CompTIA SecurityX Certification Exam 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년11월17일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 CompTIA CAS-005 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 CAS-005 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 117개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
Step by Step
Understanding the Scenario: The question describes a proactive security measure where an organization maintains a registry of software dependencies and their corresponding hashes. This registry is used to verify the integrity of software packages.
Analyzing the Answer Choices:
A. Supply chain attack: This type of attack involves compromising the software supply chain by injecting malicious code into legitimate software packages.
Reference: CASP+ objectives often emphasize supply chain security due to its growing importance. The scenario directly relates to this type of attack, as the registry helps ensure that software packages haven't been tampered with during the supply chain process.
B. Cipher substitution attack: This is a cryptographic attack focused on replacing ciphertext with a different ciphertext to deduce the key. It's not relevant to the scenario.
C. Side-channel analysis: This attack involves gathering information from the physical implementation of a system (e.g., timing, power consumption) rather than exploiting the algorithm itself. It's not applicable here.
D. On-path attack (formerly man-in-the-middle): This attack involves intercepting and potentially altering communication between two parties. While important, it's not the primary focus of the registry.
E. Pass-the-hash attack: This attack involves using a stolen hash of a user's password to authenticate without needing the actual password. It's unrelated to software package integrity.
Why A is the Correct Answer
A supply chain attack is exactly what the organization is trying to mitigate. By creating a registry of known-good software packages and their hashes, they can verify that the packages they are using are legitimate and haven't been altered.
If an attacker were to compromise a software package in the supply chain, the hash of the altered package would not match the hash in the organization's registry. This would immediately alert the organization to a potential compromise.
CASP+ Relevance: This aligns with the CASP+ exam objectives, which emphasize the importance of risk management, threat intelligence, and implementing security controls to address various attack vectors, including supply chain risks.
How the Registry Works (Elaboration based on CASP+principles):
Hashing: When a package is vetted, a cryptographic hash function (like SHA-256) is used to generate a unique "fingerprint" (the hash) of the package's contents.
Verification: Before installing or using a package, its hash is calculated and compared to the hash stored in the registry. A match confirms the package's integrity. A mismatch indicates tampering.
Incident Response: If a vulnerability is discovered in a commonly used package, the registry helps the organization quickly identify which systems are affected based on the dependency list and the stored hashes.
In conclusion, maintaining a registry of software dependencies with hashes is a crucial security control that directly addresses the threat of supply chain attacks by ensuring the integrity and authenticity of software packages. The use of hash functions for verification is a common practice in security and is emphasized in the CASP+ material.
정답:
Explanation:
Comprehensive and Detailed Step-by-Step
Understand the Question Requirements:
The goal is to use a regular expression (regex) to match software versions 10.0 through 10.3, but exclude version 10.4.
Review Regex Syntax:
[ ] indicates a character set (matches any one character in the set).
[0-3] matches any digit between 0 and 3.
\. escapes the period (.) so it matches a literal period instead of acting as a wildcard. ( ) groups parts of the regex together.
Analyze Each Option:
Option A: Reader(*)[1][0].[0-4:
Incorrect. The use of (*) is not valid syntax in this context and [0-4 is incomplete or misformatted.
Option B: Reader[11[01X.f0-3'
Incorrect. This is an invalid regex syntax, mixing character sets and mismatched brackets.
Option C: Reader( )[1][0].[0-3:
Correct. This regex is valid and matches "Reader 10.0", "Reader 10.1", "Reader 10.2", and "Reader 10.3" while excluding "Reader 10.4".
Breakdown:
Reader: Matches the text "Reader".
[1][0]: Matches "10" as a combination of two characters.
\.: Matches the literal period.
[0-3]: Matches any single digit between 0 and 3.
Option D: Reader( )[1][0] X.[1-3:
Incorrect. The syntax X.[1-3 is invalid, and this does not match the required versions.
Conclusion: The regex in Option C correctly identifies all affected versions (10.0, 10.1, 10.2, 10.3) while excluding the unaffected version (10.4).
Reference: CompTIA Advanced Security Practitioner (CASP+) Study Guide, Chapter on Vulnerability Management.
CompTIA CASP+ Exam Objectives: "Analyze risks associated with new vulnerabilities." Regular Expressions Documentation from CASP+ Official Reference Materials.
