Nutanix Certified Professional - Multicloud Automation (NCP-MCA) 5 Exam 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년10월10일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 Nutanix NCP-MCA 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 NCP-MCA 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 75개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
A playbook REST API action allows the administrator to send an HTTP request to a specified endpoint, such as the Prism Central API, to perform an operation, such as deleting a VM. A playbook webhook action allows the administrator to send a payload to a specified URL, such as a ServiceNow webhook, to trigger an event, such as an approval flow. Both of these actions can be used to automate the deletion of VMs from a ServiceNow approval flow, where the developers can request and confirm the removal of their environments. A playbook webhook trigger and a playbook REST API trigger are not valid options, as they are used to initiate a playbook based on an external event, not to perform an action within a playbook.
Reference: Nutanix Certified Professional - Multicloud Automation (NCP-MCA) 6.5 Exam Blueprint Guide, page 10; Nutanix Certified Professional - Multicloud Automation (NCP-MCA), section 4; NCP-MCA Exam Dumps - Nutanix Certified Professional - Multicloud …, question 70.
Reference: https://portal.nutanix.com/page/documents/details?targetId=Prism-Central-Guide-Prism-v6_0:mul-service-now-configure-webhook-playbooks-pc-t.html
정답:
Explanation:
Scaling VM replica settings allow you to specify the minimum, maximum, and default number of VMs that can be created from a blueprint service. The minimum and default values must be equal to or greater than the number of VMs needed at any time and at time of deployment, which is 2 in this case. The maximum value must be equal to or less than the project quota divided by the VM resources, which is 100/12 = 8 for vCPUs and 300/24 = 12 for memory. The lowest of these two values is the limit for the maximum value, which is 8. Therefore, the only option that meets all the requirements is B. MIN: 2, MAX: 7, Default: 2.
Reference: Nutanix Certified Professional - Multicloud Automation (NCP-MCA) Exam Blueprint Guide, page 10, Objective 3.1: Given a scenario, create a blueprint to deploy infrastructure and applications using Self-Service
Nutanix Multicloud Automation Administration (NMCAA), Module 5: Self-Service, Lesson 5.2: Blueprint Design, slide 23: Scaling VM Replica Settings
Nutanix Certified Professional Multicloud Automation (NCP-MCA) 6 Exam, page 10, Objective 3.1: Given a scenario, create a blueprint to deploy infrastructure and applications using Self-Service
정답:
Explanation:
A Playbook is a set of actions that are triggered by an event or a schedule. To run a Playbook, it must be enabled first. If a Playbook is not enabled, it will not respond to any events or schedules, and no Plays will be recorded for it. Therefore, the most likely cause of the issue is that the administrator forgot to enable the Playbook after building it.
Reference: Nutanix Certified Professional - Multicloud Automation (NCP-MCA) Exam Blueprint Guide, page 13, section 3.2. Nutanix Multicloud Automation Administration (NMCAA) course, module 4, lesson 2.
Reference: https://portal.nutanix.com/page/documents/details?targetId=Prism-Central-Guide-Prism-v6_0:Prism-Central-Guide-Prism-v6_0
정답:
Explanation:
According to the Nutanix Multicloud Automation Administration (NMCAA) course, the recommended Prism Central VM size depends on the number of VMs that are managed by Calm and the number of concurrent users. For a large-scale environment with more than 5000 VMs and more than 100 concurrent users, the recommended size is 3 nodes Large - 10vCPU and 52GB Memory per node1.
This size provides enough resources for the Prism Central cluster to handle the workload and performance requirements of Calm.
Reference: Nutanix Multicloud Automation Administration (NMCAA) course, Module 2: Nutanix Calm
Installation and Configuration, Lesson 2: Nutanix Calm Installation and Configuration2
Nutanix Certified Professional - Multicloud Automation (NCP-MCA) v6.5 Exam Blueprint Guide, Section 2: Deploy and Configure Self-service and Related Components, Objective 2.2: Identify required configuration settings for a Self-Service deployment3 Scaling out Prism Central | Nutanix Community1
Reference: https://portal.nutanix.com/page/documents/solutions/details?targetId=Nutanix_Hybrid_Cloud_Reference_Architecture:Nutanix_Hybrid_Cloud_Reference_Architecture
정답:
Explanation:
A Brownfield Application is a type of application that allows you to import and manage existing VMs that were not deployed by Calm. You can use a Brownfield Application to perform actions such as start, stop, restart, delete, or execute scripts on the imported VMs. You can also add services, credentials, variables, and policies to the Brownfield Application blueprint. To create a Brownfield Application, you need to select a multi-VM blueprint and then choose the VMs that you want to include in the application from the drop down list. You can also filter the VMs by name, cluster, or power state.
