FCP - FortiGate 7.6 Administrator 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년10월10일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 Fortinet FCP_FGT_AD-7.6 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 FCP_FGT_AD-7.6 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 267개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
When NAT-T is enabled on both ends, peers can detect any NAT device along the path.
If NAT is found, then the following occurs:
- Both phase 2 and remaining phase 1 packets change to UDP port 4500.
- Both ends encapsulate ESP within UDP port 4500.
Reference: https://kb.fortinet.com/kb/documentLink.do?externalID=FD48755
정답:
Explanation:
The correct statements regarding FortiGate in transparent mode are:
A. By default, all interfaces are part of the same broadcast domain.
D. FortiGate forwards frames without changing the MAC address.
In transparent mode, FortiGate operates at Layer 2 and doesn't change the MAC addresses of the packets it forwards. Also, all interfaces are part of the same broadcast domain by default. This means that devices connected to different interfaces of the FortiGate can communicate with each other as if they are on the same network segment.
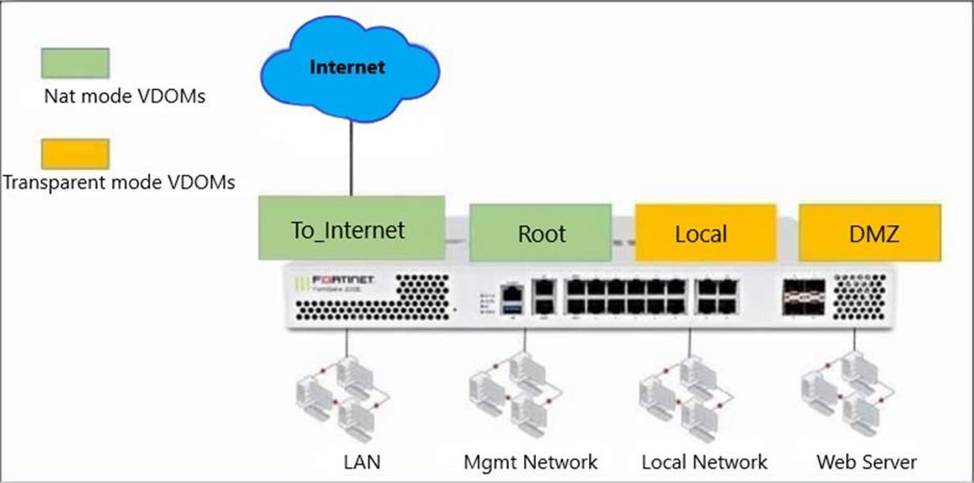
정답:
Explanation:
A. Inter-VDOM links are required to allow traffic between the Local and Root VDOMs.
Incorrect:
B. A default static route is not required on the To_Internet VDOM to allow LAN users to access the internet.
C. Inter-VDOM links are required to allow traffic between the Local and DMZ VDOMs. (transparent-transparent)
D. Inter-VDOM links are not required between the Root and To_Internet VDOMs because the Root VDOM is used only as a management VDOM.
Each VDOM has independent security policies and routing tables. Also, and by default, traffic from one VDOM cannot go to a different VDOM.
You cannot create an inter-VDOM link between Layer 2 transparent mode VDOMs. At least one of the VDOMs must be operating in NAT mode.
Similar to FortiGate without VDOMs enabled, the management VDOM should have outgoing internet access. Otherwise, features such as scheduled FortiGuard updates, fail.
정답:
Explanation:
D. get system arp
The get system arp command allows administrators to view the ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) table on the FortiGate unit. This table maps IP addresses to MAC addresses and can be used to troubleshoot Layer 2 issues, such as an IP address conflict, by checking for duplicate IP addresses or incorrect MAC address mappings.
If you suspect that there is an IP address conflict, or that an IP has been assigned to the wrong device, you may need to look at the ARP table. The get system arp command is used for that purpose.
정답:
Explanation:
B. It is available only on a proxy-based firewall policy.
Video filtering on FortiGate is available only on a proxy-based firewall policy. This means that in order to filter video content, the traffic must be routed through a proxy-based firewall policy where the FortiGate can inspect and filter the video content based on its policies.
To apply the video filter profile, proxy-based firewall polices currently allow you to enable the video filter profile. You must enable full SSL inspection on the firewall policy.