Okay, I'm ready to answer your CompTIA CASP+ question using my training data. Here's the question and answer in the requested format:
정답:
Explanation:
Step-by-Step
Option A: Deny list
Deny lists block specific applications or processes identified as malicious.
This approach is reactive and may inadvertently block the non-standard applications that are currently in use without proper ownership.
Option B: Allow list
Allow lists permit only pre-approved applications to run.
While secure, this approach requires defining all non-standard applications, which may disrupt operations in an environment where ownership is unclear.
Option C: Audit mode
Correct Answer.
Audit mode allows monitoring and logging of applications without enforcing restrictions.
This is ideal in environments with non-standard applications and undefined ownership because it enables the engineer to observe the environment and gradually implement control without interruption.
Audit mode provides critical visibility into the software landscape, ensuring that necessary applications remain functional.
Option D: MAC list
Mandatory Access Control (MAC) lists restrict access based on classification and clearance levels.
This does not align with application control objectives in this context.
CompTIA CASP+ Study Guide - Chapters on Endpoint Security and Application Control.
CASP+ Objective 2.4: Implement appropriate security controls for enterprise endpoints.
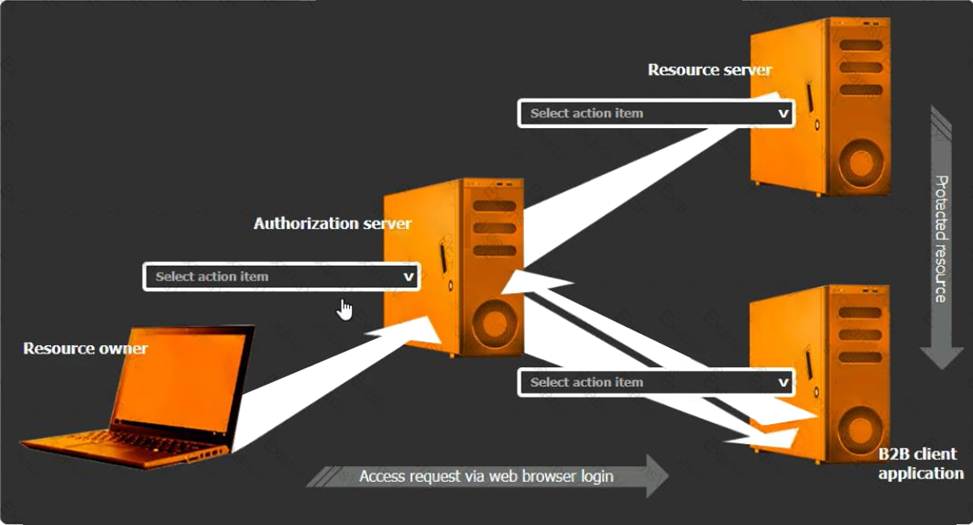
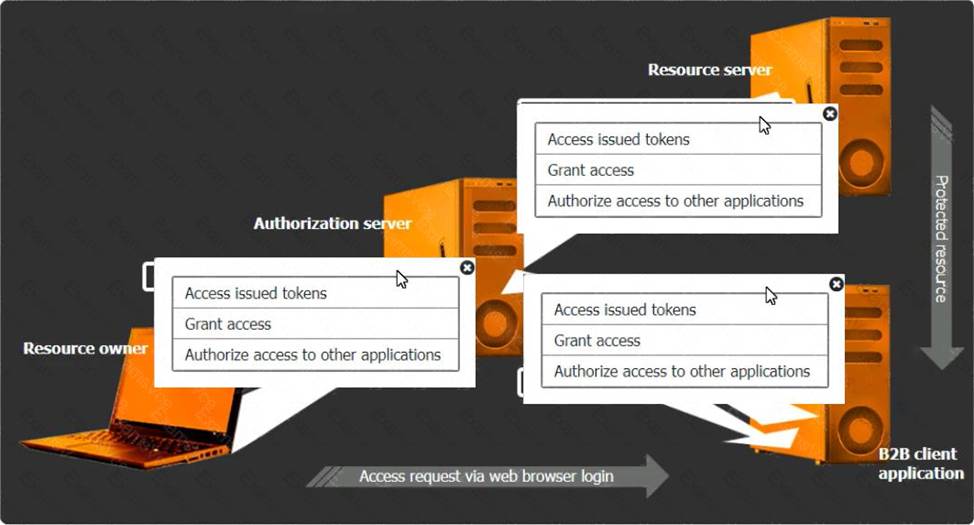
정답: Select the Action Items for the Appropriate Locations:
Authorization Server:
Action Item: Grant access
The authorization server's role is to authenticate the user and then issue an authorization code or token that the client application can use to access resources. Granting access involves the server authenticating the resource owner and providing the necessary tokens for the client application. Resource Server:
Action Item: Access issued tokens
The resource server is responsible for serving the resources requested by the client application. It must verify the issued tokens from the authorization server to ensure the client has the right permissions to access the requested data.
