Certified in Planning and Inventory Management (CPIM 8.0) 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년11월17일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 APICS CPIM-8.0 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 CPIM-8.0 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 150개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
A company that uses two-level master scheduling has a master production schedule (MPS) for the end items (kits) and a final assembly schedule (FAS) for the components (tools). The forecasts that are input to master scheduling should reflect the total number of kits and the specific kit configurations, as these determine the demand for the components. The other options are not relevant for master scheduling, as they do not reflect the end item demand or the bill of materials structure.
Reference: EXAM CONTENT MANUAL PREVIEW, page 10, section 4.1.2. Manufacturing Planning and Control for Supply Chain Management: The CPIM Reference, Second Edition, page 163, section 6.2.
정답:
Explanation:
Proximity to suppliers would be classified as a cost factor in preparing for a facility location decision. Cost factors are the expenses associated with operating a facility in a specific location, such as labor, materials, utilities, taxes, and transportation. Proximity to suppliers can affect the cost of inbound transportation, inventory holding, and quality control. Choosing a location that is close to suppliers can reduce these costs and improve the efficiency and reliability of the supply chain.
Reference: Managing Supply Chain Operations, Chapter 2: Global Supply Chain Strategy, Section 2.3: Facility Location
CPIM Exam Content Manual, Module 1: Supply Chains and Strategy, Section 1.4: Facility Location,
Subsection 1.4.1: Facility Location Concepts
정답:
Explanation:
An effective approach to projecting requirements for materials with long lead times is to initiate a multilevel master schedule. A multilevel master schedule is a detailed plan that shows the quantities and timing of the end items and all of their components at each level of the bill of materials (BOM). By using a multilevel master schedule, a planner can determine the requirements for materials with long lead times and place orders in advance to avoid shortages or delays. A phantom bill of materials (BOM) is a temporary grouping of components that are used in the production of a parent item, but do not exist as a separate item in inventory. A phantom BOM is not an effective approach to projecting requirements for materials with long lead times, as it does not reflect the actual demand for the components. Increasing the level of safety stock is a way of mitigating the risk of uncertainty in demand or supply, but it is not an effective approach to projecting requirements for materials with long lead times, as it increases the inventory carrying costs and does not address the root cause of the problem. Decreasing the planning horizon is the opposite of an effective approach to projecting requirements for materials with long lead times, as it reduces the visibility and accuracy of the forecast and increases the likelihood of stockouts or excess inventory.
Reference: CPIM Part 2 Learning System, Module 1: Supply Chain Strategy, Section 1.4: Master Scheduling
CPIM Part 2 Learning System, Module 3: Supply, Section 3.2: Material Requirements Planning
정답:
Explanation:
Point-of-use storage is a stock location system that places inventory close to where it is needed or consumed in the production process. This reduces waste, handling, and transportation costs, and improves material flow and visibility. Point-of-use storage is a key element of a lean environment, where inventory is minimized and replenished frequently based on demand signals.
Reference: EXAM CONTENT MANUAL PREVIEW, page 15, section 7.1.2. Manufacturing Planning and Control for Supply Chain Management: The CPIM Reference, Second Edition, page 462, section 13.3.
정답:
Explanation:
The tracking signal is a measurement that indicates there may be bias in the forecast model. The tracking signal is the ratio of the cumulative forecast error to the mean absolute deviation (MAD). It measures how well the forecast is tracking the actual demand over time. A tracking signal of zero means that the forecast is perfectly accurate. A tracking signal within the range of -4 to +4 is considered acceptable. A tracking signal outside this range indicates that the forecast is consistently overestimating or underestimating the demand, which implies that there is bias in the forecast model. Bias is the tendency of a forecast to be consistently higher or lower than the actual demand. Bias can be caused by factors such as inaccurate data, inappropriate forecasting methods, or changes in demand patterns.
Reference: Managing Supply Chain Operations, Chapter 5: Demand Management and Forecasting, Section 5.2:
Forecasting Methods, Subsection 5.2.3: Forecast Accuracy and Control
CPIM Exam Content Manual, Module 3: Demand, Section 3.2: Forecasting, Subsection 3.2.2:
Forecasting Methods, Subsubsection 3.2.2.3: Forecast Accuracy and Control
정답:
Explanation:
Plan-do-check-action (PDCA) is a technique that would best be used to return a process under control when it is outside its upper control limit (UCL). PDCA is a four-step cycle of continuous improvement that involves planning a change, implementing the change, checking the results, and acting on the findings. PDCA can help identify and eliminate the root causes of variation, improve the process performance, and prevent the recurrence of problems. PDCA is also known as the Deming cycle or the Shewhart cycle.