정답:
Explanation:
C. NTP
D. DNS
In an active-active HA cluster, the NTP (Network Time Protocol) and DNS (Domain Name System) settings are synchronized between the cluster members. This ensures that both devices have consistent time synchronization and DNS resolution configurations, which are important for network operations and security.
C and D are Correct: Fortigate Hostname is not synchronized between cluster member. By elimination, its C (DNS) and D (NTP)
The list of configuration settings that are NOT synchronized includes both 'FortiGate host name' and 'Cache'.
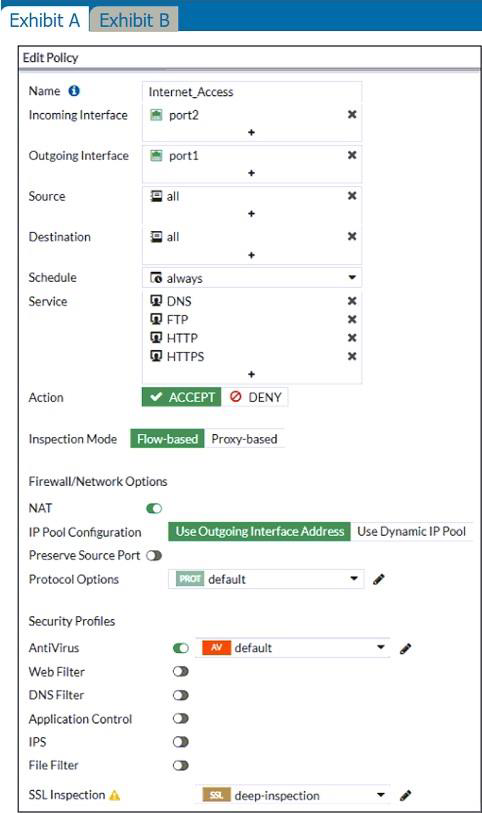
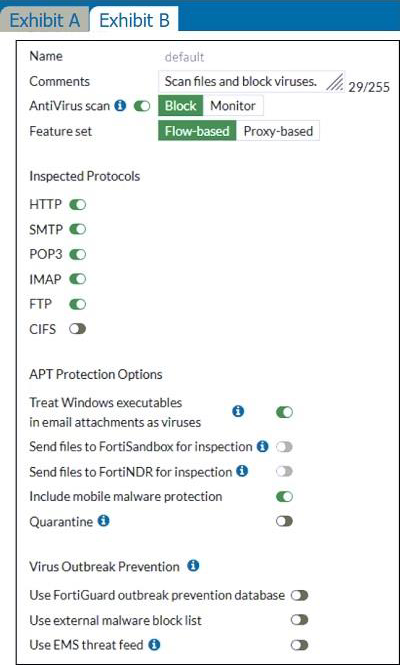
정답:
Explanation:
The flow-based inspection is used, which resets the last packet to the user.
Key to right answer is "unable to receive a block replacement message when downloading an infected file for the first time".
• "ONLY" If the virus is detected at the "START" of the connection, the IPS engine sends the block replacement message immediately
• When a virus is detected on a TCP session (FIRST TIME), but where "SOME PACKETS" have been already forwarded to the receiver, FortiGate "resets the connection" and does not send the last piece of the file. Although the receiver got most of the file content, the file has been truncated and therefore, can’t be opened. The IPS engine also caches the URL of the infected file, so that if a "SECOND ATTEMPT" to transmit the file is made, the IPS engine will then send a block replacement message to the client instead of scanning the file again.
Two possible scenarios can occur when a virus is detected:
- When a virus is detected on a TCP session where some packets have been already forwarded to the receiver, FG resets the connection and does not send the last piece of the file. Although the receiver got most of the file content, the file has been truncated and therefore, can't be opened. The IPS engine also caches the URL of the infected file, so that IF A SECOND ATTEMPT TO TRANSMIT THE FILE IS MADE, THE IPS ENGINE WILL SEND A BLOCK REPLACEMENT MESSAGE to the client instead of scanning the file again.
- If the virus is detected at the start of the connection, the IPS engine sends the block replacement message immediately.
In flow based inspection, when a virus is detected on a TCP session where some packets have been already forwarded to the receiver, FortiGate resets the connection and does not send the last piece of the file. Although the receiver got most of the file content, the file has been truncated and therefore, can’t be opened. The IPS engine also caches the URL of the infected file, so that if a second attempt to transmit the file is made, the IPS engine will then send a block replacement message to the client instead of scanning the file again.