B2B Client Application:
Action Item: Authorize access to other applications
The B2B client application must handle the OAuth flow to authorize access on behalf of the user without requiring direct knowledge of the user's credentials. This includes obtaining authorization tokens from the authorization server and using them to request access to the resource server.
Detailed
OAuth 2.0 is designed to provide specific authorization flows for web applications, desktop applications, mobile phones, and living room devices.
The integration involves multiple steps and components, including:
Resource Owner (User):
The user owns the data and resources that are being accessed.
Client Application (B2B Client Application):
Requests access to the resources controlled by the resource owner but does not directly handle the user's credentials. Instead, it uses tokens obtained through the OAuth flow. Authorization Server:
Handles the authentication of the resource owner and issues the access tokens to the client application upon successful authentication.
Resource Server:
Hosts the resources that the client application wants to access. It verifies the access tokens issued by the authorization server before granting access to the resources. OAuth Workflow:
The resource owner accesses the client application.
The client application redirects the resource owner to the authorization server for authentication. The authorization server authenticates the resource owner and asks for consent to grant access to the client application.
Upon consent, the authorization server issues an authorization code or token to the client application.
The client application uses the authorization code or token to request access to the resources from the resource server.
The resource server verifies the token with the authorization server and, if valid, grants access to the
requested resources.
Reference: CompTIA Security+ Study Guide: Provides comprehensive information on various authentication and authorization protocols, including OAuth.
OAuth 2.0 Authorization Framework (RFC 6749): The official documentation detailing the OAuth 2.0 framework, its flows, and components.
OAuth 2.0 Simplified: A book by Aaron Parecki that provides a detailed yet easy-to-understand explanation of the OAuth 2.0 protocol.
By ensuring that each component in the OAuth workflow performs its designated role, the B2B client
application can securely access the necessary resources without compromising user credentials, adhering to the principle of least privilege.
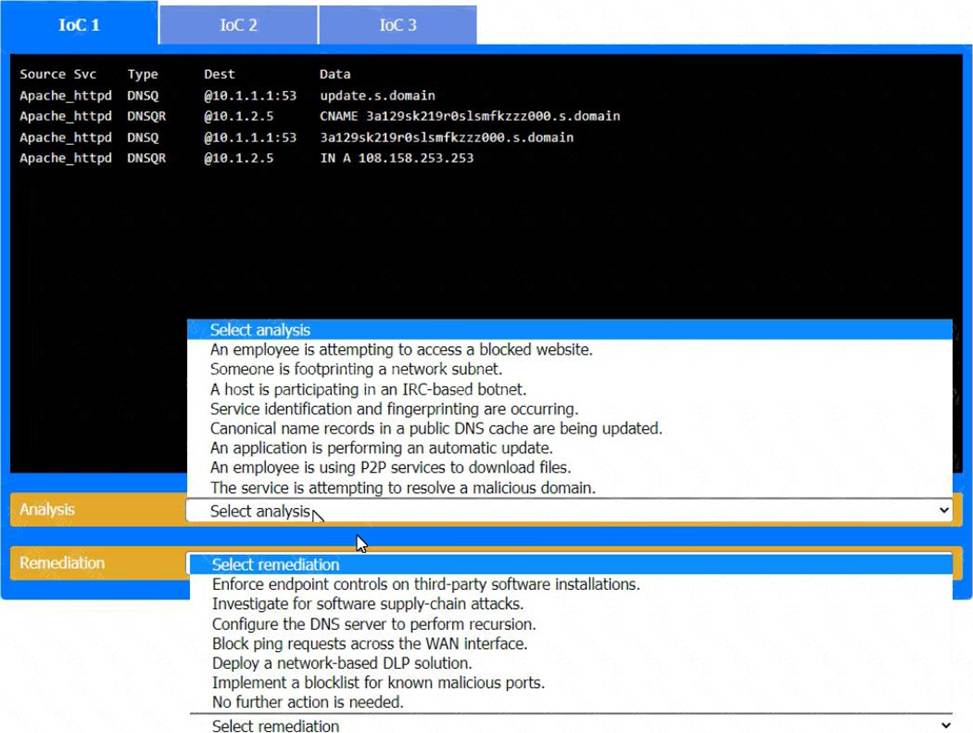
정답: Analysis and Remediation Options for Each IoC:
IoC 1:
Evidence:
Source: Apache_httpd
Type: DNSQ
Dest: @10. 1.1. 1: 53, @10. 1. 2.5
Data: update.s.domain, CNAME 3a129sk219r9slmfkzzz000.s.domain, 108.158.253.253
Analysis:
Analysis: The service is attempting to resolve a malicious domain.