A Greenfield Application is a type of application that allows you to deploy new VMs from scratch using Calm. You can use a Greenfield Application to provision and configure VMs on different cloud platforms, such as Nutanix AHV, VMware ESXi, AWS, Azure, or GCP. You can also add services, credentials, variables, and policies to the Greenfield Application blueprint. To create a Greenfield Application, you need to select a single-VM or a multi-VM blueprint and then specify the VM properties, such as name, image, flavor, network, storage, etc.
Reference: Nutanix Calm DSL C Brownfield Apps the Easy Way
Nutanix Support & Insights
Getting started with Nutanix Calm
정답:
Explanation:
Nutanix provides a documented process to seed Github based scripts into the Calm Task Library, which allows users to import and use custom tasks from the Nutanix public Github repository or any other Github repository. This process is described in the Nutanix Calm DSL User Guide and the Nutanix Calm DSL Tutorial.
Nutanix also publishes official vetted blueprints and tasks to Nutanix’s public Github Calm repository, which is located at https://github.com/nutanix/blueprints. These blueprints and tasks are created and maintained by Nutanix engineers and can be used as reference or templates for building Calm applications.
Some examples of these blueprints and tasks are:
Kubernetes Cluster: A blueprint that deploys a Kubernetes cluster on Nutanix AHV using Calm. MySQL HA: A blueprint that deploys a MySQL cluster with high availability on Nutanix AHV using Calm.
Windows Server: A blueprint that deploys a Windows Server 2019 VM on Nutanix AHV using Calm.
[Install Python]: A task that installs Python on a Linux VM using Calm.
Calm’s public repository does not contain Nutanix-vetted custom scripts created and published by community members. These scripts are hosted in a separate repository called [Automation], which is a centralized repo for community driven Nutanix automation. These scripts are not officially supported or endorsed by Nutanix and may not be compatible with the latest versions of Calm or Nutanix products.
Nutanix does not provide documented processes to seed scripts from any source repository. Users can only import scripts from Github repositories using the Calm Task Library.
Other source repositories are not supported by Calm.
Reference: Nutanix Calm DSL User Guide
Nutanix Calm DSL Tutorial
Nutanix Calm Blueprints
Kubernetes Cluster
MySQL HA
Windows Server
[Install Python]
[Automation]
정답:
Explanation:
The Calm Marketplace acts as an application store, providing end users with a catalog of available applications. By default, Calm comes pre-seeded with validated Blueprints for multiple open source and enterprise applications. These are the set of pre-seeded application Blueprints. Additionally, Marketplace Manager acts as a staging area for publishing default and user-created Blueprints to your local Marketplace. These are the published and versioned Blueprints. The other two options, library of executable tasks and store of all Blueprints created in Calm, are not features of the Calm Marketplace.
Reference: Calm: Marketplace - Read the Docs and Calm: Marketplace - Read the Docs
정답:
Explanation:
The styx.log file contains the logs related to blueprint packaging and deployment. It can be accessed by SSHing to Prism Central and navigating to the /home/calm/log directory. The other options are not relevant for blueprint package failures, as they show the application status, audit events, or service logs.
Reference: Nutanix Certified Professional - Multicloud Automation (NCP-MCA) 6.5 Exam Blueprint Guide, page 9; Nutanix Certified Professional - Multicloud Automation (NCP-MCA), section 3; NCP-MCA Exam Dumps - Nutanix Certified Professional - Multicloud …, question 63.
정답:
Explanation:
Reference: https://portal.nutanix.com/page/documents/details?targetId=Prism-Central-Guide-Prism-v6_0:mul-playbooks-create-manual-triggers-pc-t.html#suppression-rules-add-aws-sc-t
정답:
Explanation:
A Playbook is a collection of tasks that can be executed based on a trigger, such as a time, a webhook, or a manual action. A Playbook can be used to automate workflows across different systems and services, such as Nutanix Prism, VMs, hosts, and external APIs. A Playbook can also use variables, conditions, and loops to customize the execution logic and data.
In this scenario, the administrator wants to automate the batch processing application on the Linux VM, which can only be controlled by a command on the VM console. The application should run only outside of business hours, and the VM should send REST API calls to Prism to report its status.
The best way to configure a Playbook for this process is to use a Time Trigger, which allows the administrator to specify a schedule for the Playbook execution, such as daily, weekly, or monthly. The Time Trigger can also be configured to run only on certain days or hours, such as weekdays or nights. This way, the administrator can ensure that the Playbook runs only outside of business hours, without requiring any manual intervention.
The Playbook should then have two VM SSH tasks, one to initiate the batch processing application, and one to terminate it. A VM SSH task is a task that executes a command or script on a target VM using SSH. A VM SSH task can be used to control applications or services that do not have a programmatic interface, such as the batch processing application in this scenario. The VM SSH task can also use variables to pass data to or from the command or script, such as the VM name, IP address, or output.
The Playbook should also have a Wait for Some Time task, which is a task that pauses the Playbook execution for a specified duration or until a condition is met. A Wait for Some Time task can be used to ensure that the batch processing application has enough time to complete its work, or to wait for a certain event or state to occur, such as a file creation, a service status, or a VM power state.
The Playbook should also have two REST API tasks, one before and one after the Wait for Some Time task. A REST API task is a task that executes an HTTP request to a specified URL, with optional headers, body, and authentication. A REST API task can be used to interact with external systems or services that expose an API, such as Nutanix Prism in this scenario. The REST API task can also use variables to pass data to or from the HTTP request, such as the VM name, IP address, or response. The REST API tasks should be configured to send the VM status to Prism, such as the start and end time of the batch processing, the CPU and memory usage, or the output of the application. This way, the administrator can monitor and manage the VM and the application from Prism, without having to connect to the VM console.
The Playbook configuration should look something like this:
Time Trigger: Set the schedule to run daily, only on weekdays, and only at night (e.g., 10 PM to 6 AM).
VM SSH: Set the target VM to the Linux VM, and set the command or script to initiate the batch processing application (e.g., ./batch.sh start).
REST API: Set the URL to the Prism API endpoint, and set the HTTP method, headers, body, and authentication as required. Use variables to pass the VM name, IP address, and start time of the batch processing to the HTTP request (e.g., {"vm_name": "{{vm_name}}", "vm_ip": "{{vm_ip}}", "start_time": "{{start_time}}"}).
Wait for Some Time: Set the duration to the expected time for the batch processing to finish, or set a condition to wait until a certain event or state occurs (e.g., wait until file /tmp/batch.done exists). REST API: Set the URL to the Prism API endpoint, and set the HTTP method, headers, body, and authentication as required. Use variables to pass the VM name, IP address, end time, and output of the batch processing to the HTTP request (e.g., {"vm_name": "{{vm_name}}", "vm_ip": "{{vm_ip}}", "end_time": "{{end_time}}", "output": "{{output}}"}).
VM SSH: Set the target VM to the Linux VM, and set the command or script to terminate the batch processing application (e.g., ./batch.sh stop).
Reference:
https://www.nutanix.com/content/dam/nutanix/resources/datasheets/ds-ncp-mca-6-5.pdf
https://www.nutanix.com/content/dam/nutanix/resources/support/ds-ncp-mca.pdf
정답:
Explanation:
Within a Calm blueprint, an administrator can apply two actions to a Service under the Guest Customization section: Apply a Cloudinit Script and Apply a Sysprep file. These actions allow the administrator to customize the configuration and behavior of the virtual machines that are provisioned from the blueprint. A Cloudinit Script is a set of commands or scripts that run on Linux-based virtual machines during the boot process. A Sysprep file is a configuration file that specifies the Windows settings and options for the virtual machines. These actions can be used to perform tasks such as setting the hostname, network configuration, user accounts, software installation, and more.
Reference: Nutanix Certified Professional - Multicloud Automation (NCP-MCA) v6.5, Section 2 - Deploy and Configure Nutanix Calm and Related Components, page 3
Nutanix Multicloud Automation Administration (NMCAA), Module 2 - Nutanix Calm, Lesson 2.2 - Blueprint Management, page 9
Nutanix Calm User Guide, Blueprint, Guest Customization
Reference: https://portal.nutanix.com/page/documents/details?targetId=Nutanix-Calm-Admin-Operations-Guide-v3_2_7:nuc-nucalm-blueprints-intro-c.html
정답:
Explanation:
Runbooks are a feature of Calm that allows for the creation of task-based automation against dynamic lists of Windows or Linux VMs. A runbook is a collection of tasks that can be executed on one or more VMs or services. A task is a unit of automation that can perform actions such as executing commands, running scripts, invoking APIs, or sending notifications. A runbook can be triggered manually, on a schedule, or based on an event. Runbooks can be used to automate common operations such as backup, restore, patching, scaling, or troubleshooting.
Reference: Nutanix Certified Professional - Multicloud Automation (NCP-MCA) Exam Blueprint Guide, page 16; Nutanix Calm User Guide, section 3.4.
Reference: https://portal.nutanix.com/page/documents/details?targetId=Nutanix-Calm-Admin-Operations-Guide-v3_2_7:nuc-nucalm-using-nucalm-c.html
정답:
Explanation:
A Calm Developer is a role that allows a user to create, update, and execute Playbooks in Calm. A Playbook is a collection of Tasks that can be executed on one or more Targets, such as VMs, applications, or services. A Calm Developer can also create and use Runbooks, Blueprints, and Library items in Calm. A Prism Admin is a role that allows a user to manage the Prism Central instance and its features, such as users, roles, alerts, policies, etc. A Calm Admin is a role that allows a user to manage the Calm service and its settings, such as endpoints, credentials, projects, etc. A Project Admin is a role that allows a user to manage a specific project and its resources, such as applications, Blueprints, Runbooks, etc.
