TOGAF Enterprise Architecture Part 1 Exam (English) 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년10월10일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 The Open Group OGEA-101 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 OGEA-101 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 92개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
Gap Analysis is a technique that compares the Baseline Architecture and the Target Architecture to identify the differences and gaps between them. The purpose of this technique is to determine the changes and additions that are required to achieve the desired future state of the architecture. One of the main aspects of Gap Analysis is to identify the functions that are missing or overlapping in the current and future architectures, and to plan how to address them. This helps to ensure that the architecture is complete, consistent, and aligned with the business objectives and requirements3
정답:
Explanation:
An Architecture Board is an executive-level group responsible for the review and maintenance of the strategic architecture and all of its sub-architectures1. It is a key element in a successful Architecture Governance strategy2.
An Architecture Board is typically made responsible, and accountable, for achieving some or all of the following goals2:
o Providing the basis for all decision-making with regard to the architectures
o Consistency between sub-architectures
o Establishing targets for re-use of components
o Flexibility of the Enterprise Architecture: To meet changing business needs
To leverage new technologies
o Enforcement of Architecture Compliance
o Improving the maturity level of architecture discipline within the organization
o Ensuring that the discipline of architecture-based development is adopted
o Supporting a visible escalation capability for out-of-bounds decisions
Therefore, the correct answer is option D, which captures one of the goals of an Architecture Board as stated in the TOGAF Standard, Version 9.22.
Option A is incorrect, because conducting assessments of the maturity level of architecture discipline within the organization is not a direct responsibility of an Architecture Board, but rather a part of the Architecture Capability Framework3.
Option B is incorrect, because allocating resources for architecture projects is not a direct responsibility of an Architecture Board, but rather a part of the Architecture Governance Framework4.
Option C is incorrect, because creating the Statement of Architecture Work is not a direct responsibility of an Architecture Board, but rather a part of the Architecture Development Method5.
Reference:
1: Architecture Board - The Open Group3
2: TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Part VI: Architecture Governance Framework - Architecture Board
3: TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Part VI: Architecture Governance Framework - Architecture Capability Framework
4: TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Part VI: Architecture Governance Framework - Architecture Governance Framework
5: TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Part II: Architecture Development Method - Phase A: Architecture Vision

정답:
Explanation:
The Request for Architecture Work is a deliverable that is sent from the sponsor and triggers the start of an architecture development cycle. It defines the scope, budget, schedule, and deliverables for a specific architecture project. The Statement of Architecture Work is a deliverable that is produced by the architect and defines the approach and resources needed to complete an architecture project. It forms the basis of a contractual agreement between the sponsor and the architecture organization. The Architecture Principles are a deliverable that is produced by the architect and defines the general rules and guidelines for the architecture work. They reflect the business principles, business goals, and business drivers of the organization. The Architecture Requirements Specification is a deliverable that is produced by the architect and defines the requirements that govern the architecture work. It covers both functional and non-functional requirements as well as constraints and assumptions.
정답:
Explanation:
The purpose of the Architecture Roadmap is to provide a high-level view of how the Baseline Architecture will transition to the Target Architecture over time. It lists work packages on a timeline showing progress towards the Target Architecture, as well as dependencies, risks, and benefits. The
Architecture Roadmap forms part of the Implementation and Migration Plan and guides the execution of the architecture projects.
Reference: https://pubs.opengroup.org/architecture/togaf9-doc/arch/chap20.html
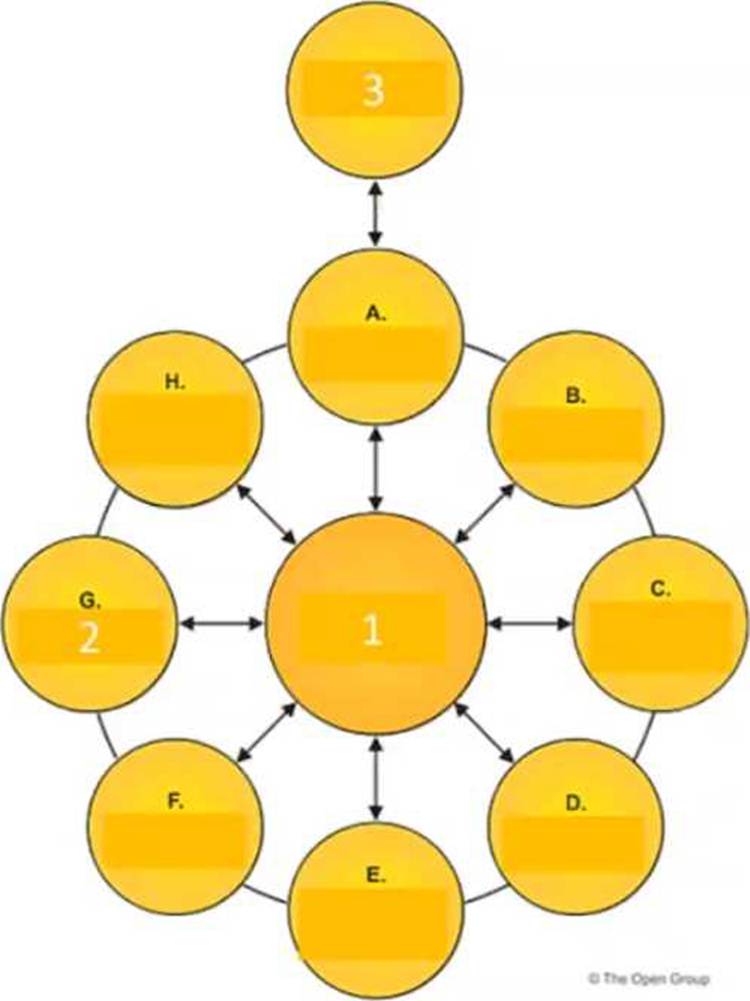
정답:
Explanation:
The illustration shows an architecture development cycle based on the TOGAF ADM (Architecture Development Method), which is a method for developing and managing an enterprise architecture1.
