PECB Certified ISO/IEC 27001 Lead Auditor exam 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년10월10일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 PECB ISO-IEC-27001 Lead Auditor 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 ISO-IEC-27001 Lead Auditor 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 100개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
The overall competence of the12:
The audit scope and criteria: The audit scope defines the extent and boundaries of the audit, such as the locations, processes, functions, and time period to be audited. The audit criteria are the set of policies, procedures, standards, or requirements used as a reference against which the audit evidence is compared. The audit scope and criteria determine the complexity and extent of the audit, and thus influence the number and expertise of the auditors needed to cover all the relevant aspects of the audit.
The overall competence of the audit team needed to achieve audit objectives: The audit team should have the appropriate knowledge, skills, and experience to conduct the audit effectively and efficiently, and to provide credible and reliable audit results. The audit team competence should include the following elements12:
Generic competence: The ability to apply the principles and methods of auditing, such as planning, conducting, reporting, and following up the audit, as well as the personal behaviour and attributes of the auditors, such as ethical conduct, fair presentation, professional care, independence, and impartiality.
Discipline and sector-specific competence: The ability to understand and apply the audit criteria and the relevant technical or industry aspects of the audited organization, such as the information security management system (ISMS) requirements, the information security risks and controls, the legal and regulatory obligations, the organizational context and culture, the processes and activities, the products and services, etc.
Audit team leader competence: The ability to manage the audit team and the audit process, such as coordinating the audit activities, communicating with the audit programme manager and the auditee, resolving any audit-related problems, ensuring the quality and consistency of the audit work and the audit report, etc.
The person responsible for managing the audit programme should not consider the following factors when deciding the size and composition of the audit team for a specific audit, as they are either irrelevant or inappropriate for the audit process12:
Customer relationships: The audit team should not be influenced by any personal or professional relationships with the auditee or other interested parties, as this may compromise the objectivity and impartiality of the audit. The audit team should avoid any conflicts of interest or self-interest that may affect the audit results or the audit decisions.
Seniority of the audit team leader: The audit team leader should be selected based on their competence and experience, not on their seniority or rank within the organization or the audit programme. The audit team leader should have the authority and responsibility to manage the audit team and the audit process, regardless of their seniority or position.
The cost of the audit: The cost of the audit should not be the primary factor for determining the size and composition of the audit team, as this may compromise the quality and effectiveness of the audit. The audit team should have sufficient resources and time to conduct the audit in accordance with the audit objectives, scope, and criteria, and to provide accurate and reliable audit results and recommendations.
The duration preferred by the auditee: The duration of the audit should be based on the audit objectives, scope, and criteria, and the availability and cooperation of the auditee, not on the preference or convenience of the auditee. The audit team should have enough time to conduct the audit in a thorough and systematic manner, and to collect and evaluate sufficient and relevant audit evidence.
Reference: ISO 19011:2018 - Guidelines for auditing management systems PECB Candidate Handbook ISO 27001 Lead Auditor, pages 19-20

정답: 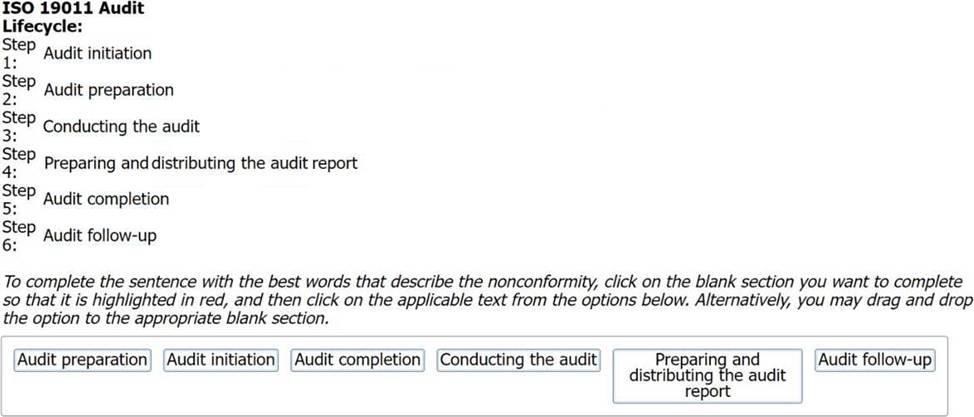
Explanation:
The correct sequence of the steps of the audit lifecycle according to ISO 19011:2018 is:
Step 1: Audit initiation
Step 2: Audit preparation
Step 3: Conducting the audit
Step 4: Preparing and distributing the audit report
Step 5: Audit completion
Step 6: Audit follow-up
This sequence reflects the logical order of the audit activities, from establishing the audit objectives, scope and criteria, to verifying the implementation and effectiveness of the corrective actions. However, ISO 19011:2018 also recognizes that some audit activities can be iterative or concurrent, depending on the nature and complexity of the audit. For example, audit preparation and conducting the audit can overlap when new information or changes occur during the audit. Similarly, audit follow-up can be integrated with audit completion when the corrective actions are verified shortly after the audit. Therefore, the audit lifecycle should be adapted to the specific context and needs of each audit.
정답:
Explanation:
Establishing the audit programme objectives, scope and criteria
Determining the resources necessary for the audit programme, such as the audit team members, the budget, the time, the tools, etc.
Selecting and appointing the audit team leaders and auditors Reviewing and approving the audit plans and arrangements
Ensuring the effective communication and coordination among the audit programme stakeholders, such as the auditors, the auditees, the certification bodies, the accreditation bodies, etc.
Keeping informed the accreditation body on the progress of the audit programme, especially in case of any significant changes, issues, or nonconformities
Monitoring and reviewing the performance and results of the audit programme and the audit teams
Evaluating the feedback and satisfaction of the auditees and other interested parties
Identifying and implementing the opportunities for improvement of the audit programme
The individual(s) managing the audit programme are not responsible for the following tasks, which are delegated to the audit team leaders or the auditors12:
Communicating with the auditee during the audit, such as conducting the opening and closing meetings, resolving any audit-related problems, reporting any audit findings, etc. Determining the legal requirements applicable to each audit, such as the confidentiality, the impartiality, the consent, the liability, etc.
Defining the objectives, scope and criteria for an individual audit, which are derived from the audit programme and agreed with the auditee
Defining the plan of an individual audit, which includes the audit schedule, the audit activities, the audit methods, the audit documents, etc.
Reference: ISO 19011:2018 - Guidelines for auditing management systems PECB Candidate Handbook ISO 27001 Lead Auditor, pages 19-20

정답: 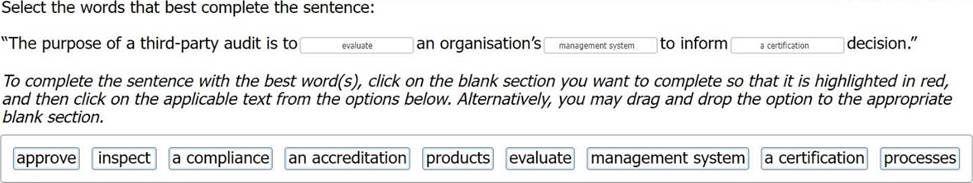
Explanation:
A third-party audit is an independent assessment of an organisation’s management system by an external auditor, who is not affiliated with the organisation or its customers. The auditor verifies that the management system meets the requirements of a specific standard, such as ISO 27001, and evaluates its effectiveness and performance. The auditor also identifies any strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, or risks of the management system, and provides recommendations for improvement. The purpose of a third-party audit is to provide an objective and impartial evaluation of the organisation’s management system, and to inform a certification decision by a certification body. A certification body is an organisation that grants a certificate of conformity to the organisation, after reviewing the audit report and evidence, and confirming that the management system meets the certification criteria. A certification decision is the outcome of the certification process, which can be positive (granting, maintaining, renewing, or expanding the scope of certification) or negative (suspending, withdrawing, or reducing the scope of certification).