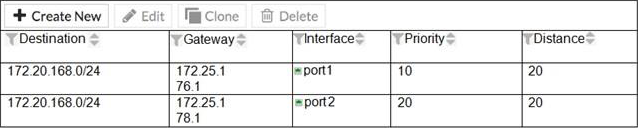
정답:
Explanation:
B. FortiGate will use the port1 route as the primary candidate.
FortiGate will use the port1 route as the primary candidate. It has better priority.
정답:
Explanation:
A. Shut down/reboot a downstream FortiGate device.
This is correct. The root FortiGate has the ability to control the power state of downstream FortiGate devices.
D. Ban or unban compromised hosts.
This is also correct. The root FortiGate can take actions to ban or unban compromised hosts, helping to manage and control security incidents.
Therefore, the correct answers are A and D.
정답:
Explanation:
The correct statements are:
C. Uninterruptable upgrade is enabled by default: This statement is true. Uninterruptable upgrade (also known as "non-stop upgrade" or NSU) is enabled by default in an active-active HA cluster. This allows the cluster to upgrade the firmware without interrupting traffic.
D. Traffic load balancing is temporarily disabled while upgrading the firmware: This statement is true. During the firmware upgrade process, traffic load balancing is temporarily disabled to avoid potential issues that may arise from traffic distribution while the firmware is being upgraded.
정답:
Explanation:
The correct statements about security associations (SA) in IPsec are:
A. Phase 2 SAs are used for encrypting and decrypting the data exchanged through the tunnel.
C. A phase 1 SA is bidirectional, while a phase 2 SA is directional.
D. Phase 2 SA expiration can be time-based, volume-based, or both.
Here's an explanation for the correct statements:
A. Phase 2 SAs (Security Associations) are established for the purpose of encrypting and decrypting the actual data that is exchanged through the IPsec tunnel. Phase 1 SAs, on the other hand, are primarily responsible for setting up the initial secure connection.
C. A phase 1 SA is bidirectional, meaning it covers both directions of communication between two peers. However, a phase 2 SA is directional, and separate SAs are established for inbound and outbound traffic.
D. Phase 2 SAs can have expiration based on time, volume (data transferred), or a combination of both. This allows for better control and security management in IPsec implementations.
정답:
Explanation:
B. The administrator must use a FortiAuthenticator device.
B is correct due to the FortiToken, a different OTP cannot use FortiToken. So we have to choose the fortiAuthenticator.
To achieve VPN user access for multiple sites using the same soft FortiToken, the administrator can use a FortiAuthenticator device. FortiAuthenticator is designed to provide centralized authentication services for Fortinet devices, including VPN authentication. It allows for the centralized management of user identities, authentication methods, and FortiTokens. By using FortiAuthenticator, the administrator can register the same FortiToken for users across multiple FortiGate devices, providing a seamless and centralized user access experience.
정답:
정답:
Explanation:
B. Many of the security issues can be fixed immediately by clicking Apply where available: This statement is true. The Security Fabric rating often identifies security issues that can be resolved immediately by clicking "Apply" where available, making it a valuable tool for quickly addressing security concerns.
C. The Security Fabric rating must be run on the root FortiGate device in the Security Fabric: This statement is also true. The Security Fabric rating must be run on the root FortiGate device in the Security Fabric to provide an overall security rating and analysis of the Security Fabric.
On checks that support Easy Apply, you can run the remediation on all the associated VDOMs.
To view the complete network, you must access the topology views on the root FortiGate in the Security
Fabric.
Incorrect:
A. The Security Fabric rating is a free service that comes bundled with all FortiGate devices. (subscription service that requires a security rating license)
D. It provides executive summaries of the four largest areas of security focus. (three largest areas of security focus)
정답:
Explanation:
Subject Key Identifier value.
FortiGate can use the Subject Key Identifier and Authority Key Identifier values to determine the relationship between the issuer of the certificate (identified in the Issuer field) and the certificate.
The Subject Key Identifier (SKI) is a value in a certificate that is used to uniquely identify the public key associated with a particular private key. It allows FortiGate to determine the relationship between the issuer (who signed the certificate) and the certificate itself. This identifier is often used in various cryptographic protocols and is included in the certificate extensions. By comparing the SKI in the certificate to the SKI of the issuing certificate, FortiGate can verify the certificate's authenticity and maintain the chain of trust in the certificate hierarchy.