The ADM consists of nine phases, each with a specific purpose and output.
The phases are1:
o Preliminary Phase: To prepare and initiate the architecture development cycle, including defining the architecture framework, principles, and governance.
o Phase A: Architecture Vision: To define the scope, vision, and stakeholders of the architecture initiative, and to obtain approval to proceed.
o Phase B: Business Architecture: To describe the baseline and target business architecture, and to identify the gaps between them.
o Phase C: Information Systems Architectures: To describe the baseline and target data and application architectures, and to identify the gaps between them.
o Phase D: Technology Architecture: To describe the baseline and target technology architecture, and to identify the gaps between them.
o Phase E: Opportunities and Solutions: To identify and evaluate the opportunities and solutions for implementing the target architecture, and to define the work packages and transition architectures.
o Phase F: Migration Planning: To finalize the implementation and migration plan, and to ensure alignment with the enterprise portfolio and project management.
o Phase G: Implementation Governance: To provide architecture oversight and guidance for the implementation projects, and to manage any architecture change requests.
o Phase H: Architecture Change Management: To monitor the changes in the business and technology environment, and to assess the impact and performance of the architecture.
In addition to these phases, there is a central process called Requirements Management, which is labeled as item 1 in the illustration. This process operates throughout the ADM cycle, and its purpose is to manage the architecture
requirements throughout the architecture development, ensuring that they are aligned with the business requirements and the stakeholder concerns2.
Therefore, the description that matches the phase of the ADM labeled as item 1 is
C. Operates the process of managing architecture requirements.
Reference:
1: The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2, Chapter 5: Architecture Development Method (ADM)
2: The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2, Chapter 17: Requirements Management
정답:
Explanation:
Gap analysis is a technique that is used to validate an architecture by highlighting the shortfall between the Baseline Architecture and the Target Architecture. One of the purposes of gap analysis is to identify missing functions that are either deliberately omitted, accidentally left out, or not yet defined in the Target Architecture. Missing functions are marked as gaps that need to be filled by developing or procuring the building blocks.
정답:
Explanation:
A content metamodel is a formal structure that defines the types of entities and relationships that are used to capture, store, filter, query, and represent architectural information in a way that supports consistency, completeness, and traceability12.
A stakeholder map is a tool that identifies and analyzes the key stakeholders and their interests, influence, and expectations in relation to the architecture3. It is not used to structure architectural information, but rather to understand the stakeholder needs and concerns.
An architecture framework is a set of principles, guidelines, standards, and tools that provide a common structure and methodology for developing architectures4. It is not used to structure architectural information, but rather to guide the architecture development process and ensure alignment with the business strategy and objectives.
An EA library is a repository that stores and manages the architecture artifacts, deliverables, and other relevant information produced and consumed during the architecture development and governance. It is not used to structure architectural information, but rather to provide access, security, and version control for the architecture content.
Reference: 1: The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Content Metamodel 2: TOGAF 9.2 Content Metamodel Framework - A Quick Guide - KnowledgeHut 3: The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Stakeholder Management 4: The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Architecture Framework: The TOGAF Standard, Version 9.2 - Architecture Repository
정답:
Explanation:
A set of architecture principles that cover every situation perceived meets the recommended criteria of completeness. Completeness is one of the six criteria that should be applied when developing or assessing architecture principles. Completeness means that there are no gaps or overlaps in the coverage of principles across all relevant aspects of the enterprise’s architecture.
Reference: The TOGAF® Standard | The Open Group Website, Section 3.3.7 Architecture Principles.
정답:
Explanation:
The class of information known as the Reference Library within the Architecture Repository contains guidelines and templates used to create new architectures. The Reference Library provides a set of resources that can be leveraged or customized for specific architecture development purposes. It includes generic building blocks, patterns, models, standards, frameworks, methods, techniques, best practices, etc.
Reference: The TOGAF® Standard | The Open Group Website, Section 2.4 Architecture Repository.
정답:
Explanation:
The purpose of Enterprise Architecture is to guide effective change by providing a coherent and consistent view of the enterprise’s current and future state, as well as the roadmap and principles for achieving it. Enterprise Architecture helps to align business and IT strategies, optimize resources and investments, reduce complexity and risks, enhance agility and innovation, and deliver value to stakeholders.
Reference: The TOGAF® Standard | The Open Group Website, Section 1.3 Executive Overview.
정답:
Explanation:
The ability to develop, use, and sustain the architecture of a particular enterprise using architecture to govern change is an EA Capability. An EA Capability is a set of skills, processes, roles, responsibilities, tools, and techniques that enable an enterprise to successfully develop and maintain its Enterprise Architecture and achieve its desired outcomes. An EA Capability is part of an enterprise’s overall capability portfolio and should be aligned with its strategy and objectives.
Reference: The TOGAF® Standard | The Open Group Website, Section 3.2 Preliminary Phase.
정답:
Explanation:
The statement illustrates iteration and the ADM. Iteration is the technique of repeating a process or a phase with the aim of improving or refining the outcome. Iteration allows for feedback loops and adaptations at any point in the architecture development and transition process. Separate projects may operate their own ADM cycles concurrently, with relationships between the different projects, to address different aspects or levels of the architecture in an iterative manner.
Reference: The TOGAF® Standard | The Open Group Website, Section 3.1 Introduction to the ADM.
정답:
Explanation:
The four dimensions used to scope an architecture are Breadth, Depth, Time Period, and Architecture Domains1, p. 8.
Breadth refers to the extent of the enterprise covered by the architecture, which can range from a specific business unit to the entire organization1, p. 8.
Depth refers to the level of detail and completeness of the architecture, which can vary depending on the purpose, scope, and stakeholders of the architecture1, p. 8.
Time Period refers to the temporal aspects of the architecture, such as the current state, the target state, and the transition plan1, p. 8.
Architecture Domains refers to the classification of the architecture into four domains: Business,
Data, Application, and Technology1, p. 8.
These four dimensions help define the scope and boundaries of the architecture and ensure that it meets the needs and expectations of the stakeholders.
Reference: 1: The Open Group (2018). The TOGAF® Standard, Version 9.2. 1
정답:
Explanation:
This statement best describes iteration and the ADM. The ADM is iterative over the whole process between phases and within phases because it allows for feedback loops and refinements at any point in the architecture development and transition process. Iteration enables architects to address changing requirements, assumptions, constraints, and environments; to validate and improve architectures; to manage risks and issues; and to ensure stakeholder satisfaction and value realization.
Reference: The TOGAF® Standard | The Open Group Website, Section 3.1 Introduction to the ADM.
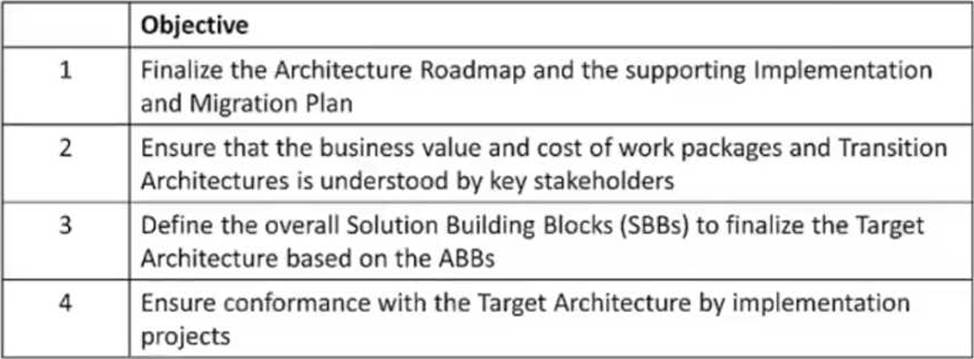
정답:
Explanation:
1E: To identify delivery vehicles (projects programs portfolios) that will deliver the Target
Architecture 2F: To confirm readiness and ability to undergo change 3E: To determine whether an incremental approach is required and if so identify Transition Architectures that will deliver continuous business value 4G: To perform appropriate governance functions while the solution is being implemented
Reference: The TOGAF® Standard | The Open Group Website, Section 3.2 ADM Phases.