Reason: The DNS queries and the nature of the CNAME resolution indicate that the service is trying to resolve potentially harmful domains, which is a common tactic used by malware to connect to command-and-control servers.
Remediation:
Remediation: Implement a blocklist for known malicious ports.
Reason: Blocking known malicious domains at the DNS level prevents the resolution of harmful domains, thereby protecting the network from potential connections to malicious servers.
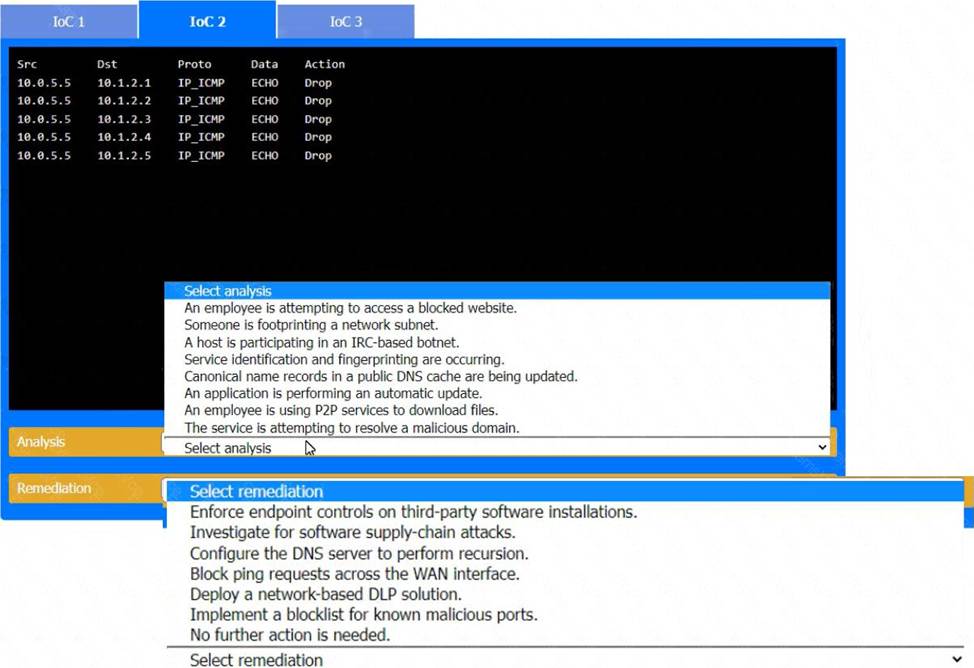
IoC 2:
Evidence:
Src: 10.0.5.5
Dst: 10. 1. 2.1, 10. 1. 2.2, 10. 1. 2.3, 10. 1. 2.4, 10. 1. 2.5
Proto: IP_ICMP
Data: ECHO
Action: Drop
Analysis:
Analysis: Someone is footprinting a network subnet.
Reason: The repeated ICMP ECHO requests to different addresses within a subnet indicate that someone is scanning the network to discover active hosts, a common reconnaissance technique used by attackers.
Remediation:
Remediation: Block ping requests across the WAN interface.
Reason: Blocking ICMP ECHO requests on the WAN interface can prevent attackers from using ping sweeps to gather information about the network topology and active devices.
