Dell PowerMax Operate v2 Exam 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년10월10일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 DELL EMC D-PVM-OE-01 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 D-PVM-OE-01 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 255개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
Step by Step Comprehensive Detailed
TimeFinder SnapVX is a snapshot technology in PowerMax that allows you to create point-in-time copies of data. When using SnapVX, you can link target volumes to a snapshot to create writable copies of the data at that specific point in time.
The maximum number of target volumes that can be linked to a single snapshot on a source volume is 255. This limitation ensures efficient management and performance of the SnapVX snapshots and linked targets.
Why other options are incorrect:
B. 256,
C. 512,
D. 1024: These numbers exceed the maximum limit of linked targets per snapshot.
Reference and documents of Dell's public documentation for PowerMax Operate v.2:
Dell Solutions Enabler 10.0.0 TimeFinder SnapVX CLI User Guide: This guide provides detailed information about SnapVX features and limitations, including the maximum number of linked targets per snapshot. You can find this document on the Dell Support website by searching for "Solutions Enabler TimeFinder SnapVX CLI User Guide."
Dell PowerMax Family: Essentials and Best Practices Guide: This guide offers a comprehensive overview of PowerMax technologies, including SnapVX. It may provide context for understanding the limitations and best practices for using SnapVX snapshots and linked targets.
정답:
Explanation:
Step by Step Comprehensive Detailed
The Workload Planner in Unisphere for PowerMax helps you analyze and predict the performance impact of adding new workloads to your storage array. It uses sophisticated algorithms to calculate how the addition of a new workload will affect the existing workloads and whether it will violate any service level objectives (SLOs).
To determine if a Storage Group workload is stable, the Planner considers two key calculated values:
Read Response Time: The predicted read response time of the Storage Group after the new workload is added.
Write Response Time: The predicted write response time of the Storage Group after the new workload is added.
The Planner compares these calculated values against the service level (SL) defined for the Storage Group. If both the calculated read and write response times fall within the defined SL response time, the Planner considers the workload to be stable. This means that the new workload can be added without negatively impacting the performance of the existing workloads or violating the SLOs.
Why other options are incorrect:
A. One of the calculated values is within 10-20% of the SL-defined response time: Both read and write response times must be within the defined SL, not just one.
B. Both calculated values are within a 10-15% threshold of the SL-defined response time: The threshold is not fixed at 10-15%. The calculated values must be within the actual SL-defined response time.
C. One of the calculated values remains within the SL-defined response time: Again, both read and write response times need to be within the defined SL.
Reference and documents of Dell's public documentation for PowerMax Operate v.2:
Dell Unisphere for PowerMax 10.0.0 Online Help: The online help for Unisphere provides detailed information about the Workload Planner feature, including how it calculates and analyzes workload stability. You can access this help within Unisphere itself or on the Dell Support website.
Dell PowerMax Family: Essentials and Best Practices Guide: This guide may offer general information about performance management and workload planning in PowerMax, providing context for understanding the Workload Planner's functionality.
정답:
Explanation:
The storsrvd daemon is a critical component of the Solutions Enabler (SYMCLI) software suite used to manage Dell PowerMax and VMAX storage arrays. Its primary function is to:
Listen for SYMAPI Sessions: It acts as a communication endpoint, listening for incoming SYMAPI sessions from clients or management tools like Unisphere.
Handle Management Requests: When a client connects, storsrvd receives and processes SYMAPI commands and requests, forwarding them to the appropriate components within Solutions Enabler
for execution.
Essentially, storsrvd acts as an intermediary between SYMCLI clients and the storage array, facilitating communication and management operations.
Why other options are incorrect:
A. Manages Composite Groups and Device Groups: This is handled by other components within Solutions Enabler.
B. Provides centralized gatekeeper device management: While storsrvd plays a role in device management, it's not the sole component responsible for it.
C. Provides replication consistency protection: This is a function of SRDF (Symmetrix Remote Data Facility) and related components.
Reference and documents of Dell's public documentation for PowerMax Operate v.2:
Dell Solutions Enabler 10.0.0 CLI User Guide: This guide provides information about the architecture and components of Solutions Enabler, including the role of the storsrvd daemon in handling SYMAPI communication. You can find this document on the Dell Support website by searching for "Solutions Enabler CLI User Guide."
