Google Cloud Certified – Associate Cloud Engineer 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년10월10일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 Google Associate Cloud Engineer 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 Associate Cloud Engineer 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 328개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답: A
Explanation:
https://cloud.google.com/sdk/gcloud
https://cloud.google.com/sdk/docs/configurations#multiple_configurations
정답:
Explanation:
"large quantity" : Cloud Storage or BigQuery "files" a file is nothing but an Object
Reference: https://cloud.google.com/solutions/performing-etl-from-relational-database-into-bigquery
정답:
Explanation:
When setting support levels for permissions in custom roles, you can set to one of SUPPORTED, TESTING or NOT_SUPPORTED.
Ref: https://cloud.google.com/iam/docs/custom-roles-permissions-support
정답:
Explanation:
https://cloud.google.com/logging/docs/audit
Data Access audit logs Data Access audit logs contain API calls that read the configuration or metadata of resources, as well as user-driven API calls that create, modify, or read user-provided resource data.
https://cloud.google.com/logging/docs/audit#data-access
정답:
Explanation:
Reference: https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/gcp/best-practices-for-working-with-google-cloud-audit- logging
bigquery.dataViewer role provides permissions to read the datasets metadata and list tables in the dataset as well as Read data and metadata from the datasets tables. This is exactly what we need to fulfil this requirement and follows the least privilege principle.
Ref: https://cloud.google.com/iam/docs/understanding-roles#bigquery-roles
정답: A
Explanation:
https://cloud.google.com/run/docs/tutorials/gcloud https://cloud.google.com/resource-manager/docs/creating-managing-projects https://cloud.google.com/iam/docs/understanding-roles#primitive_roles
You can shut down projects using the Cloud Console. When you shut down a project, this immediately happens: All billing and traffic serving stops, You lose access to the project, The owners of the project will be notified and can stop the deletion within 30 days, The project will be scheduled to be deleted after 30 days. However, some resources may be deleted much earlier.
정답:
Explanation:
Navigate to Stackdriver Logging and select resource.labels.project_id=*. is not right.
Log entries are held in Stackdriver Logging for a limited time known as the retention period which is 30 days (default configuration). After that, the entries are deleted. To keep log entries longer, you need to export them outside of Stackdriver Logging by configuring log sinks.
Ref: https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/gcp/best-practices-for-working-with-google-cloud-audit-logging
Configure a Cloud Scheduler job to read from Stackdriver and store the logs in BigQuery. Configure the table expiration to 60 days. is not right.
While this works, it makes no sense to use Cloud Scheduler job to read from Stackdriver and store the logs in BigQuery when Google provides a feature (export sinks) that does exactly the same thing and works out of the box.
Ref: https://cloud.google.com/logging/docs/export/configure_export_v2
Create a Stackdriver Logging Export with a Sink destination to Cloud Storage. Create a lifecycle rule to delete objects after 60 days. is not right.
You can export logs by creating one or more sinks that include a logs query and an export destination. Supported destinations for exported log entries are Cloud Storage, BigQuery, and Pub/Sub.
Ref: https://cloud.google.com/logging/docs/export/configure_export_v2
Sinks are limited to exporting log entries from the exact resource in which the sink was created: a Google Cloud project, organization, folder, or billing account. If it makes it easier to exporting from all projects of an organication, you can create an aggregated sink that can export log entries from all the projects, folders, and billing accounts of a Google Cloud organization. Ref: https://cloud.google.com/logging/docs/export/aggregated_sinks
Either way, we now have the data in Cloud Storage, but querying logs information from Cloud Storage is harder than Querying information from BigQuery dataset. For this reason, we should prefer Big Query over Cloud Storage.
Create a Stackdriver Logging Export with a Sink destination to a BigQuery dataset. Configure the table expiration to 60 days. is the right answer.
You can export logs by creating one or more sinks that include a logs query and an export destination. Supported destinations for exported log entries are Cloud Storage, BigQuery, and Pub/Sub.
Ref: https://cloud.google.com/logging/docs/export/configure_export_v2
Sinks are limited to exporting log entries from the exact resource in which the sink was created: a Google Cloud project, organization, folder, or billing account. If it makes it easier to exporting from all projects of an organication, you can create an aggregated sink that can export log entries from all the projects, folders, and billing accounts of a Google Cloud organization. Ref: https://cloud.google.com/logging/docs/export/aggregated_sinks
Either way, we now have the data in a BigQuery Dataset. Querying information from a Big Query dataset is easier and quicker than analyzing contents in Cloud Storage bucket. As our requirement is to Quickly analyze the log contents, we should prefer Big Query over Cloud Storage.
Also, You can control storage costs and optimize storage usage by setting the default table expiration for newly created tables in a dataset. If you set the property when the dataset is created, any table created in the dataset is deleted after the expiration period. If you set the property after the dataset is created, only new tables are deleted after the expiration period.
For example, if you set the default table expiration to 7 days, older data is automatically deleted after 1 week.
Ref: https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/docs/best-practices-storage
Reference: https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/gcp/best-practices-for-working-with-google-cloud-audit- logging
정답:
Explanation:
Google Cloud provides Cloud Audit Logs, which is an integral part of Cloud Logging. It consists of two log streams for each project: Admin Activity and Data Access, which are generated by Google Cloud services to help you answer the question of who did what, where, and when? within your Google Cloud projects.
