CCRN (Adult) - Direct Care Eligibility Pathway 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년11월17일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 AACN CCRN Adult 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 CCRN Adult 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 150개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
Subcutaneous emphysema (SE) is a condition where gas or air accumulates in the subcutaneous tissue layer of the skin, causing swelling and a crackling sensation when touched. SE can occur after esophagectomy, a surgical procedure to remove part or all of the esophagus, due to air leakage from the anastomosis site or the lung. SE can also be a sign of a more serious complication, such as anastomotic leakage, mediastinitis, or tracheal injury12. Therefore, the nurse should expect an order for a CT scan, which is a diagnostic imaging test that can detect the source and extent of the air leakage and any associated complications. A CT scan can also guide the appropriate management of SE, which may include conservative measures, such as increasing the suction of the chest tube, or more invasive interventions, such as surgical repair or drainage123. Chest tube insertion, IV antibiotics, and gastric decompression are not likely to be ordered for SE after esophagectomy, as they do not address the underlying cause of the air leakage or the potential complications. Chest tube insertion may be indicated for pneumothorax, but not for SE alone. IV antibiotics may be indicated for infection, but not for SE alone. Gastric decompression may be indicated for gastric distension, but not for SE alone.
정답:
Explanation:
Verified Answer
B. Consult with the pharmacist on the effects of the specific herbs. Herbal therapy is a type of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) that uses plants or plant extracts to treat various health conditions. Many patients use herbal therapy for various reasons, such as cultural beliefs, personal preferences, or dissatisfaction with conventional medicine. However, herbal therapy is not without risks and challenges, especially in the hospital setting. Some of the potential problems include lack of standardization, quality control, and regulation of herbal products; adverse effects and interactions with other medications; and ethical and legal issues regarding informed consent, documentation, and liability12. Therefore, the nurse’s first action should be to consult with the pharmacist on the effects of the specific herbs that the family wants to administer to the patient. The pharmacist can provide information on the safety, efficacy, dosage, and compatibility of the herbs with the patient’s condition and current medications. The nurse should also inform the patient’s primary provider and obtain an order for the herbs before allowing the patient to take them. The nurse should document the use of herbal therapy in the patient’s medical record and monitor the patient for any adverse effects or changes in response to other treatments. Informing the family that herbal therapy is not appropriate in the hospital is not respectful of the patient’s autonomy and cultural values. Allowing the patient to take the herbs without consulting the pharmacist and obtaining an order is not safe and may violate the hospital’s policies and standards of care.
정답:
Explanation:
Nimodipine is a calcium channel blocker that is used to prevent or treat cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. It works by relaxing the smooth muscle of the cerebral arteries and improving blood flow to the brain. Nimodipine is the only FDA-approved agent for vasospasm and has been shown to reduce the risk of ischemic complications and improve neurological outcomes12. Lorazepam, propranolol, and pentobarbital are not effective for treating cerebral vasospasm and may have adverse effects on the patient’s blood pressure, heart rate, and level of consciousness.
정답:
Explanation:
Verified Answer:
C. establish a schedule with the provider. Neurological assessments are important for monitoring the patient’s neurological status and detecting any changes that may indicate a complication or improvement. However, frequent interruptions of sleep can have negative effects on the patient’s health and well-being, such as impaired cognition, mood, immune function, and wound healing. Therefore, the nurse should collaborate with the provider to establish a schedule for neurologic assessments that balances the need for monitoring and the need for rest. This may involve reducing the frequency of assessments during the night, clustering other interventions to minimize disruptions, and using non-invasive methods of assessment when possible. Discontinuing neurologic assessments, encouraging the patient to sleep between assessments, or moving the patient to a quieter part of the unit are not appropriate actions as they do not address the root cause of the problem or ensure adequate monitoring of the patient’s condition.
정답:
정답:
Explanation:
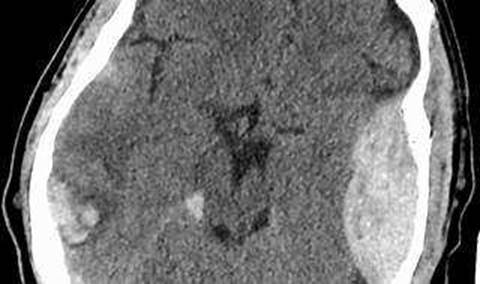
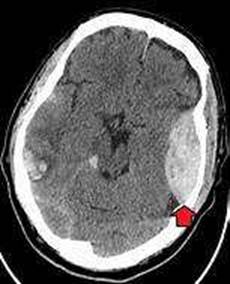
An epidural hematoma is a collection of blood that forms between the skull and the dura mater, the outermost layer of the meninges that cover the brain. The most common cause of an epidural hematoma is a head injury that fractures the temporal bone and tears the middle meningeal artery, which runs along the inner surface of the skull. Arterial bleeding is under high pressure and can rapidly expand the hematoma, compressing the brain and causing neurological deterioration. A typical symptom of an epidural hematoma is a brief loss of consciousness followed by a lucid interval and then a rapid decline in consciousness and brain function. This condition requires urgent surgical evacuation of the hematoma to prevent brain damage or death12. Venous bleeding, clot formation, and intracranial aneurysm are not the main factors associated with the deterioration of the patient’s condition in this case.