Reference: PECB Candidate Handbook ISO 27001 Lead Auditor, pages 19-25 ISO 19011:2018 - Guidelines for auditing management systems The ISO 27001 audit process | ISMS.online
정답:
Explanation:
The two phrases that would apply to ‘check’ in the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle for a business process are:
C. Verifying training
F. Auditing processes
C. This phrase applies to ‘check’ in the PDCA cycle because it involves measuring and evaluating the effectiveness of the training activities that were implemented in the ‘do’ phase. Training is an important aspect of information security awareness, education, and competence, which are required by clause 7.2 of ISO 27001:20221. Verifying training can help the organisation to assess whether the staff have acquired the necessary knowledge, skills, and behaviour to perform their roles and responsibilities in relation to information security. Verifying training can also help the organisation to identify any gaps or weaknesses in the training program and to plan for improvement actions.
F. This phrase applies to ‘check’ in the PDCA cycle because it involves examining and reviewing the performance and conformity of the processes that were implemented in the ‘do’ phase. Auditing is a systematic, independent, and documented process for obtaining objective evidence and evaluating it to determine the extent to which the audit criteria are fulfilled2. Auditing processes can help the organisation to verify whether the information security objectives and requirements are met, whether the information security controls are effective and efficient, and whether the information security risks are adequately managed. Auditing processes can also help the organisation to identify any nonconformities or opportunities for improvement and to plan for corrective or preventive actions.
Reference: 1: ISO/IEC 27001:2022 - Information technology ― Security techniques ― Information security management systems ― Requirements, clause 7.2 2: ISO 19011:2018 - Guidelines for auditing management systems, clause 3.2

정답: 
Explanation:
According to ISO 27001:2013, clause 5.2, the top management of an organization must establish, implement and maintain an information security policy that is appropriate to the purpose of the organization and provides a framework for setting information security objectives. The information security policy must also include a commitment to comply with the applicable legal, regulatory and contractual requirements, as well as any other requirements that the organization subscribes to. Therefore, maintaining regulatory compliance is part of fulfilling the management system policy and ensuring its effectiveness and suitability.
Reference: ISO/IEC 27001:2013, Information technology ― Security techniques ― Information security management systems ― Requirements, clause 5.2
PECB Candidate Handbook ISO 27001 Lead Auditor, page 10 ISO 27001 Policy: How to write it according to ISO 27001
정답:
Explanation:
The benefits of implementing an ISMS primarily result from a reduction in information security risks.
E. The purpose of an ISMS is to apply a risk management process for preserving information security. Comprehensive and Detailed
According to the ISO 27001 standard, the benefits of implementing an ISMS include the following1:
Assuring customers and other stakeholders of the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information Enhancing the ability to respond to information security incidents and minimize their impacts Improving the governance and management of information security
Reducing the costs and losses associated with information security breaches Increasing the competitiveness and reputation of the organization
Complying with legal, regulatory and contractual obligations The purpose of an ISMS is to provide a systematic approach to managing information security risks, based on the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA)
cycle1. The ISMS enables the organization to establish, implement, maintain and continually improve its information security performance, in alignment with its business objectives and the needs and expectations of interested parties1.
The ISMS consists of the following elements1:
The information security policy and objectives
The scope and boundaries of the ISMS
The processes and procedures for information security risk assessment and treatment
The resources and competencies for information security
The roles and responsibilities for information security
The performance evaluation and improvement of the ISMS
The internal and external communication and awareness of the ISMS
Reference: ISO/IEC 27001:2013, Information technology ― Security techniques ― Information security management systems ― Requirements, clauses 1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10
PECB Candidate Handbook ISO 27001 Lead Auditor, pages 9-11 ISO/IEC 27001:2013 Information Security Management Standards 4 Key Benefits of ISO 27001 Implementation | ISMS.online ISO/IEC 27001:2022
An Introduction to the ISO 27001 ISMS | Secureframe
정답:
Explanation:
This is the definition of an interested party according to ISO 27001:2013, clause 3.16. An interested party is essentially a stakeholder, i.e., a person or organization that can influence or be influenced by the information security management system (ISMS) or its activities. Interested parties can have different needs and expectations regarding the ISMS, and these should be identified and addressed by the organization.
Reference: ISO/IEC 27001:2013, Information technology ― Security techniques ― Information security management systems ― Requirements, clause 3.16
PECB Candidate Handbook ISO 27001 Lead Auditor, page 10
Identifying interested parties and their expectations for an ISO 27001 ISMS Examples of ISO 27001 interested parties
정답: B, F, G
Explanation:
According to the ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Lead Auditor (Information Security Management Systems) course, the following corrections and corrective actions are expected from ABC in response to the nonconformity:
B. The Service Manager provides evidence of analysis of the cause of nonconformity and how the ABC evaluates the effectiveness of implemented corrective actions. This is part of the requirement of clause 10.1 of ISO/IEC 27001:2022, which states that the organization shall determine the causes of nonconformities and evaluate the need for action to ensure that they do not recur or occur elsewhere12. The organization shall also evaluate the effectiveness of any corrective actions taken12.
F. ABC identifies and checks compliance with all applicable legislation and contractual requirements involving third parties. This is part of the requirement of clause 4.2 of ISO/IEC 27001:2022, which states that the organization shall determine the external and internal issues that are relevant to its purpose and that affect its ability to achieve the intended outcome(s) of its information security management system12. This includes the legal and contractual requirements related to the information security aspects of the organization’s activities, products and services12.
G. The Service Manager implements the corrective actions and Customer Service Representatives evaluate the effectiveness of implemented corrective actions. This is part of the requirement of clause 10.1 of ISO/IEC 27001:2022, which states that the organization shall implement any action needed and retain documented information as evidence of the results of any action taken12. The organization shall also monitor, measure, analyze and evaluate the information security performance and the effectiveness of the information security management system12.
Reference: 1: ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Lead Auditor (Information Security Management Systems) course, CQI and IRCA Certified Training, 1
2: ISO/IEC 27001 Lead Auditor Training Course, PECB, 2
정답:
Explanation:
According to the ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Lead Auditor (Information Security Management Systems) course, the following actions should be taken when a nonconformity identified for completion before the follow-up audit is still outstanding:
A. Report the failure to address the corrective action for the outstanding nonconformity to the organisation’s top management. This is part of the auditor’s responsibility to communicate the audit results and ensure that the audit objectives are met12.
C. If the delay is justified agree on a revised date for clearing the nonconformity with the auditee/audit client. This is part of the auditor’s responsibility to verify the effectiveness of the corrective actions taken by the auditee and to close the nonconformity when the evidence is satisfactory12.
. Decide whether the delay in addressing the nonconformity is justified. This is part of the auditor’s responsibility to evaluate the evidence presented by the auditee and to use professional judgement and objectivity to determine the validity of the reasons for the delay12.
G. Note the nonconformity is still outstanding and follow audit trails to determine why. This is part of
the auditor’s responsibility to collect and verify audit evidence and to identify the root causes of the
nonconformity12.