Reference: Nutanix Certified Professional - Multicloud Automation (NCP-MCA) Exam Blueprint Guide, page 14, section 4.1.1
Nutanix Calm Roles and Permissions
Nutanix Calm Playbooks
정답:
Explanation:
The most likely reason for this behavior is that the developer created a post-create task for reserving the IP address. A post-create task is executed after the VM is created and powered on, which means that the VM already obtained a DHCP IP address before the task is run. To reserve the IP address in IPAM as part of the deployment process, the developer should create a pre-create task instead. A pre-create task is executed before the VM is created and powered on, which allows the task to reserve the IP address in IPAM and assign it to the VM.
Reference: Nutanix Certified Professional - Multicloud Automation (NCP-MCA) Exam Blueprint Guide, page 15; Nutanix NCP-MCA Questions, question 57.
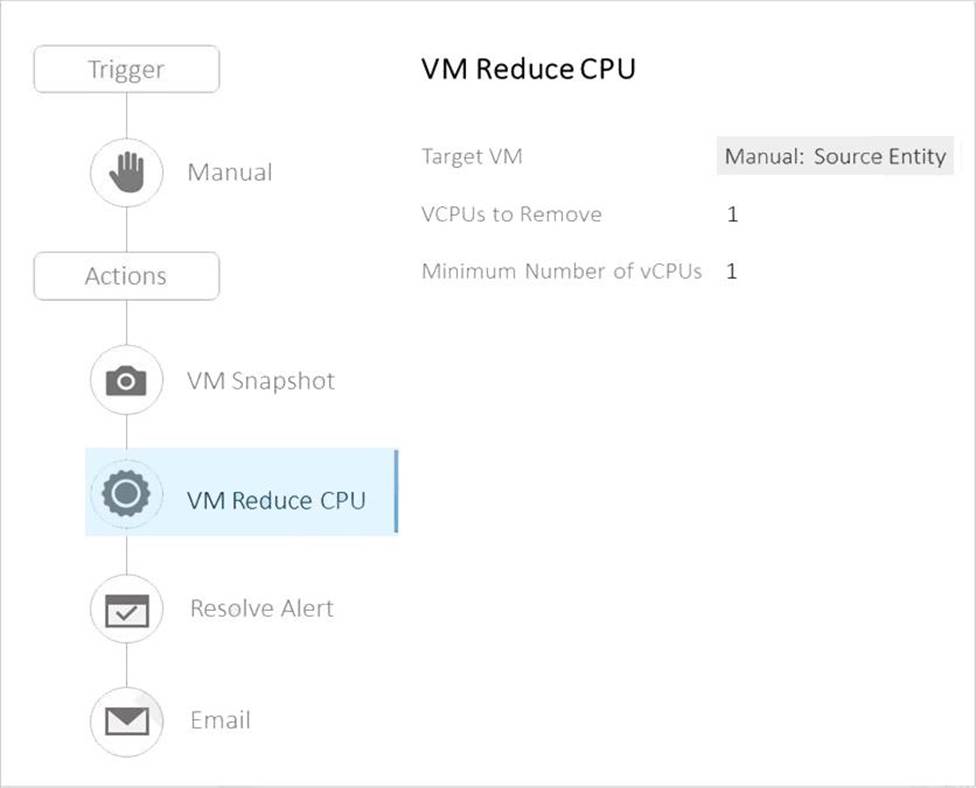
정답:
Explanation:
The Playbook is designed to manually reduce the vCPU count on any selected VM within the environment. However, it failed during a test run on VM2 because there was a running snapshot of the VM. According to Nutanix Multicloud Automation (NCP-MCA) principles, you cannot reduce the vCPU count on a VM that has an active snapshot1. This is because the snapshot captures the state of the VM configuration and data, and reverting to a snapshot will restore both the guest OS and the virtual hardware2. Therefore, changing the vCPU count while a snapshot is running will cause inconsistency and error.
The other options are incorrect because:
A. The Playbook can be executed against a VM on AHV, as long as there is no snapshot running3.
B. The VM does not need to be powered off before vCPU can be reduced, as this can be done using hot-plug CPU feature4.
D. The play will not cause the VM to go below the minimum vCPU, as the minimum number of vCPUs is set to 1 in the Playbook, and the VM has 4 vCPUs initially.
Reference: Nutanix Support & Insights, Solved: Snapshot query !! - VMware Technology Network VMTN, Calm on ESXi Deployment | Nutanix Community, Virtual CPU Configuration and Limitations - VMware Docs