Reference: Managing Supply Chain Operations, Chapter 9: Quality Management, Section 9.3: Quality
Improvement, Subsection 9.3.1: Plan-Do-Check-Act Cycle
CPIM Exam Content Manual, Module 8: Quality, Technology and Continuous Improvement, Section
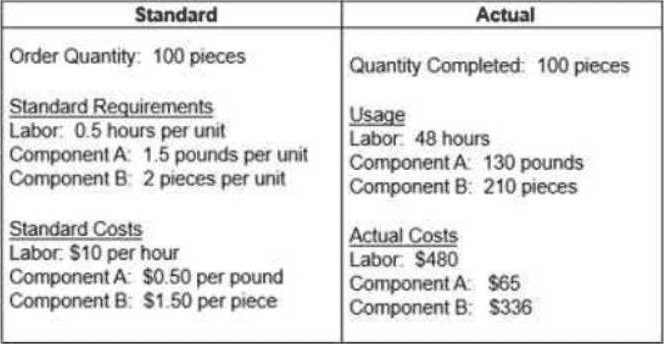
정답:
Explanation:
The labor efficiency variance is the difference between the standard labor hours allowed for the actual output and the actual labor hours used, multiplied by the standard labor rate. In this case, the standard labor hours allowed for 100 pieces are 0.5 * 100 = 50 hours. The actual labor hours used are 48 hours. The standard labor rate is $10 per hour. Therefore, the labor efficiency variance = (50 - 48) * $10 = $20 favorable. This means that the actual labor hours used were less than the standard labor hours allowed, which indicates a higher labor efficiency12
Reference:
1: CPIM Part 2 - Section B - Module 2 - Session 2 - Variance Analysis
2: CPIM Part 2 - Section B - Module 2 - Session 3 - Variance Analysis Example
정답:
Explanation:
A localized multi-country strategy is a type of global strategy that involves adapting products, marketing, and operations to the specific needs and preferences of each country or region where the company operates. This strategy allows the company to increase its market share by appealing to the local customers and differentiating itself from the competitors. A localized multi-country strategy requires the company to sell different product versions in different countries under different brand names, as this reflects the high degree of customization and localization that the strategy entails. The other options are not consistent with a localized multi-country strategy, as they imply a low degree of adaptation and a high degree of standardization across the markets. Selling the same products under the same brand name worldwide is a global strategy that assumes universal customer preferences and seeks economies of scale. Locating plants on the basis of maximum location advantage is a transnational strategy that balances global integration and local responsiveness. Using the best suppliers regardless of geographic location is a sourcing strategy that does not necessarily reflect the degree of localization of the products or the marketing.
Reference: CPIM Part 2 Exam Content Manual, p. 19
Multidomestic strategy: Global success through localization
Localization strategy - How to build with examples
정답:
Explanation:
A company with a global strategy seeks to achieve a competitive advantage by standardizing its products, processes, and marketing across different countries. It leverages economies of scale and scope, as well as global brand recognition, to gain market share and profitability. It does not adapt to local preferences or conditions, but rather imposes a uniform approach to all markets.
Reference: EXAM CONTENT MANUAL PREVIEW, page 6, section 1.1.2. Strategic Supply Chain Management: The Five Core Disciplines for Top Performance, Second Edition, page 19, section 1.2.
정답:
Explanation:
Concurrent engineering is a product design approach that involves the simultaneous and collaborative involvement of different functional areas, such as engineering, marketing, manufacturing, and suppliers, in the product development process. Concurrent engineering aims to reduce time to market, improve quality, lower costs, and enhance customer satisfaction by integrating and coordinating the inputs and feedback of all the stakeholders from the early stages of design. Concurrent engineering can also facilitate the standardization and modularization of product components, which can improve the flexibility and responsiveness of a global supply chain.