Reference: 1: ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Lead Auditor (Information Security Management Systems) course, CQI and IRCA Certified Training, 1
2: ISO/IEC 27001 Lead Auditor Training Course, PECB, 2
정답:
Explanation:
According to ISO 27001:2022 clause 9.1.2, the organisation shall conduct internal audits at planned intervals to provide information on whether the information security management system conforms to the organisation’s own requirements, the requirements of ISO 27001:2022, and is effectively implemented and maintained12
According to ISO 27001:2022 clause 10.1, the organisation shall react to the nonconformities and take action, as applicable, to control and correct them and deal with the consequences. The organisation shall also evaluate the need for action to eliminate the causes of nonconformities, in order to prevent recurrence or occurrence. The organisation shall implement any action needed, review the effectiveness of any corrective action taken, and make changes to the information security management system, if necessary12
A follow-up audit is a type of internal audit that is conducted after a previous audit to verify whether the nonconformities and corrective actions have been addressed and resolved, and whether the information security management system has been improved12
Therefore, the following statements are true for preparing a follow-up audit plan:
Verification should focus on whether any action undertaken is complete. This means that the auditor should check whether the organisation has implemented all the planned actions to correct and prevent the nonconformities, and whether the actions have been documented and communicated as required12
Verification should focus on whether any action undertaken has been undertaken effectively. This means that the auditor should check whether the organisation has achieved the intended results and objectives of the actions, and whether the actions have eliminated or reduced the nonconformities and their causes and consequences12
The following statements are false for preparing a follow-up audit plan:
Verification should focus on whether any action undertaken has been undertaken efficiently. This is false because efficiency is not a criterion for verifying the actions taken to address the nonconformities and corrective actions. Efficiency refers to the optimal use of resources to achieve the desired outcomes, but it is not a requirement of ISO 27001:2022. The auditor should focus on the effectiveness and completeness of the actions, not on the efficiency12
Corrections should be verified first, followed by corrective actions and finally opportunities for improvement. This is false because there is no prescribed order for verifying the corrections, corrective actions, and opportunities for improvement. The auditor should verify all the actions taken by the organisation, regardless of their sequence or priority. The auditor may choose to verify the actions based on their relevance, significance, or impact, but this is not a mandatory requirement12
Opportunities for improvement should be verified first, followed by corrections and finally corrective actions. This is false because there is no prescribed order for verifying the opportunities for improvement, corrections, and corrective actions. The auditor should verify all the actions taken by the organisation, regardless of their sequence or priority. The auditor may choose to verify the actions based on their relevance, significance, or impact, but this is not a mandatory requirement12 Corrective actions should be reviewed first, followed by corrections and finally opportunities for improvement. This is false because there is no prescribed order for reviewing the corrective actions, corrections, and opportunities for improvement. The auditor should review all the actions taken by the organisation, regardless of their sequence or priority. The auditor may choose to review the actions based on their relevance, significance, or impact, but this is not a mandatory requirement12
Reference: 1: ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Lead Auditor (Information Security Management Systems) Course by CQI and IRCA Certified Training 1 2: ISO/IEC 27001 Lead Auditor Training Course by PECB 2
정답:
Explanation:
According to ISO 27001:2022 clause 8.1.4, the organisation shall ensure that externally provided processes, products or services that are relevant to the information security management system are controlled. This includes implementing appropriate contractual requirements related to information security with external providers, such as customers who send ICT equipment for reclamation12
In this case, ABC is a residential nursing home that provides healthcare services to its residents and collects their personal data and their family members’ personal data. ABC has a signed service agreement with the residents’ family members that states that the collected personal data will not be used for marketing or any other purposes than nursing and medical care. However, ABC has violated this contractual requirement by sharing the personal data with WeCare, a medical device manufacturer, who has used the data to send promotional advertisements to the residents’ family members via email and SMS. This has caused dissatisfaction and complaints from the residents’ family members, who have a strong reason to believe that ABC is leaking their personal information to a non-relevant third party.
Therefore, the audit finding is a nonconformity with clause 8.1.4 of ISO 27001:2022, as ABC has failed to control the externally provided processes, products or services that are relevant to the information security management system, and has breached the contractual requirements related to information security with its customers. The fact that ABC has taken corrective actions to stop working with WeCare and to apologise to the customers does not eliminate the nonconformity, but only mitigates its consequences. The nonconformity still needs to be recorded, evaluated, and reviewed for effectiveness and improvement.