정답:
Explanation:
Step by Step Comprehensive Detailed
In SRDF (Symmetrix Remote Data Facility), an "update" operation refers to a specific process where changes made on the target (R2) side are copied back to the source (R1) side.
This is typically used in disaster recovery scenarios where:
Failover: A failover occurs, and the target (R2) becomes the active production site.
Data Modification: Data is modified or updated on the target (R2) while it's acting as the primary.
Update Operation: An "update" is initiated to synchronize the changes from the target (R2) back to the source (R1), ensuring that the source has the latest data.
This process is crucial for maintaining data consistency and ensuring a smooth transition back to the original production site after a failover event.
Why other options are incorrect:
A. process to retain the data on the target R2 side: This is not specific to an "update" operation. Data retention on the target is a general aspect of SRDF.
B. A process used to return to the original production site after a failover event: While an "update" is part of the failback process, it's not the entire process itself. Failback involves other steps like reversing replication direction and restoring host access.
D. A process that allows separate hosts to access the same data independently: This describes a different SRDF configuration (like Active/Active) and is not related to the "update" operation.
Reference and documents of Dell's public documentation for PowerMax Operate v.2:
Dell Solutions Enabler 10.0.0 SRDF Family CLI User Guide: This guide provides detailed information about SRDF commands and operations, including the symrdf update command used to initiate an update from R2 to R1. You can find this document on the Dell Support website by searching for "Solutions Enabler SRDF Family CLI User Guide."
Dell PowerMax Family: Essentials and Best Practices Guide: This guide offers a comprehensive overview of SRDF and its functionalities, including disaster recovery scenarios and the use of the "update" operation.
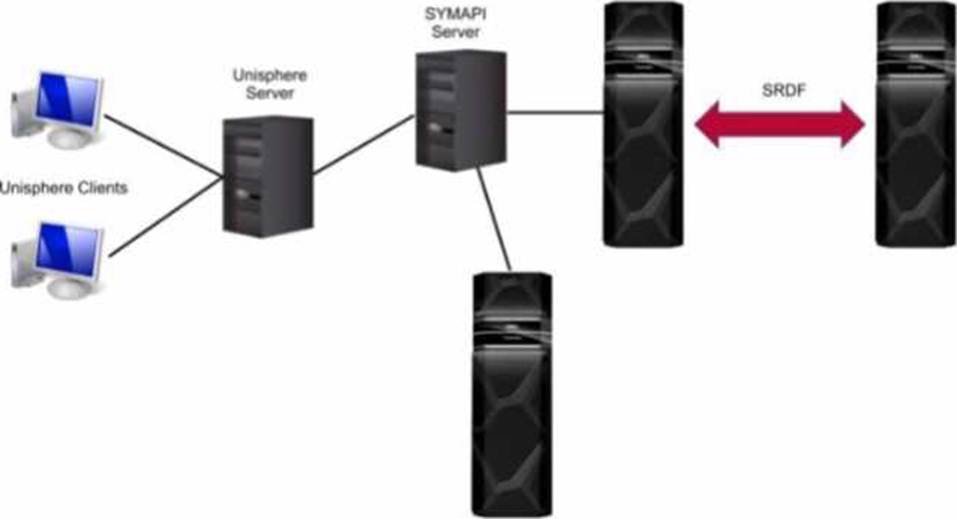
정답:
Explanation:
Step by Step Comprehensive Detailed
Unisphere for PowerMax offers different deployment options to manage PowerMax storage arrays.
Based on the exhibit, we can identify the following:
Separate SYMAPI Server: The diagram shows a dedicated SYMAPI server. SYMAPI (Symmetrix Application Programming Interface) is a command-line interface used to manage PowerMax and VMAX storage arrays. This indicates that the Unisphere server is not directly connected to the storage arrays.
Unisphere Server Connected to SYMAPI Server: The Unisphere server is shown to be connected to the SYMAPI server. This means that the Unisphere server relies on the SYMAPI server to communicate with the PowerMax arrays.
No Direct Connection to Arrays: The Unisphere server does not have a direct connection to the PowerMax arrays.