Reference: Managing Supply Chain Operations, Chapter 3: Product Design and Development, Section 3.2:
Concurrent Engineering
CPIM Exam Content Manual, Module 1: Supply Chains and Strategy, Section 1.3: Product and Process
Design, Subsection 1.3.1: Product and Process Design Concepts
정답:
Explanation:
The demonstrated capacity last week is the total number of models completed by both modelers in 40 hours. One modeler finished 5 models a day, which means 25 models in a week. The other modeler finished 1 model a day, which means 5 models in a week. Therefore, the demonstrated capacity last week is 25 + 5 = 30 models. However, this is not one of the options given. The reason is that the question does not account for the setup time of each model, which can vary depending on the complexity. If we assume that the average setup time of 3 hours is applicable to all models, then we need to subtract the total setup time from the total working hours to get the actual capacity. The total setup time for 30 models is 30 x 3 = 90 hours. The total working hours for both modelers is 2 x 40 = 80 hours. Since the setup time exceeds the working hours, the actual capacity is less than 30 models.
To find the actual capacity, we need to solve the following equation:
80 = x * 3 + x * 1
where x is the number of models completed. Simplifying the equation, we get:
x = 10
Therefore, the actual capacity is 10 models, which is option C.
Reference: Managing Supply Chain Operations, Chapter 6: Capacity Management, Section 6.1: Capacity
Concepts, Subsection 6.1.1: Capacity Definitions
CPIM Exam Content Manual, Module 4: Supply, Section 4.2: Capacity Management, Subsection 4.2.1:
Capacity Concepts
정답:
Explanation:
In an assemble-to-order (ATO) manufacturing environment, the MPS is used to plan subassemblies and components that have long lead times or high demand variability. These subassemblies and components are produced and stocked in anticipation of customer orders. The end items are only scheduled in the MPS when a customer order is received, and they are assembled from the available subassemblies and components. This reduces the lead time and inventory for the end items, while increasing the flexibility and responsiveness to customer needs. ATO is a hybrid strategy between make-to-stock (MTS) and make-to-order (MTO).
Reference: =
CPIM Exam Content Manual, Module 4: Supply, Section 4.1: Master Production Schedule, p. 14
Manufacturing Planning and Control for Supply Chain Management, Chapter 8: Master Production
Scheduling, Section 8.3: Master Production Scheduling in Different Environments, pp. 191-192
정답:
Explanation:
In a rapidly changing business environment, a primary advantage of an effective customer relationship management (CRM) program is earlier identification of shifts in customer preferences. CRM is a strategy that focuses on building and maintaining long-term relationships with customers by understanding their needs, preferences, and behaviors. CRM enables organizations to anticipate and respond to changes in customer demand, improve customer satisfaction and loyalty, and increase profitability and competitiveness. CRM also helps organizations to segment and target customers based on their value and potential, and to customize products and services accordingly. CRM involves the use of various tools and techniques, such as data collection and analysis, communication channels, feedback mechanisms, and loyalty programs.
Reference: Managing Supply Chain Operations, Chapter 4: Customer Relationship Management, Section 4.1:
Introduction to Customer Relationship Management
CPIM Exam Content Manual, Module 1: Supply Chains and Strategy, Section 1.2: Customer
Relationship Management, Subsection 1.2.1: Customer Relationship Management Concepts
정답:
Explanation:
Changing the due dates of open orders is a common practice to cope with demand fluctuations, capacity constraints, or material shortages. However, it can have a negative effect on the stability and reliability of the schedule, causing “nervousness”. Nervousness is the tendency of the schedule to change frequently and significantly due to minor changes in inputs or parameters. Nervousness can result in increased costs, reduced efficiency, lower quality, and lower customer satisfaction. To avoid or reduce nervousness, some strategies are: using time fences, freezing the schedule, aggregating the demand, and using safety stock or safety time.
Reference: =
CPIM Exam Content Manual, Module 5: Detailed Schedules, Section 5.1: Capacity Management, p. 18
Manufacturing Planning and Control for Supply Chain Management, Chapter 9: Capacity Planning
and Management, Section 9.3: Capacity Planning and Scheduling, pp. 222-223
정답:
Explanation:
The time spent in queue by a specific manufacturing job is determined by the priority of the order. Priority is the relative importance or urgency of an order compared to other orders in the system. Priority can be assigned based on various criteria, such as due date, customer preference, profitability, or first-come-first-served. Priority determines the order in which jobs are processed at each workstation and affects the waiting time and flow time of each job. Higher priority jobs have shorter waiting times and lower priority jobs have longer waiting times. Priority can be used as a tool to manage the trade-offs between customer service, capacity utilization, and inventory levels.
Reference: Managing Supply Chain Operations, Chapter 7: Scheduling and Sequencing, Section 7.2: Priority Rules
CPIM Exam Content Manual, Module 6: Detailed Schedules, Section 6.2: Scheduling and Sequencing,
Subsection 6.2.2: Priority Rules