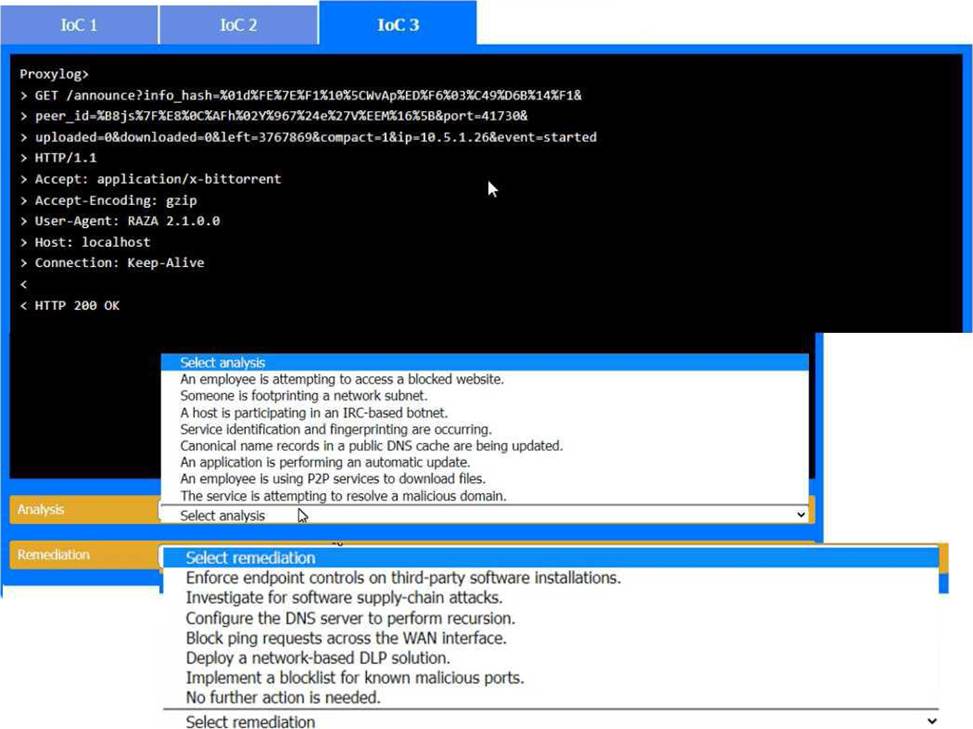
IoC 3:
Evidence:
Proxylog:
GET
/announce?info_hash=%01dff%27f%21%10%c5%wp%4e%1d%6f%63%3c%49%6d&peer_i
Uploaded=0&downloaded=0&left=3767869&compact=1&ip=10.5. 1. 26&event=started
User-Agent: RAZA 2. 1. 0.0
Host: localhost
Connection: Keep-Alive
HTTP 200 OK
Analysis:
Analysis: An employee is using P2P services to download files.
Reason: The HTTP GET request with parameters related to a BitTorrent client indicates that the employee is using peer-to-peer (P2P) services, which can lead to unauthorized data transfer and potential security risks.
Remediation:
Remediation: Enforce endpoint controls on third-party software installations.
Reason: By enforcing strict endpoint controls, you can prevent the installation and use of unauthorized software, such as P2P clients, thereby mitigating the risk of data leaks and other security threats associated with such applications.
References:
CompTIA Security+ Study Guide: This guide offers detailed explanations on identifying and mitigating various types of Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) and the corresponding analysis and remediation strategies.
CompTIA Security+ Exam Objectives: These objectives cover key concepts in network security monitoring and incident response, providing guidelines on how to handle different types of security events.
Security Operations Center (SOC) Best Practices: This resource outlines effective strategies for analyzing and responding to anomalous events within a SOC, including the use of blocklists, endpoint controls, and network configuration changes.
By accurately analyzing the nature of each IoC and applying the appropriate remediation measures, the organization can effectively mitigate potential security threats and maintain a robust security posture.
정답: Matching Relevant Findings to the Affected Hosts:
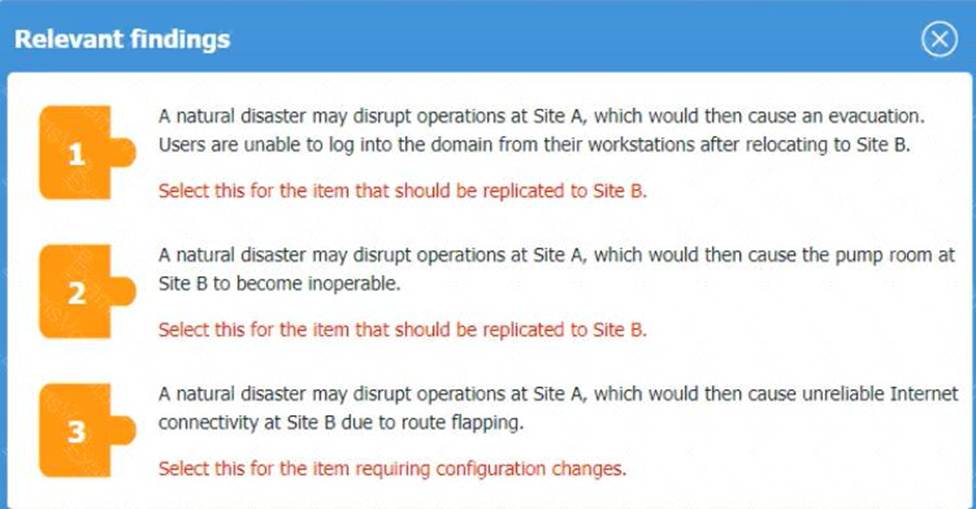
Finding 1:
Affected Host: DNS
Reason: Users are unable to log into the domain from their workstations after relocating to Site B, which implies a failure in domain name services that are critical for user authentication and domain login.
Finding 2:
Affected Host: Pumps
Reason: The pump room at Site B becoming inoperable directly points to the critical infrastructure components associated with pumping operations.
Finding 3:
Affected Host: VPN Concentrator
Reason: Unreliable internet connectivity at Site B due to route flapping indicates issues with network routing, which is often managed by VPN concentrators that handle site-to-site connectivity.
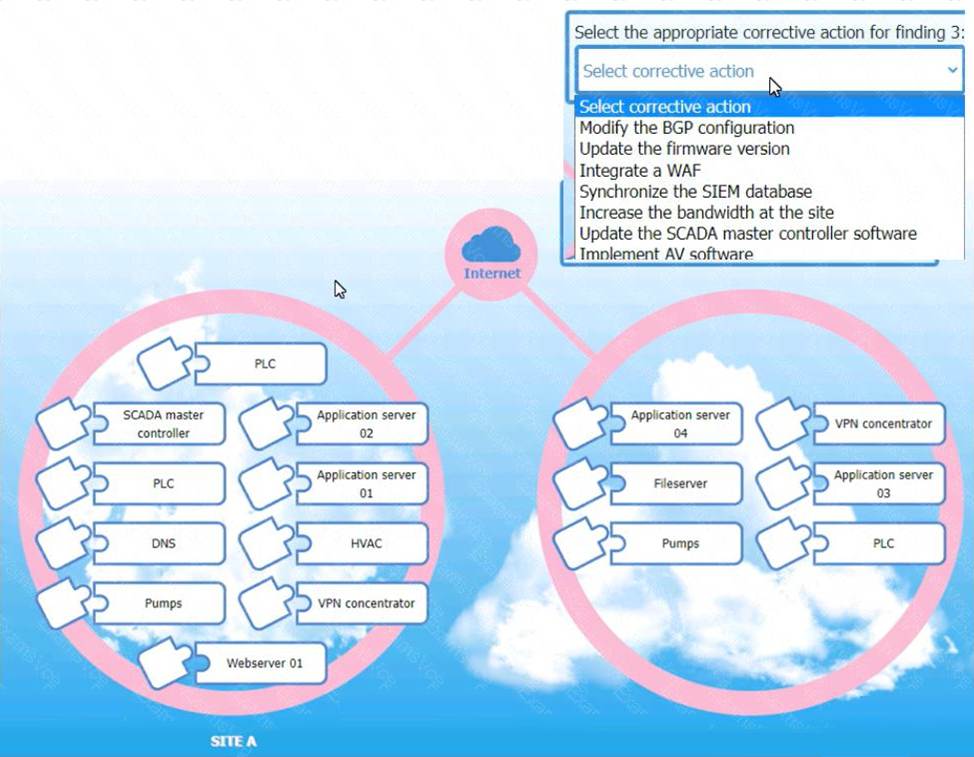
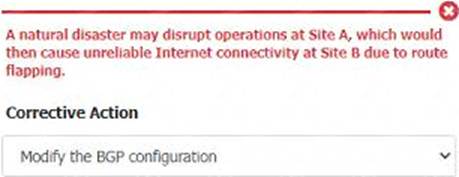
Corrective Actions for Finding 3:
Finding 3 Corrective Action:
Action: Modify the BGP configuration
Reason: Route flapping is often related to issues with Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) configurations.
