HPE Network Switching Professional Exam 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년11월17일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 HP HPE7-A08 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 HPE7-A08 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 342개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
For an interface connected to an untrusted device regarding DSCP markings, the recommended configurations are:
Apply a classifier-based policy to assign a Local Priority value (Option B). This overrides or marks traffic based on predefined criteria.
Configure qos trust none (Option E) to disable trusting DSCP or CoS markings from the device, preventing manipulation of QoS.
Trusting CoS (Option A) is incorrect because the device is untrusted.
DSCP maps and Weighted Fair Queuing (Options C and D) are additional QoS features but do not specifically address untrusted markings.
Reference: ArubaOS-CX QoS Configuration Guide
HPE Aruba Networking QoS Best Practices
Aruba CX Trust Model Documentation
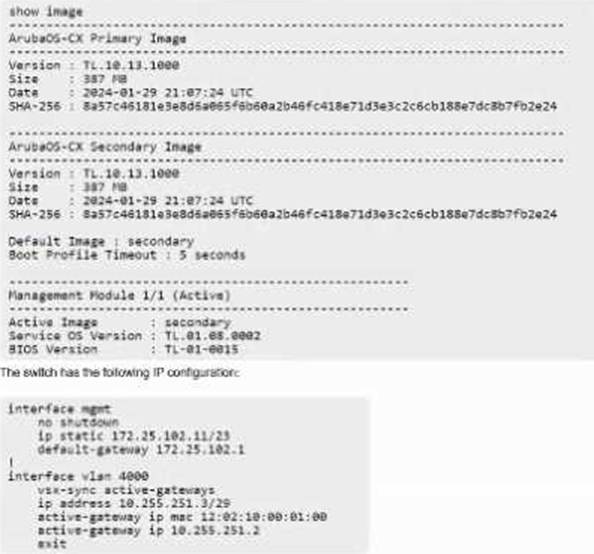
정답:
Explanation:
To upgrade an HPE Aruba Networking CX 8320 VSX cluster with minimal downtime from a remote server, the correct command is:
vsx update-software scp://172.25.101.10/image vrf mgmt
Using SCP (Secure Copy Protocol) ensures secure transfer.
Specifying vrf mgmt ensures the update uses the management VRF for connectivity.
Using TFTP is less secure and not recommended for production upgrades.
The primary keyword is not valid for the vsx update-software command.
This method allows an in-service software upgrade (ISSU) with least disruption.
Reference: Aruba VSX Software Upgrade Guide
HPE Aruba CX Upgrade Best Practices
ArubaOS-CX CLI Reference for VSX Commands
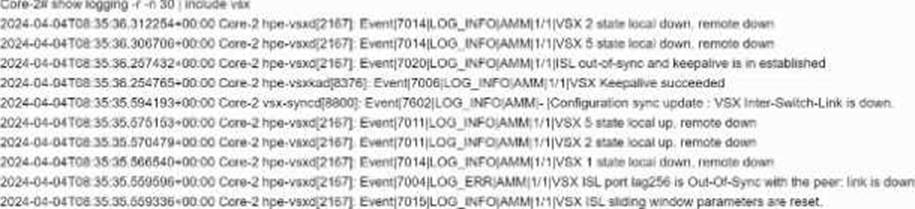
정답:
Explanation:
If the ISL between two VSX core switches is down and logs indicate that Core-2 has disabled its VSX LAG interfaces, it means Core-2 has disabled its VSX LAG interfaces, likely as a protective or failover mechanism.
Keepalive packets being dropped (Option B) may cause issues but logs specifically state interface disablement.
Both switches forwarding traffic (Option C) is unlikely if ISL is down.
Downstream switches inability to forward traffic (Option D) is a consequence, not the cause.
Reference: Aruba VSX Troubleshooting and Logs Documentation
HPE Aruba VSX High Availability Design Guide
ArubaOS-CX VSX Monitoring Best Practices
정답:
Explanation:
After enabling ARP protection, many users lose network access because ARP protection relies on DHCP snooping to build IP-to-MAC binding tables. Without DHCP snooping enabled and correctly configured, ARP inspection cannot verify ARP packets, causing legitimate traffic to be dropped.
Enabling DHCP snooping allows ARP inspection to validate ARP requests and responses.
Other options like dynamic IP lockdown, IGMP snooping, or DHCP reservations are unrelated or secondary.