Reference: 1: ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Lead Auditor (Information Security Management Systems) Course by CQI and IRCA Certified Training 1 2: ISO/IEC 27001 Lead Auditor Training Course by PECB 2

정답: 
정답:
Explanation:
According to ISO 27001:2022 clause 8.1.4, the organisation shall ensure that externally provided processes, products or services that are relevant to the information security management system are controlled. This includes implementing appropriate contractual requirements related to information security with external providers, such as customers who send ICT equipment for reclamation12
In this case, the organisation offers ICT reclamation services, which involves processing customer ICT equipment that may contain sensitive or confidential information. The organisation should have a process in place to ensure that the customer ICT equipment is handled securely and in accordance with the customer’s information security requirements. The process should include steps such as verifying the customer’s identity and authorisation, checking the inventory and condition of the equipment, removing or destroying any labels or stickers that contain information about the equipment or the customer, wiping or erasing any data stored on the equipment, and documenting the actions taken and the results achieved12
The fact that the auditor noticed two servers on a bench with stickers that reveal the server’s name, IP address and admin password indicates that the process for dealing with incoming shipments relating to customer IT security is not effective or not followed. This could pose a risk of unauthorised access, disclosure, or modification of the customer’s information or systems. Therefore, the auditor should note the audit finding and check the process for dealing with incoming shipments relating to customer IT security, and determine whether there is a nonconformity with clause 8.1.4 of ISO 27001:202212
The other actions are not appropriate for the following reasons:
A. Asking the ICT Manager to record an information security incident and initiate the information security incident management process is not appropriate because this is not an information security incident that affects the organisation’s own information or systems. An information security incident is defined as a single or a series of unwanted or unexpected information security events that have a significant probability of compromising business operations and threatening information security12 In this case, the information security event affects the customer’s information or systems, not the organisation’s. Therefore, the organisation should follow the process for dealing with incoming shipments relating to customer IT security, not the process for information security incident management.
C. Recording what the auditor has seen in the audit findings, but taking no further action is not appropriate because this would not address the root cause or the impact of the issue. The auditor has a responsibility to verify the effectiveness and compliance of the organisation’s information security management system, and to report any nonconformities or opportunities for improvement12 Therefore, the auditor should check the process for dealing with incoming shipments relating to customer IT security, and determine whether there is a nonconformity with clause 8.1.4 of ISO 27001:2022.
D. Raising a nonconformity against control 5.31 Legal, statutory, regulatory and contractual requirements is not appropriate because this control is not relevant to the issue. Control 5.31 requires the organisation to identify and comply with the legal, statutory, regulatory and contractual requirements that are applicable to the information security management system12 In this case, the issue is not about the organisation’s compliance with the legal, statutory, regulatory and contractual requirements, but about the organisation’s control of the externally provided processes, products or services that are relevant to the information security management system. Therefore, the auditor should check the process for dealing with incoming shipments relating to customer IT security, and determine whether there is a nonconformity with clause 8.1.4 of ISO 27001:2022.
E. Raising a nonconformity against control 8.20 'network security’ (networks and network devices shall be secured, managed and controlled to protect information in systems and applications) is not appropriate because this control is not relevant to the issue. Control 8.20 requires the organisation to secure, manage and control its own networks and network devices to protect the information in its systems and applications12 In this case, the issue is not about the organisation’s network security, but about the organisation’s control of the externally provided processes, products or services that are relevant to the information security management system. Therefore, the auditor should check the process for dealing with incoming shipments relating to customer IT security, and determine whether there is a nonconformity with clause 8.1.4 of ISO 27001:2022.
F. Asking the auditee to remove the labels, then carry on with the audit is not appropriate because this would not address the root cause or the impact of the issue. The auditor should not interfere with the auditee’s operations or suggest corrective actions during the audit, as this would compromise the auditor’s objectivity and impartiality12 The auditor should check the process for dealing with incoming shipments relating to customer IT security, and determine whether there is a nonconformity with clause 8.1.4 of ISO 27001:2022.