정답:
Explanation:
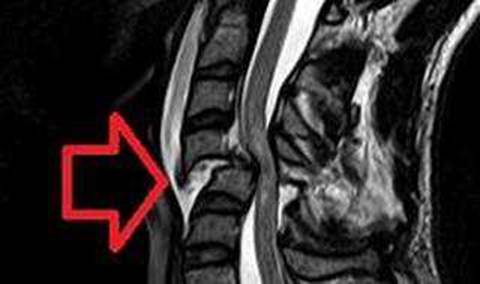
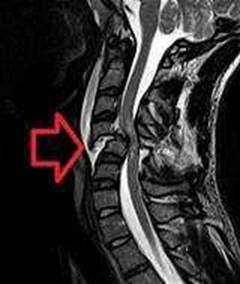
The patient with a C5 spinal cord injury may have anxiety, fear, or depression due to the loss of function and independence. The patient may also have difficulty breathing, swallowing, or regulating body temperature. The patient may call the nurse frequently to seek reassurance, attention, or comfort. The nurse should respond with empathy and compassion, and provide the patient with emotional support and psychological counseling. The nurse should also assess the patient’s physical needs and provide adequate hydration, nutrition, and skin care. The nurse should not dismiss the patient’s requests, ignore the patient’s feelings, or limit the patient’s contact with the nurse. The nurse should also not give false reassurance or minimize the patient’s concerns. Therefore, the best response is to get someone to sit with the patient, such as a family member, a friend, or a volunteer. This will help the patient feel less isolated, anxious, or depressed, and provide the patient with a sense of security and companionship.
정답:
Explanation:
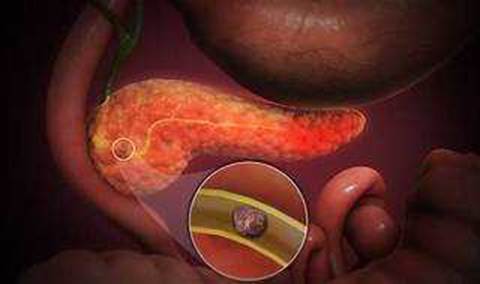
Shortness of breath is a sign of respiratory distress that may indicate a serious complication of acute pancreatitis, such as pleural effusion, atelectasis, or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). These conditions can impair oxygenation and ventilation, and may require supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation. The provider should be notified immediately if the patient has shortness of breath, as well as other signs of respiratory distress, such as cyanosis, tachypnea, or use of accessory muscles12. Hypoactive bowel sounds, hyperglycemia, and vomiting are common findings in acute pancreatitis, but they are not as urgent as shortness of breath. They may indicate paralytic ileus, pancreatic insufficiency, or gastric outlet obstruction, respectively. These conditions can be managed with supportive measures, such as intravenous fluids, antiemetics, analgesics, and nutritional support3.
정답:
Explanation:
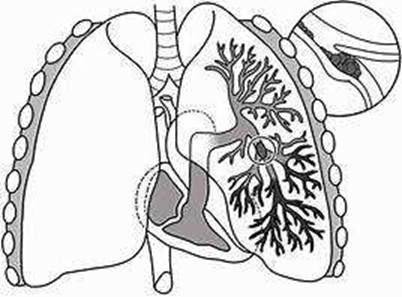
Pulmonary angiography is the most definitive diagnostic test for pulmonary embolism, as it provides a clear picture of the blood flow in the arteries of the lungs. It can detect even small clots and determine the location and extent of the obstruction. However, because it requires a high degree of skill to perform and has potentially serious risks, it is usually done when other tests fail to provide a definite diagnosis1. Other tests that can be used to diagnose pulmonary embolism include CT pulmonary angiography, ventilation-perfusion scan, D-dimer test, chest X-ray, ultrasound, and MRI23. However, these tests may have limitations such as low sensitivity, low specificity, radiation exposure, contrast allergy, or availability4.
Reference: Pulmonary embolism - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic, under “Pulmonary angiogram”. Pulmonary Embolism (PE): Symptoms, Signs & Treatment - Cleveland Clinic, under “How is a pulmonary embolism diagnosed?”.
Diagnosis of Pulmonary embolism and what are its different treatment options?, under “Diagnosis for Pulmonary embolism”.
Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism - UpToDate, under “Overview”.
정답:
Explanation:
Hypoperfusion is a condition in which the blood flow to the organs and tissues is insufficient to meet their metabolic demands. Hypoperfusion can result from third-degree AV block, which is a complete loss of communication between the atria and the ventricles. This causes the ventricles to beat very slowly or not at all, leading to a low cardiac output and reduced blood pressure. Hypoperfusion can cause symptoms such as dizziness, fainting, confusion, chest pain, shortness of breath, and shock12. Heart failure, hypoxia, and chest pain are possible complications of hypoperfusion, but they are not the most common problem in patients with third-degree AV block.
