in coordinating team efforts, maintaining consistency in response activities, and ensuring that all aspects of an incident are thoroughly investigated and resolved. Workbooks can be customized to fit the specific processes and procedures of an organization, making them a versatile tool for managing security operations.
정답:
Explanation:
To get playbook results for a single artifact, a user can utilize the contextual menu option directly from the artifact itself. This method allows for targeted execution of a playbook on just that artifact, facilitating a focused analysis or action based on the data within that specific artifact. This approach is particularly useful when a user needs to drill down into the details of an individual piece of evidence or data point within a larger incident or case, allowing for granular control and execution of playbooks in the Splunk SOAR environment.
정답:
Explanation:
A filter block with only one condition configured which states: artifact.*.cef .sourceAddress !- , would permit only non-null IP addresses to pass forward to the next block. The !- operator means “is not null”. The other options are not valid because they either include null values or other fields than sourceAddress. See Filter block for more details. A filter block in Splunk SOAR that is configured with the condition artifact.*.cef.sourceAddress != (assuming the intention was to use "!=" to denote 'not equal to') is designed to allow data that has non-null sourceAddress values to pass through to subsequent blocks. This means that any artifact data within the container that includes a sourceAddress field with a defined value (i.e., an actual IP address) will be permitted to move forward in the playbook. The filter effectively screens out any artifacts that do not have a source address specified, focusing the playbook's actions on those artifacts that contain valid IP address information in the sourceAddress field.