Considering these points, the deployment option depicted in the exhibit is a remote deployment. In a remote deployment, the Unisphere server is installed on a separate host and communicates with the PowerMax arrays through a SYMAPI server. This allows for centralized management of multiple arrays from a single Unisphere instance.
Why other options are incorrect:
A. Embedded: In an embedded deployment, the Unisphere software runs directly on the PowerMax array itself. This eliminates the need for a separate Unisphere server.
B. Either remote or local: While the diagram could technically represent a local deployment with a dedicated SYMAPI server, the presence of the separate SYMAPI server and the lack of direct connection to the arrays strongly suggest a remote deployment.
D. Local: In a local deployment, the Unisphere server is typically installed on the same host as Solutions Enabler, which has direct connectivity to the storage arrays.
Reference and documents of Dell's public documentation for PowerMax Operate v.2:
Dell Unisphere for PowerMax 10.0.0 Installation Guide: This guide provides detailed information about the different Unisphere deployment options, including local, remote, and embedded. It also includes diagrams and explanations of each deployment scenario. You can find this document on the Dell Support website by searching for "Unisphere for PowerMax Installation Guide."
Dell PowerMax Family: Essentials and Best Practices Guide: This guide offers a general overview of PowerMax systems and their management using Unisphere. It may provide context for understanding the different deployment options.
정답:
Explanation:
Step by Step Comprehensive Detailed
Non-Disruptive Migration (NDM) is a feature in PowerMax that allows you to migrate data between storage arrays without any downtime or disruption to host applications. During NDM, SRDF (Symmetrix Remote Data Facility) is used to replicate data between the source and target arrays. Here are the configuration rules that apply to SRDF groups and connections during NDM:
A. The source and target arrays are at most one hop away from the control host: The control host, which manages the NDM process, must have direct connectivity to both the source and target arrays. This ensures efficient communication and control during the migration.
E. DM RDF groups are configured with a minimum of one path: SRDF groups used for NDM (DM RDF groups) must have at least one active path between the source and target arrays. This ensures that data can be replicated continuously during the migration.
Why other options are incorrect:
B. Two DM RDF groups are created per SG migration session: This is not a strict requirement. The number of DM RDF groups may vary depending on the configuration and the specific NDM operation.
C. RF and RE ports are supported, with RF ports being selected if both types are available: While RF and RE ports are supported for SRDF, there's no specific preference for RF ports during NDM. The choice of ports depends on the overall network configuration and availability.
D. A single array cannot have multiple DM RDF groups: An array can have multiple DM RDF groups if needed for different NDM operations or configurations.
Reference and documents of Dell's public documentation for PowerMax Operate v.2:
Dell PowerMax Family: Essentials and Best Practices Guide: This guide provides an overview of NDM and its requirements, including information about SRDF configuration.
Dell Solutions Enabler 10.0.0 CLI User Guide: This guide provides detailed information about SRDF
commands and configuration options, which are relevant for NDM operations.
정답:
Explanation:
Step by Step Comprehensive Detailed
Host I/O Limits in PowerMax allow you to control the maximum IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) or bandwidth that a storage group can consume. This helps prevent performance issues caused by one application or workload monopolizing resources.
When setting Host I/O Limits, you can choose from different dynamic I/O distribution modes:
Never: This is the default mode. It means that the I/O limits are statically distributed across the directors in the associated masking view. If a director fails, its allocated portion of the I/O limit is lost.
Balanced: In this mode, the I/O limits are dynamically adjusted based on the number of online directors. If a director fails, its I/O limit is redistributed among the remaining online directors. This helps maintain performance even in the event of a director failure.
Always: This mode provides full dynamic distribution of I/O limits. The limits are continuously adjusted across all online directors based on the current workload and demand. This ensures optimal resource utilization and performance.
Reference and documents of Dell's public documentation for PowerMax Operate v.2:
Dell PowerMax and VMware vSphere Configuration Guide: This guide provides detailed information about Host I/O Limits, including the different distribution modes and their benefits. You can find this document on the Dell Support website by searching for "PowerMax and VMware vSphere Configuration Guide."
Dell Solutions Enabler 10.0.0 CLI User Guide: This guide provides information on how to set Host I/O Limits using SYMCLI commands, including the -dynamic option for specifying the distribution mode.
정답:
Explanation:
Step by Step Comprehensive Detailed
When you install Unisphere for PowerMax on a Microsoft Windows host, it installs several services necessary for its operation.
The two primary services that are active after installation are:
SMAS (Storage Management Agent Service): This service is responsible for communication between the Unisphere server and the PowerMax storage array. It handles tasks like collecting data, sending commands, and receiving alerts from the array.
smasdb: This service manages the local database used by Unisphere for storing configuration information, performance data, and other relevant information.
Why other options are incorrect:
A. SYMAPI and symrdfg: SYMAPI is a command-line interface tool, not a service. symrdfg is a service related to SRDF (Symmetrix Remote Data Facility) replication, which may not be active if SRDF is not configured.
B. SMASandGNS: GNS is not a standard service associated with Unisphere for PowerMax.
C. SMASandSTP: STP is not a standard service associated with Unisphere for PowerMax. Reference and documents of Dell's public documentation for PowerMax Operate v.2:
Dell Unisphere for PowerMax 10.0.0 Installation Guide: This guide provides detailed instructions for installing Unisphere for PowerMax on different operating systems, including Windows. It also lists the services that are installed and their functions. You can find this document on the Dell Support website by searching for "Unisphere for PowerMax Installation Guide."
Dell Unisphere for PowerMax 10.0.0 Online Help: The online help documentation for Unisphere may also provide information about the services it uses and their roles.
정답:
Explanation:
Step by Step Comprehensive Detailed
Unisphere for PowerMax provides a "System > Hardware" view that offers insights into the physical components of your PowerMax storage array.
On newly installed 2000 and 8000 series arrays, this view would typically show information about:
Front-end directors: These directors handle host connectivity and data transfer to and from the array. The view would likely display details about the number of front-end directors, their types, and their status.
Back-end directors: These directors manage the connection to the physical disks (storage media) within the array. The view may show the number of back-end directors, their types, and their status.
RDF (Remote Data Facility): If the array is configured for SRDF replication, the hardware view might display information about the RDF directors or components responsible for managing remote replication.
Why other options are incorrect:
A. Capacity, performance, and protection: While these are important aspects of a PowerMax system, they are typically found in other sections of Unisphere, such as the "Dashboard" or "Storage" views.
B. Provision, protect and set host I/O limits: These are management functions accessible through Unisphere, but not typically displayed directly under the "System > Hardware" view.
D. I/O Profile, performance thresholds, and anomaly detection: These are related to performance monitoring and analysis, which are usually found in the "Performance" section of Unisphere.
Reference and documents of Dell's public documentation for PowerMax Operate v.2:
Dell Unisphere for PowerMax 10.0.0 Online Help: The online help for Unisphere provides detailed information about the different views and functionalities available within the tool. You can access this help within Unisphere itself or on the Dell Support website.
Dell PowerMax Family: Essentials and Best Practices Guide: This guide offers a general overview of PowerMax systems and their management using Unisphere. It may provide context for understanding the information displayed in the "System > Hardware" view.
정답: 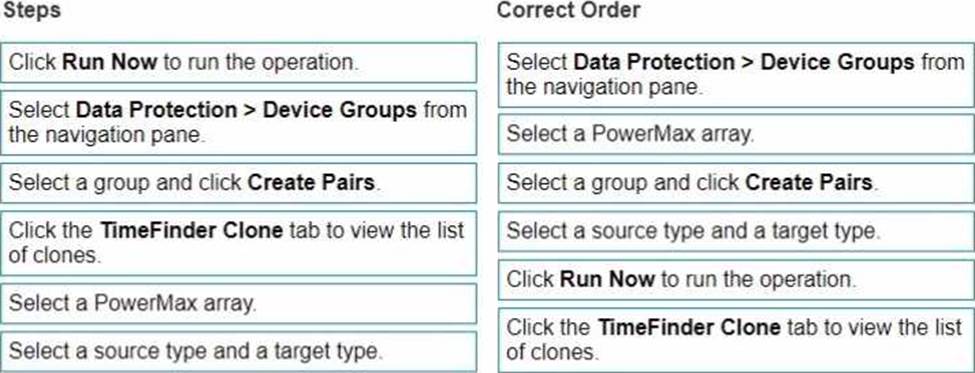
Explanation:
Here's the correct sequence of steps along with explanations:
Correct Order:
Select Data Protection > Device Groups from the navigation pane.
Why: This is the starting point within Unisphere for PowerMax. You need to navigate to the section where device groups are managed and where TimeFinder operations are initiated.
Select a PowerMax array.
Why: In an environment with multiple PowerMax arrays, you must specify the array on which you want to create the clone copy sessions.
Select a group and click Create Pairs.
Why: You are selecting the specific device group that will be the source for the clone operation and choosing the "Create Pairs" action to initiate the clone session creation process. This implies you are creating a clone from an existing group of devices.
Select a source type and a target type.
Why: This step defines the characteristics of the source and target devices for the clone session. This could involve selecting from different storage groups, specifying thin or thick provisioning, or other relevant settings. Note that in a clone context, the "target type" often refers to how the clone will be linked to the source (e.g., a full copy or a linked target).
Click Run Now to run the operation.
Why: After configuring all the settings for the clone session, this action triggers the actual creation of the clone pairs based on the selected source and target types and other parameters.
Click the TimeFinder Clone tab to view the list of clones.
Why: Once the operation has been initiated, this is how you would verify that the clone sessions were created successfully and monitor their status.
Select Data Protection > Device Groups from the navigation pane.
Select a PowerMax array.
Select a group and click Create Pairs.
Select a source type and a target type.
Click Run Now to run the operation.
Click the TimeFinder Clone tab to view the list of clones.
정답:
Explanation:
Step by Step Comprehensive Detailed
The Dell PowerMax 2500 is a mid-range storage array designed for enterprise environments. It offers a balance of performance, capacity, and scalability.
Scalability: The PowerMax 2500 scales from a single node pair to a maximum of two node pairs. This allows for increased performance and capacity as needed. Each node pair provides processing power, cache memory, and connectivity.
Why other options are incorrect:
A. Supports up to 16 nodes: This is incorrect. The PowerMax 8500, the higher-end model, supports up to 16 nodes.
B. Supports up to 15 PB of effective capacity: While the PowerMax 2500 offers significant capacity, its maximum effective capacity is lower than 15 PB.
D. Uses Storage Class Memory: Both the PowerMax 2500 and 8500 utilize Storage Class Memory (SCM) for enhanced performance.
Reference and documents of Dell's public documentation for PowerMax Operate v.2:
Dell PowerMax 2500 Hardware Information Guide: This guide provides detailed technical specifications for the PowerMax 2500, including its scalability options, node configurations, and capacity limits. You can find this document on the Dell Support website by searching for "PowerMax 2500 Hardware Information Guide."
Dell PowerMax Family: Essentials and Best Practices Guide: This guide offers a general overview of the PowerMax family, including the 2500 and 8500 models. It highlights the key differences in scalability and performance between the two models.
정답:
Explanation:
Step by Step Comprehensive Detailed
SnapVX Clones: SnapVX clones are full, writable copies of a source volume created using the SnapVX snapshot technology. They are independent volumes that can be used for various purposes, such as testing, development, or data analysis.
Secure Snapshots: SnapVX offers the capability to create "secure snapshots." When a clone is derived from a secure snapshot, it inherits the same protection, making it immutable and preventing any modifications or deletion. This ensures data integrity and protection against accidental or malicious changes.
Crash Consistent: SnapVX clones can be made crash consistent. This means that the clone captures a point-in-time copy of the source volume that is consistent with a database or application crash. This is important for ensuring data integrity and recoverability in situations where the source volume experiences an unexpected outage.
Why other options are incorrect:
A. Maximum 1024 snaps per volume: This limit applies to the source volume, not the clones themselves. Each clone is an independent volume.
C. Restores directly to the source volume: Clones are independent copies and do not directly restore
to the source volume. Data can be copied or moved from the clone to the source if needed.
D. Is Read-only: SnapVX clones are fully writable copies, not read-only.
Reference and documents of Dell's public documentation for PowerMax Operate v.2:
Dell Solutions Enabler 10.0.0 TimeFinder SnapVX CLI User Guide: This guide provides detailed information about SnapVX features and commands, including how to create and manage clones. It confirms the ability to create secure clones and the option to make them crash consistent.
Dell PowerMax Family: Essentials and Best Practices Guide: This guide offers a comprehensive overview of PowerMax technologies, including SnapVX. It highlights the benefits of SnapVX clones for various use cases.

정답: 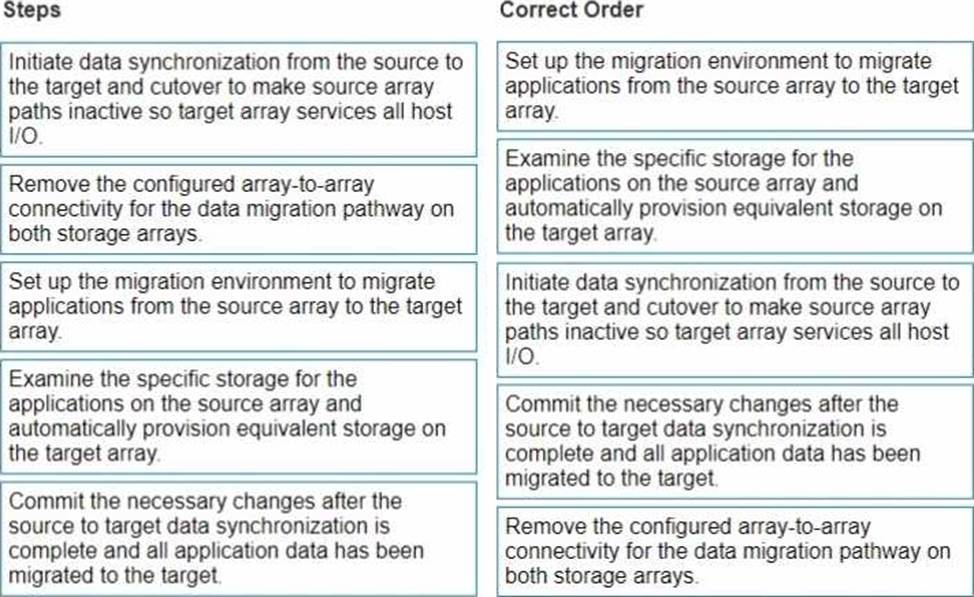
Explanation:
Set up the migration environment to migrate applications from the source array to the target array.
Examine the specific storage for the applications on the source array and automatically provision equivalent storage on the target array.
Initiate data synchronization from the source to the target and cutover to make source array paths inactive so target array services all host I/O.
Commit the necessary changes after the source to target data synchronization is complete and all application data has been migrated to the target.
Remove the configured array-to-array connectivity for the data migration pathway on both storage arrays.
Correct Order:
Set up the migration environment to migrate applications from the source array to the target array.
Why: This is the initial setup phase, where you configure the necessary settings on both the source and target arrays to enable the migration.
This involves actions like:
Verifying compatibility between the source and target arrays.
Ensuring that the required licenses are in place (e.g., NDM license).
Configuring network connectivity (FC or iSCSI) for data transfer between the arrays.
Examine the specific storage for the applications on the source array and automatically provision equivalent storage on the target array.
Why: Before migrating data, you need to ensure that the target array has the appropriate storage capacity and configuration to host the applications.
How: NDM can often automatically provision equivalent storage on the target based on the source configuration. This includes creating storage groups, volumes, and masking views that mirror the source.
Initiate data synchronization from the source to the target and cutover to make source array paths inactive so target array services all host I/O.
Why: This is the core of the migration process. Data is copied from the source to the target while the application continues to run. Cutover is the final step where I/O is redirected to the target array.
How:
Synchronization: Data is copied in the background.
Cutover: Once synchronization is complete, a brief cutover is performed. In a well-planned NDM, this cutover is designed to be within the I/O timeout limits of most applications.
Commit the necessary changes after the source to target data synchronization is complete and all application data has been migrated to the target.
Why: This step finalizes the migration and makes it permanent.
What it involves: The migration session is acknowledged and the configuration is finalized on the target array.
Remove the configured array-to-array connectivity for the data migration pathway on both storage arrays.
Why: After the migration is complete, the temporary connections used for data transfer between the arrays should be removed to free up resources and maintain a clean configuration.
What it involves: This typically means removing the FC zones or iSCSI settings that were configured specifically for the NDM process.
정답:
Explanation:
Step by Step Comprehensive Detailed
Dell PowerMax storage arrays utilize different device types for various purposes. Solutions Enabler (SYMCLI) and Unisphere for PowerMax are management tools that can interact with these device types. Here's a breakdown:
SRDF Thin Devices (RDF1 or RDF2): These devices are specifically used for SRDF (Symmetrix Remote Data Facility) replication. RDF1 devices represent the local copy of data in an SRDF relationship, while RDF2 devices represent the remote copy. Both Solutions Enabler and Unisphere can manage these devices to configure and monitor SRDF replication.
Internal Thin Devices (Int+TDEV): These are thin provisioned devices that reside within the PowerMax storage array. They are used for general storage purposes and can be managed by both Solutions Enabler and Unisphere for tasks like provisioning, allocating capacity, and monitoring performance.
Thin Devices (TDEV): This is a general term for thin provisioned devices in PowerMax. Thin provisioning allows for efficient storage utilization by allocating capacity on demand. 1 Both Solutions Enabler and Unisphere can manage these devices.
https://www.n-able.com/blog/thin-provision-vs-thick-provision#:~:text=Thin%20provisioning%20allocates%20disk%20space,need%20at%20any%20given %20time.
https://www.n-able.com/blog/thin-provision-vs-thick-provision#:~:text=Thin%20provisioning%20allocates%20disk%20space,need%20at%20any%20given %20time.
Why other options are incorrect:
B. Thin BCV Devices (BCV+TDEV): BCV (Business Continuance Volume) devices are used for creating point-in-time copies for disaster recovery. While Solutions Enabler can manage BCV devices, Unisphere for PowerMax has limited functionality for managing them directly.
D. Data Devices (TDATs): TDATs are physical devices within the PowerMax array. While Solutions Enabler can interact with TDATs at a lower level, Unisphere for PowerMax primarily focuses on managing logical devices and storage groups.
Reference and documents of Dell's public documentation for PowerMax Operate v.2:
Dell PowerMax Family: Essentials and Best Practices Guide: This guide provides an overview of PowerMax devices and their management. It mentions the different device types and how they are used in the PowerMax environment.
Dell Solutions Enabler 10.0.0 CLI User Guide: This guide provides detailed information about Solutions Enabler commands for managing various device types, including SRDF devices, thin devices, and internal devices.
Dell Unisphere for PowerMax 10.0.0 Online Help: The online help documentation for Unisphere for PowerMax explains how to manage different device types through the graphical user interface, including provisioning, monitoring, and configuring storage.
정답:
Explanation:
Step by Step Comprehensive Detailed
SnapVX Linked Targets: SnapVX is a snapshot technology used in Dell PowerMax storage arrays. A linked target is a volume that provides read/write access to a specific point-in-time copy (snapshot) of a source volume.
Read/Write Access: Unlike traditional snapshots, which are typically read-only, SnapVX linked targets allow modifications. This makes them suitable for use cases like testing, development, and data analysis where changes need to be made to a copy of the data without affecting the original source.
Secure Snapshots: SnapVX offers the capability to create "secure snapshots." These snapshots are write-protected and prevent any modifications or deletion, ensuring data integrity and protection against accidental or malicious changes.
Why other options are incorrect:
B. They support a maximum of 1024 snaps per volume: This is partially correct. While a source volume can have up to 1024 snapshots, this limit includes all types of snapshots (manual, automated, and legacy), not just linked targets.
B. They cannot send data to SRDF: This is incorrect. SnapVX linked targets can participate in SRDF (Symmetrix Remote Data Facility) replication, allowing for disaster recovery and data mobility.
Reference and documents of Dell's public documentation for PowerMax Operate v.2:
Dell Solutions Enabler 10.0.0 TimeFinder SnapVX CLI User Guide: This guide provides detailed information about SnapVX features and commands, including how to create, link, and manage snapshots. It confirms the read/write capability of linked targets and the ability to create secure snapshots. You can find this document on the Dell Support website by searching for "Solutions Enabler TimeFinder SnapVX CLI User Guide."
Dell PowerMax Family: Essentials and Best Practices Guide: This guide offers a comprehensive overview of PowerMax technologies, including SnapVX. It highlights the benefits of SnapVX linked targets for various use cases. You can find this document on the Dell Support website by searching for "PowerMax Family Essentials and Best Practices Guide."