정답:
Explanation:
A negative apnea test means that the patient does not breathe spontaneously when disconnected from the ventilator and exposed to a high level of carbon dioxide, which normally stimulates breathing. A negative apnea test is one of the criteria for brain death, as it indicates the loss of brainstem function. A positive vestibulo-ocular reflex, also known as the oculocephalic or doll’s eye reflex, means that the eyes move in the opposite direction of the head when the head is turned. A positive cough reflex means that the patient coughs when the trachea is stimulated. A negative cold caloric test means that the eyes do not move when cold water is injected into the ear canal. All these tests assess the integrity of the brainstem, and a positive result would exclude brain death.
Therefore, the correct answer is B.
Reference: Diagnosis of brain death - UpToDate, under “Apnea testing”.
Brain Death | Critical Care Medicine | JAMA | JAMA Network, under “How Is Brain Death Diagnosed?”.
The 2023 AAN/AAP/CNS/SCCM Pediatric and Adult Brain Death/Death by …, under “Apnea Testing”.
정답:
Explanation:
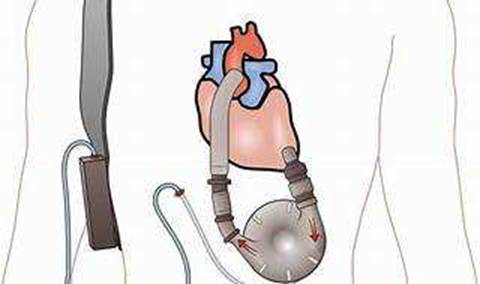
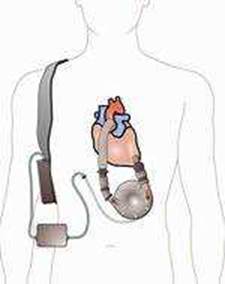
Protein calorie malnutrition (PCM) is a condition that occurs when the body does not get enough protein and calories to meet its needs. PCM can affect the immune system, wound healing, and organ function. Patients with a left ventricular assist device (LVAD) are at risk of PCM due to increased metabolic demands, fluid retention, inflammation, and poor appetite. Edema, or swelling, is a common sign of fluid overload in patients with LVADs. However, edema can also mask the physical signs of PCM, such as muscle wasting, weight loss, and skin changes. Therefore, the nurse should consider edema as a potential factor that can interfere with the assessment of the patient’s nutritional status. Other methods to evaluate the patient’s nutritional needs include laboratory tests, dietary intake, and body mass index. The nurse should also collaborate with a dietitian to provide appropriate nutritional interventions for the patient, such as oral supplements, enteral feeding, or parenteral nutrition.
Reference: Caring for patients with a left ventricular assist device, page 28.
Ventricular assist device (VAD) - Mayo Clinic, under “Why it’s done”.
Preoperative Nutritional Optimization and Physical Exercise for …, under “Introduction”.
Obesity in Patients with Advanced Heart Failure and Left Ventricular …, under “Introduction”.
정답:
Explanation:
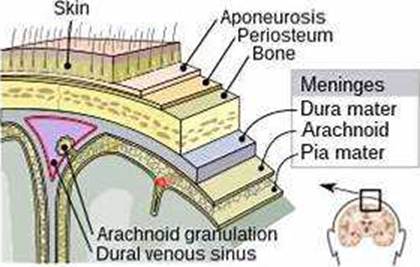
A positive Kernig’s sign is a clinical test for meningitis that involves flexing the hip and knee of the patient and then extending the knee. If the patient feels pain or resistance in the lower back or hamstring, the test is positive. A positive Kernig’s sign indicates irritation of the meninges, the membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. A positive Trousseau’s sign is a sign of hypocalcemia that involves carpal spasm after inflating a blood pressure cuff. A positive Cullen’s sign is a sign of retroperitoneal bleeding that involves bruising around the umbilicus. A positive Babinski’s sign is a sign of upper motor neuron lesion that involves fanning of the toes when the sole of the foot is stroked.
Reference: Kernig’s sign - Wikipedia
Trousseau’s sign - Wikipedia
Cullen’s sign - Wikipedia
Babinski sign - Wikipedia
정답:
Explanation:
The patient has signs of myxedema coma, a life-threatening complication of hypothyroidism. The patient needs immediate treatment with thyroid hormone replacement, glucocorticoids, and supportive care. One of the supportive measures is to correct the hypothermia that often accompanies myxedema coma. A forced air warming blanket is a device that delivers warm air through a hose to a blanket that covers the patient. This helps to raise the patient’s core temperature and prevent further complications. Insulin drip is not indicated, as the patient does not have diabetes or hyperglycemia. 3% saline is a hypertonic solution that can worsen the hyponatremia and fluid overload that are common in myxedema coma. Diuretics are not recommended, as they can cause dehydration and electrolyte imbalance in the patient.
Reference: Myxedema Coma: Diagnosis and Treatment | AAFP
Myxedema coma - UpToDate
Myxedema: Symptoms, treatment & coma - Medical News Today
정답: