FCSS - Enterprise Firewall 7.6 Administrator 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년11월17일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 Fortinet FCSS_EFW_AD-7.6 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 FCSS_EFW_AD-7.6 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 57개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
When using IPsec VPNs and VXLAN, additional headers are added to packets, which can exceed the default 1500-byte MTU. This can lead to fragmentation issues, dropped packets, or degraded performance.
To resolve this, the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) should be adjusted only if all devices in the network path support it. Otherwise, some devices may still drop or fragment packets, leading to continued issues.
Why adjusting MTU helps:
● VXLAN adds a 50-byte overhead to packets.
● IPsec adds additional encapsulation (ESP, GRE, etc.), increasing the packet size.
● If packets exceed the MTU, they may be fragmented or dropped, causing intermittent connectivity issues.
● Lowering the MTU on interfaces ensures packets stay within the supported size limit across all network devices.

정답:
Explanation:
This IPsec Phase 1 configuration defines a dynamic VPN tunnel that can accept connections from multiple peers. The settings chosen here suggest a configuration optimized for networks with intermittent traffic patterns while ensuring resources are used efficiently.
Key configurations and their impact:
● set type dynamic → This allows multiple peers to establish connections dynamically without needing predefined IP addresses.
● set ike-version 2 → Uses IKEv2, which is more efficient and supports features like EAP authentication and reduced rekeying overhead.
● set dpd on-idle → Dead Peer Detection (DPD) is triggered only when the tunnel is idle, reducing unnecessary keep-alive packets and improving resource utilization.
● set add-route enable → FortiGate automatically adds the route to the routing table when the tunnel is established, ensuring connectivity when needed.
● set proposal aes128-sha256 aes256-sha256 → Uses strong encryption and hashing algorithms, ensuring a secure connection.
● set keylife 28800 → Sets a longer key lifetime (8 hours), reducing the frequency of rekeying, which is beneficial for stable connections.
Because DPD is set to on-idle, the tunnel will not constantly send keep-alive messages but will still ensure connectivity when traffic is detected. This makes the configuration ideal for networks with regular but non-continuous traffic, balancing security and resource efficiency.
정답:
Explanation:
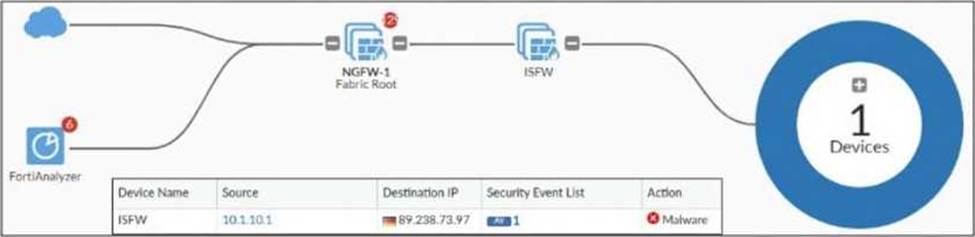
From the exhibit, ISFW is part of a Security Fabric environment with NGFW-1 as the Fabric Root. In this architecture, FortiGate devices share security intelligence, including logs and detected threats.
ISFW is in a Security Fabric environment:
● Security Fabric allows devices like ISFW to receive threat intelligence from NGFW-1, even if UTM is not enabled locally.
● If NGFW-1 detects malware from IP 10.1.10.1 to 89.238.73.97, this information can be propagated to ISFW and FortiAnalyzer.
The firewall policy in NGFW-1 has UTM enabled:
● Even though ISFW does not have UTM enabled, NGFW-1 (which sits between ISFW and the external network) does have UTM enabled and is scanning traffic.
● Since NGFW-1 detects malware in the session, it logs the event, which is then sent to FortiAnalyzer.
정답:
Explanation:
In a transparent mode Virtual Domain (VDOM) configuration, FortiGate operates as a Layer 2 bridge rather than performing Layer 3 routing. The set forward-domain <domain_ID> command is used to control how traffic is forwarded between interfaces within the same transparent VDOM.
A forward-domain acts as a broadcast domain, meaning only interfaces with the same forward-domain ID can exchange traffic. This setting is commonly used to separate different VLANs or network segments within the transparent VDOM while still allowing FortiGate to apply security policies.
정답:
Explanation:
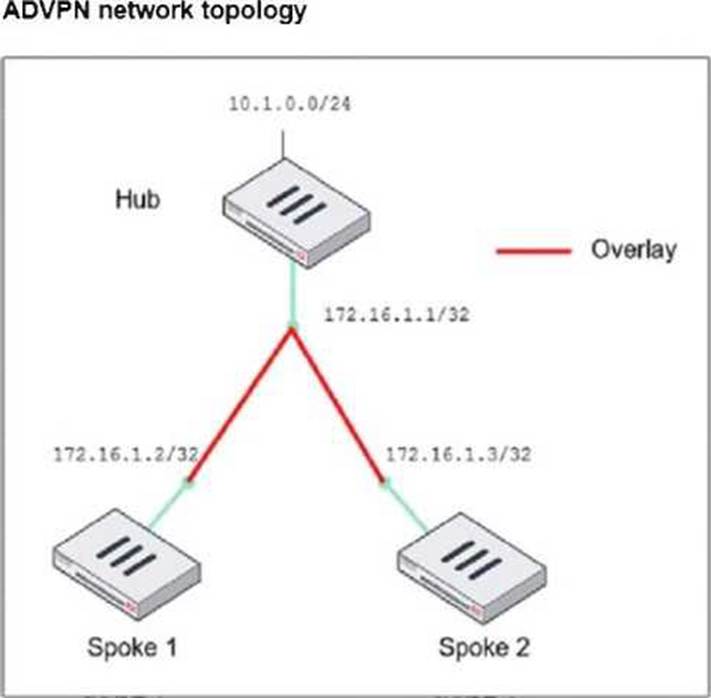
ADVPN (Auto-Discovery VPN) 2.0 is the optimal solution for enabling direct spoke-to-spoke communication without passing through the hub, while also allowing automatic link selection based on quality metrics.
● Dynamic Direct Tunnels:
● ADVPN 2.0 allows spokes to establish direct IPsec tunnels dynamically based on traffic patterns, reducing latency and improving performance.
● Unlike static VPNs, spokes do not need to pre-configure tunnels for each other.
● Automatic Link Optimization:
● ADVPN 2.0 monitors the quality of multiple internet connections on each spoke.
● It automatically switches to the best available connection when the primary link degrades or fails.
● This is achieved by dynamically adjusting BGP-based routing or leveraging SD-WAN integration.
정답:
Explanation:
IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange version 2) is an improvement over IKEv1, offering enhanced security, efficiency, and flexibility in VPN configurations.
It includes stronger Diffie-Hellman (DH) groups, such as Elliptic Curve (ECP) groups.
IKEv2 supports stronger cryptographic algorithms, including Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman (ECDH) groups such as ECP256 and ECP384, providing improved security compared to IKEv1.
It supports the extensible authentication protocol (EAP).
IKEv2 natively supports EAP authentication, which allows integration with external authentication mechanisms such as RADIUS, certificates, and smart cards. This is particularly useful for remote access VPNs where user authentication must be flexible and secure.

정답:
Explanation:
In the given ADVPN (Auto-Discovery VPN) topology, BGP is being used to dynamically establish routes between spokes. The neighbor-range configuration is crucial for simplifying BGP peer setup by automatically assigning neighbors based on their IP range.
set neighbor-group advpn
● The neighbor-group parameter is used to apply pre-defined settings (such as AS number) to dynamically discovered BGP neighbors.
● The advpn neighbor-group is already defined in the configuration, and assigning it to the neighbor-range ensures consistent BGP settings for all spoke neighbors.
set prefix 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0
● This command allows dynamic BGP peer discovery by defining a range of potential neighbor IPs (172.16.1.1 - 172.16.1.255).
● Since each spoke has a unique /32 IP within this subnet, this ensures that any spoke within the 172.16.1.0/24 range can automatically establish a BGP session with the hub.
정답:
Explanation:
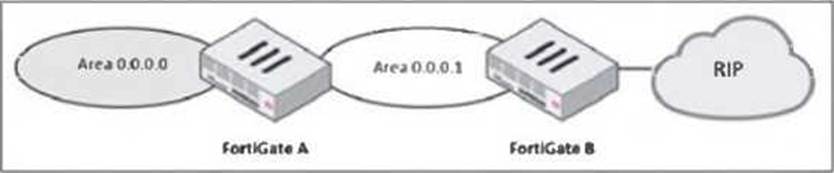
The diagram shows a multi-area OSPF network where:
● FortiGate A is in OSPF Area 0 (Backbone area).
● FortiGate B is in OSPF Area 0.0.0.1 and is connected to an RIP network.
To ensure that OSPF Area 0 (0.0.0.0) learns routes from the external RIP network, FortiGate B must redistribute RIP routes into OSPF.
Steps to achieve this:
정답:
Explanation:
VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN) is an overlay network technology that extends Layer 2 networks over Layer 3 infrastructure. When VXLAN is used extensively on FortiGate, hardware acceleration is crucial for maintaining performance.
● NP7 (Network Processor 7) is Fortinet’s latest network processor designed to accelerate high-performance networking features, including:
● VXLAN encapsulation/decapsulation
● IPsec VPN offloading
● Firewall policy enforcement
● Advanced threat protection at wire speed
NP7 significantly reduces latency and improves throughput when handling VXLAN traffic, making it the best choice for large-scale VXLAN deployments.
정답:
Explanation:
Applying an aggressive IPS profile without prior testing can disrupt legitimate applications by incorrectly identifying normal traffic as malicious.
To prevent disruptions while still monitoring for threats:
● Enable IPS in "Monitor Mode" first:
● This allows FortiGate to log and analyze potential threats without actively blocking traffic.
● Administrators can review logs and fine-tune IPS signatures to minimize false positives before switching to blocking mode.
● Verify and adjust signature patterns:
● Some signatures might trigger unnecessary blocks for legitimate application traffic.
● By analyzing logs, administrators can disable or modify specific rules causing false positives.
정답:
Explanation:
When FortiGate processes the first packets of a session, it follows a sequence of steps to determine how the traffic should be handled before establishing a session.
The initial step involves:
● Access Control List (ACL) checks: Determines if the traffic should be allowed or blocked based on predefined security rules.
● Hardware Packet Engine (HPE) inspections: Ensures that packet headers are valid and comply with protocol standards.
● IP Integrity Header Checking: Verifies if the IP headers are intact and not malformed or spoofed. Once these security inspections are completed and the session is validated, FortiGate then installs the session in hardware (if offloading is enabled) or processes it in software.
정답:
Explanation:
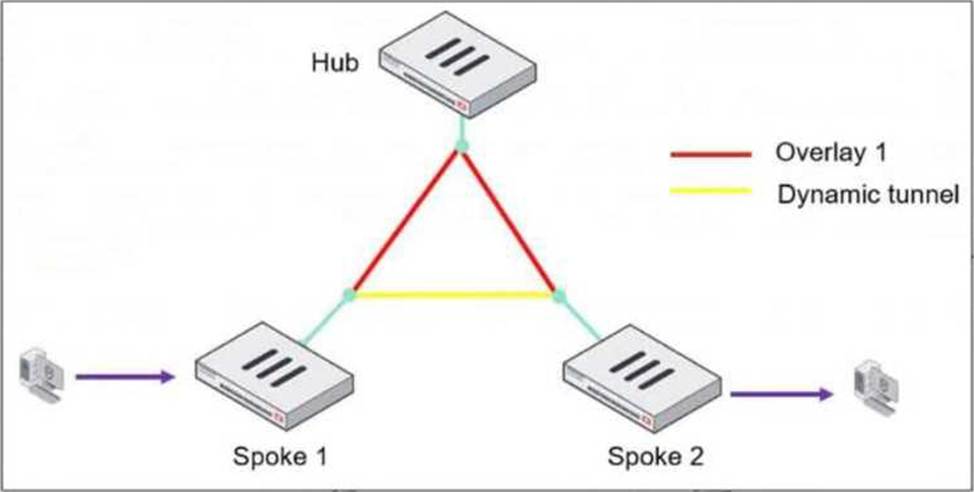
In an ADVPN (Auto-Discovery VPN) network, a dynamic VPN tunnel is established on-demand between spokes to optimize traffic flow and reduce latency.
Process:
정답:
Explanation:
FortiGate, like other security appliances, cannot analyze encrypted HTTPS traffic unless it decrypts it first. If only certificate inspection is enabled, FortiGate can see the certificate details (such as the domain and issuer) but cannot inspect the actual web content.
To fully analyze the traffic and detect potential malware threats:
● Full SSL inspection (Deep Packet Inspection) must be enabled in the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile.