Reference: 1: ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Lead Auditor (Information Security Management Systems) Course by CQI and IRCA Certified Training 1 2: ISO/IEC 27001 Lead Auditor Training Course by PECB 2
정답:
Explanation:
A. I will check the other data centres are treated as external providers, even though they are part of the same telecommunication group. This is appropriate because clause 8.1.4 of ISO 27001:2022 requires the organisation to ensure that externally provided processes, products or services that are relevant to the information security management system are controlled. Externally provided processes, products or services are those that are provided by any external party, regardless of the degree of its relationship with the organisation. Therefore, the other data centres within the same telecommunication group should be treated as external providers and subject to the same controls as any other external provider12
B. I will ensure external providers have a documented process in place to notify the organisation of any risks arising from the use of its products or services. This is appropriate because clause 8.1.4 of ISO 27001:2022 requires the organisation to implement appropriate contractual requirements related to information security with external providers. One of the contractual requirements could be the obligation of the external provider to notify the organisation of any risks arising from the use of its products or services, such as security incidents, vulnerabilities, or changes that could affect the information security of the organisation. The external provider should have a documented process in place to ensure that such notification is timely, accurate, and complete12
E. I will ensure the organisation is regularly monitoring, reviewing and evaluating external provider performance. This is appropriate because clause 8.1.4 of ISO 27001:2022 requires the organisation to monitor, review and evaluate the performance and effectiveness of the externally provided processes, products or services. The organisation should have a process in place to measure and verify the conformity and suitability of the external provider’s deliverables and activities, and to provide feedback and improvement actions as necessary. The organisation should also maintain records of the monitoring, review and evaluation results12
F. I will ensure the organisation has determined the need to communicate with external providers regarding the ISMS. This is appropriate because clause 7.4.2 of ISO 27001:2022 requires the organisation to determine the need for internal and external communications relevant to the information security management system, including the communication with external providers. The organisation should define the purpose, content, frequency, methods, and responsibilities for such communication, and ensure that it is consistent with the information security policy and objectives. The organisation should also retain documented information of the communication as evidence of its implementation12
The following activities are not appropriate for the assessment of external providers according to ISO 27001:2022:
C. I will ensure that the organisation has a reserve external provider for each process it has identified as critical to preservation of the confidentiality, integrity and accessibility of its information. This is not appropriate because ISO 27001:2022 does not require the organisation to have a reserve external provider for each critical process. The organisation may choose to have a contingency plan or a backup solution in case of failure or disruption of the external provider, but this is not a mandatory requirement. The organisation should assess the risks and opportunities associated with the external provider and determine the appropriate treatment options, which may or may not include having a reserve external provider12
D. I will limit my audit activity to externally provided processes as there is no need to audit
externally provided products or services. This is not appropriate because clause 8.1.4 of ISO 27001:2022 requires the organisation to control the externally provided processes, products or services that are relevant to the information security management system. Externally provided products or services may include software, hardware, data, or cloud services that could affect the information security of the organisation. Therefore, the audit activity should cover both externally provided processes and products or services, as applicable12
G. I will ensure that top management have assigned roles and responsibilities for those providing external ISMS processes as well as internal ISMS processes. This is not appropriate because clause 5.3 of ISO 27001:2022 requires the top management to assign the roles and responsibilities for the information security management system within the organisation, not for the external providers. The external providers are responsible for assigning their own roles and responsibilities for the processes, products or services they provide to the organisation. The organisation should ensure that the external providers have adequate competence and awareness for their roles and responsibilities, and that they are contractually bound to comply with the information security requirements of the organisation12
H. I will ensure that the organisation ranks its external providers and allocates the majority of its work to those providers who are rated the highest. This is not appropriate because ISO 27001:2022 does not require the organisation to rank its external providers or to allocate its work based on such ranking. The organisation may choose to evaluate and compare the performance and effectiveness of its external providers, but this is not a mandatory requirement. The organisation should select and use its external providers based on the information security criteria and objectives that are relevant to the organisation12
Reference: 1: ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Lead Auditor (Information Security Management Systems) Course by CQI and IRCA Certified Training 1 2: ISO/IEC 27001 Lead Auditor Training Course by PECB 2