Ref: https://cloud.google.com/iam/docs/job-functions/auditing#scenario_external_auditors
정답:
Explanation:
Best practices for persistent disk snapshots
You can create persistent disk snapshots at any time, but you can create snapshots more quickly and with greater reliability if you use the following best practices.
Creating frequent snapshots efficiently
Use snapshots to manage your data efficiently.
Create a snapshot of your data on a regular schedule to minimize data loss due to unexpected failure.
Improve performance by eliminating excessive snapshot downloads and by creating an image and reusing it.
Set your snapshot schedule to off-peak hours to reduce snapshot time.
Snapshot frequency limits
Creating snapshots from persistent disks
You can snapshot your disks at most once every 10 minutes. If you want to issue a burst of requests to snapshot your disks, you can issue at most 6 requests in 60 minutes.
If the limit is exceeded, the operation fails and returns the following error:
https://cloud.google.com/compute/docs/disks/snapshot-best-practices
정답:
Explanation:
Using primitive roles The following table lists the primitive roles that you can grant to access a project, the description of what the role does, and the permissions bundled within that role. Avoid using primitive roles except when absolutely necessary. These roles are very powerful, and include a large number of permissions across all Google Cloud services. For more details on when you should use primitive roles, see the Identity and Access Management FAQ. IAM predefined roles are much more granular, and allow you to carefully manage the set of permissions that your users have access to. See Understanding Roles for a list of roles that can be granted at the project level. Creating custom roles can further increase the control you have over user permissions. https://cloud.google.com/resource-manager/docs/access-control-proj#using_primitive_roles
https://cloud.google.com/iam/docs/understanding-custom-roles
정답:
Explanation:
This aligns with Googles recommended practices. By creating a new project, we achieve complete isolation between development and production environments; as well as isolate this production application from production applications of other departments.
Ref: https://cloud.google.com/docs/enterprise/best-practices-for-enterprise-organizations#define-hierarchy
정답:
Explanation:
Reference: https://cloud.google.com/solutions/federating-gcp-with-active-directory-introduction
Directory Sync Google Cloud Directory Sync enables administrators to synchronize users, groups and other data from an Active Directory/LDAP service to their Google Cloud domain directory
https://tools.google.com/dlpage/dirsync/
정답:
Explanation:
auto-provisioning = Attaches and deletes node pools to cluster based on the requirements. Hence creating a GPU node pool, and auto-scaling would be better https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/how-to/node-auto-provisioning
정답:
Explanation:
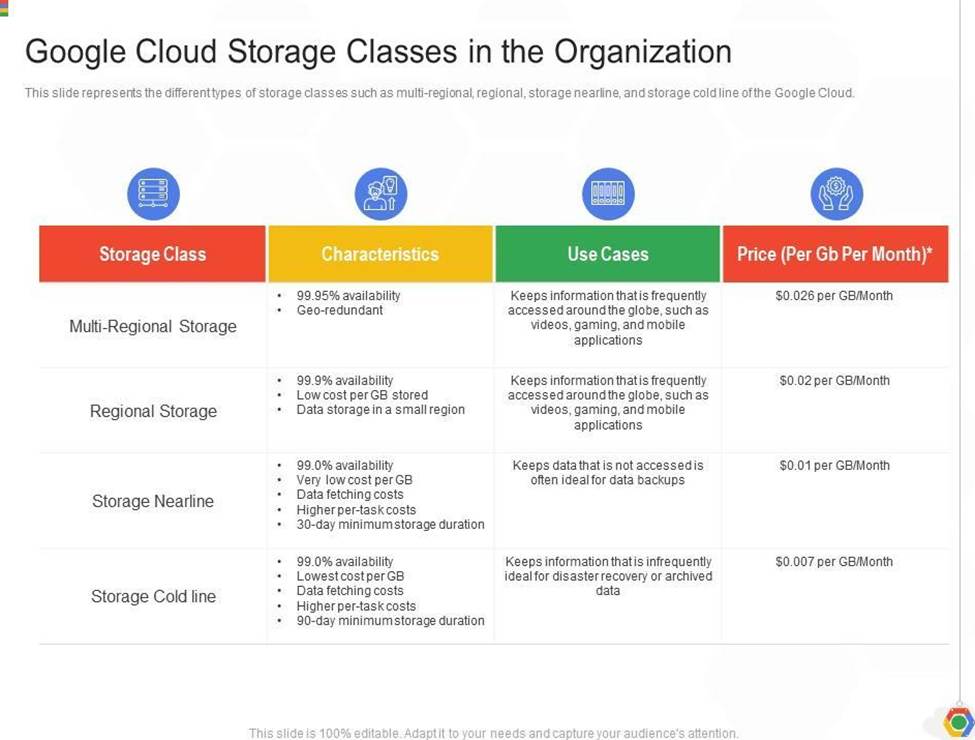
Coldline Storage is a very-low-cost, highly durable storage service for storing infrequently accessed data. Coldline Storage is ideal for data you plan to read or modify at most once a quarter. Since we have a requirement to access data once a quarter and want to go with the most cost-efficient option, we should select Coldline Storage.
Ref: https://cloud.google.com/storage/docs/storage-classes#coldline
정답:
Explanation:
Reference: https://cloud.google.com/iam/docs/creating-managing-service-accounts
Service Account User (roles/iam.serviceAccountUser): Includes permissions to list service accounts, get details about a service account, and impersonate a service account. Service Account Admin (roles/iam.serviceAccountAdmin): Includes permissions to list service accounts and get details about a service account. Also includes permissions to create, update, and delete service accounts, and to view or change the IAM policy on a service account.