● This allows FortiGate to decrypt the HTTPS traffic, inspect the content, and then re-encrypt it before forwarding it to the user.
● Without full SSL inspection, threats embedded in encrypted traffic may go undetected.
정답:
Explanation:
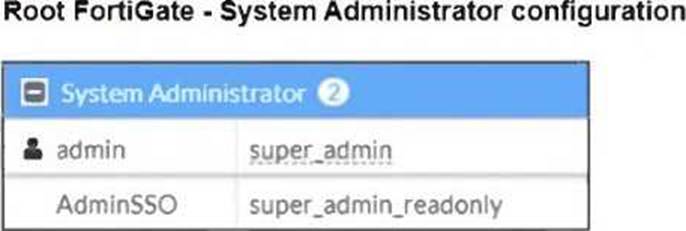
From the Root FortiGate - System Administrator Configuration exhibit:
● The AdminSSO account has the super_admin_readonly role.
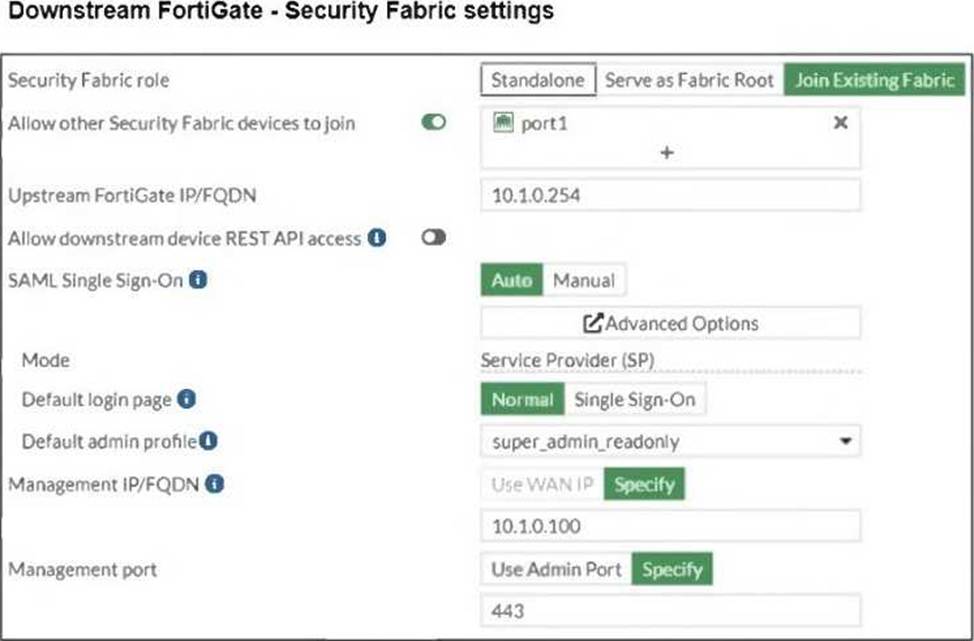
From the Downstream FortiGate - Security Fabric Settings exhibit:
● The Security Fabric role is set to Join Existing Fabric, meaning it will authenticate with the root FortiGate.
● SAML Single Sign-On (SSO) is enabled, and the default admin profile is set to
super_admin_readonly.
When the AdminSSO user logs into the downstream FortiGate using SSO, the authentication request is sent to the root FortiGate, where AdminSSO has super_admin_readonly permissions. Since the downstream FortiGate inherits this permission through the Security Fabric configuration, the user will be granted super_admin_readonly access.
정답:
Explanation:
The Internet Service Database (ISDB) in FortiGate is used to enforce content filtering at Layer 3 (Network Layer) and Layer 4 (Transport Layer) of the OSI model by identifying applications based on their predefined IP addresses and ports.
FortiGate has a predefined list of all IPs and ports for specific applications downloaded from FortiGuard:
● FortiGate retrieves and updates a predefined list of IPs and ports for different internet services from FortiGuard.
● This allows FortiGate to block specific services at Layer 3 and Layer 4 without requiring deep packet inspection.
The ISDB blocks the IP addresses and ports of an application predefined by FortiGuard:
● ISDB works by matching traffic to known IP addresses and ports of categorized services.
● When an application or service is blocked, FortiGate prevents communication by denying traffic based on its destination IP and port number.