Reference: ArubaOS-CX ARP Inspection and DHCP Snooping Configuration Guide
HPE Aruba Network Security Best Practices
Aruba Troubleshooting ARP Protection Issues
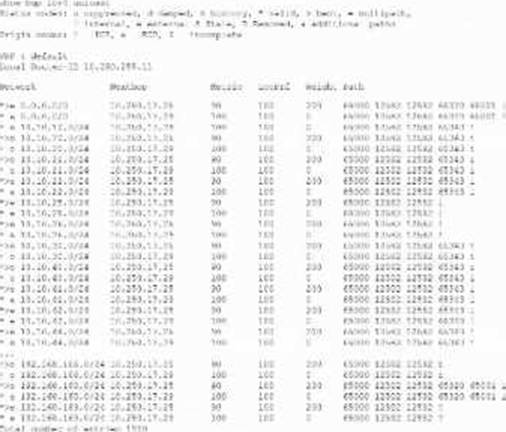
정답:
Explanation:
To keep the BGP routing table size manageable and below a specified threshold, the customer should consider enforcing routing policies with aggregation. Route aggregation reduces the number of individual routes advertised and stored by combining multiple routes into a summarized one.
Setting route metrics equal or advertising only a primary path does not reduce the number of routes as effectively.
Importing only the default route (0.0.0.0/0) is impractical for normal operations.
Thus, route aggregation is the best practice for controlling routing table size in merged BGP environments.
Reference: ArubaOS-CX BGP Route Aggregation Guide
BGP Best Practices RFCs (e.g., RFC 4271)
HPE Aruba Routing and BGP Configuration Documentation
정답:
Explanation:
For BGP in a multi-homed configuration advertising public IP blocks, the AS number should be a valid public AS number allocated by the regional internet registry (RIR). Numbers in the private AS range (64512C65534) are not suitable for public Internet announcements.
63472 falls in the public AS range (16-bit AS numbers below 64512).
64813, 65535, and 65218 are in the private or reserved range.
Therefore, 63472 is an example of a suitable public AS number.
Reference: IANA Autonomous System Number Registry
RFC 6996 (Private AS Numbers)
ArubaOS-CX BGP Configuration Guide
정답:
Explanation:
To find which changes were made on an HPE Aruba CX switch from the GUI, the correct command is:
show checkpoint diff ― this compares the running configuration with stored saved-config revisions.
Using "saved-config revisions" as the comparison base allows the GUI to show what has changed since the last saved configuration.
Other options mix checkpoint and saved-config terminology incorrectly.
Reference: ArubaOS-CX Checkpoint and Configuration Revision Guide
HPE Aruba CLI User Guide
Aruba CX Configuration Management Best Practices
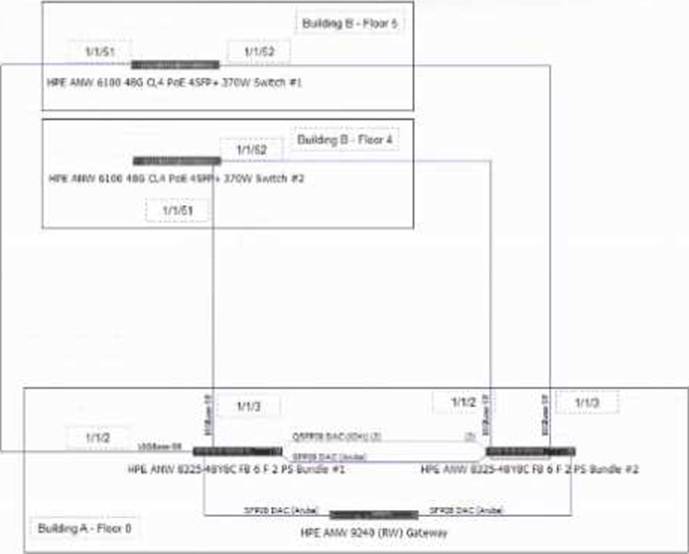
정답:
Explanation:
Dynamic Segmentation (DS) requires certain capabilities on the switches to support user role assignment and traffic segmentation based on identity. The CX 6100 series switches do not support Dynamic Segmentation due to hardware and feature limitations. Therefore, they must be replaced with CX 6300 models, which support DS features natively.
Options involving GRE tunnels or VXLAN tunnels relate to traffic forwarding but do not enable DS on unsupported hardware.
Applying licenses does not upgrade hardware capabilities for DS.
Reference: Aruba Dynamic Segmentation Deployment Guide
Aruba CX Switch Features Matrix
ArubaOS-CX Licensing and Feature Support Documentation
정답:
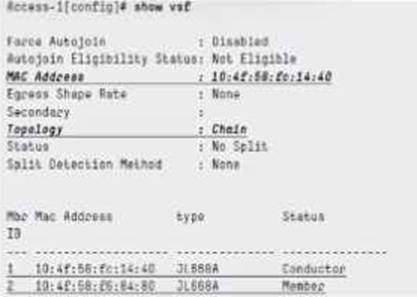
정답:
Explanation:
To avoid split-brain scenarios in VSF stacks, the VSL split-detect mgrep command is used to enable multicast group detection over the Virtual Switching Link (VSL). This helps detect when the stack links are down or partitioned, triggering appropriate failover or shutdown mechanisms.
Options like vsf start-auto-stacking, vsf secondary-member 2, or vsf conductor-member 2 are related to stack initialization and member roles but do not address split-brain detection directly.
Hence, enabling split-detect with mgrep is the best practice for VSF stack stability.
Reference: Aruba VSF Stack Configuration and Troubleshooting Guide
HPE Aruba VSF High Availability Documentation
ArubaOS-CX Stack and VSF Best Practices
정답:
Explanation:
The customer wants to tunnel traffic from APs through CX switches, similar to what they currently do with a gateway cluster. Aruba’s User-Based Tunneling (UBT) is designed specifically for this use case. UBT allows traffic from wireless and wired clients to be tunneled to a centralized gateway or controller for policy enforcement and traffic inspection.
IPSec and GRE are general tunneling protocols but not Aruba’s recommended solution for AP traffic.
VNBT relates to colorless ports and dynamic segmentation, not tunneling client traffic.
Thus, UBT is the correct tunneling solution for AP traffic through CX switches.
Reference: Aruba User-Based Tunneling Whitepaper
ArubaOS-CX Wireless Integration Guide
HPE Aruba Networking Solutions for Campus Networks
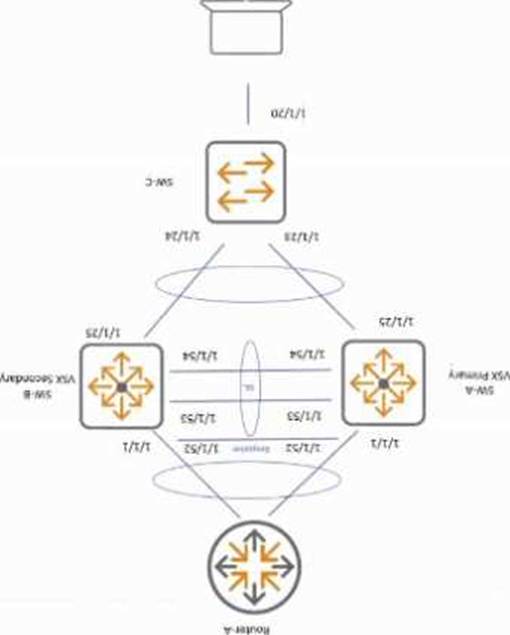
정답: D
Explanation:
If interfaces 1/1/53 and 1/1/54 connected to the primary VSX switch are disconnected and Client A experiences disruptions, configuring VSX shutdown on-split on SW-A (the primary) is necessary to prevent traffic forwarding during a split-brain scenario. This feature ensures that in case of link failure, the switch does not continue forwarding traffic independently, avoiding network loops or inconsistent states.
Configuring keepalive VLANs on downstream or upstream lags helps in monitoring but does not prevent traffic disruption.
VSX shutdown on-split must be configured on the affected primary switch to protect network integrity.
Reference: Aruba VSX Split-Brain Prevention Guide
HPE Aruba VSX High Availability Documentation
ArubaOS-CX VSX Configuration Best Practices
정답:
Explanation:
Comprehensive Detailed Explanation
To prevent man-in-the-middle attacks based on Layer 2 (Ethernet) addressing, enabling ARP inspection in the VLAN context is recommended. ARP inspection validates ARP packets and ensures only legitimate ARP responses are forwarded.
Enabling ARP inspection at VLAN level allows granular control.
Interface-level or global context is less typical or supported for ARP inspection on Aruba CX switches.
Reference: ArubaOS-CX Security Features Guide
HPE Aruba ARP Inspection Best Practices
Network Security Documentation for Aruba CX Switches
정답:
Explanation:
The LACP fallback command in Aruba VSX configurations allows the system to continue forwarding traffic even if LACP negotiation fails or is not established. This is useful when provisioning a gateway or link that does not support LACP, ensuring that the port remains operational in a static manner.
It is not specifically for backward compatibility with LACP v1.
It does not relate to operation with a single partner interface.
It also is not about active/passive LACP modes per se.
Therefore, LACP fallback is configured to support provisioning a gateway without LACP.
Reference: ArubaOS-CX LACP Configuration Guide
Aruba VSX LAG and Fallback Documentation
HPE Aruba Networking Best Practices for Link Aggregation
정답:
Explanation:
To monitor BGP neighbor state changes and automatically create a helpdesk ticket, the NAE (Network Analytics Engine) action to use is a REST API call. This allows integration with external ticketing or automation systems, enabling automated ticket creation when a monitored event occurs.
Executing shell commands, sending emails, or generating logs are limited to internal actions and do
not integrate as seamlessly with helpdesk systems.
REST API calls allow custom integration and automation.
Reference: Aruba NAE Automation and REST API Documentation
HPE Aruba Network Monitoring Best Practices
ArubaOS-CX Network Analytics Engine User Guide