Adjusting BGP settings can stabilize routes and improve internet connectivity reliability.
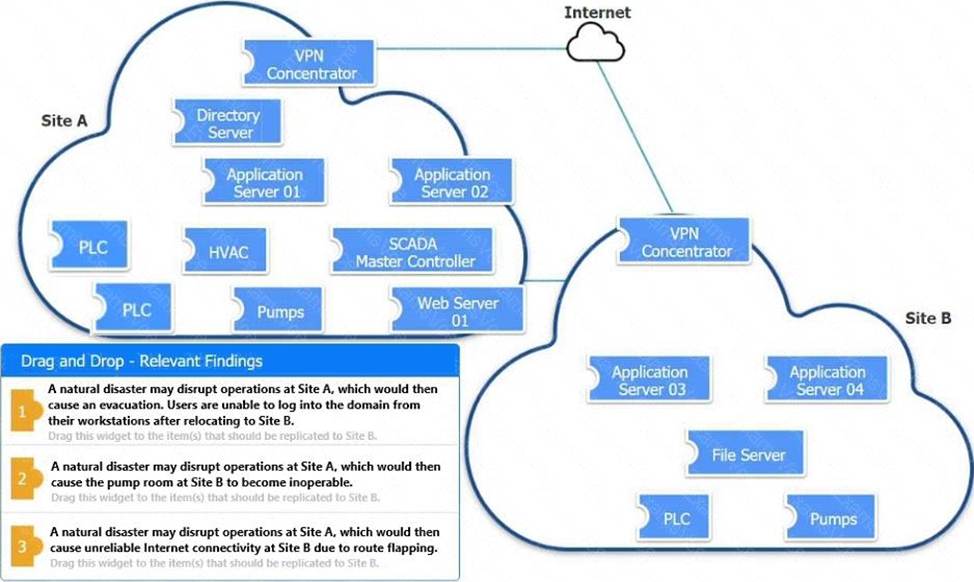
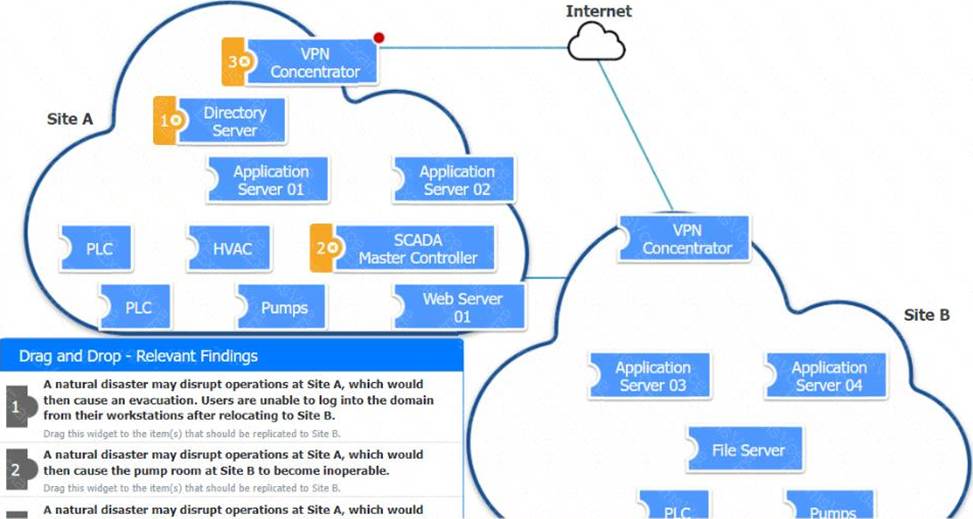
Replication to Site B for Finding 1:
Affected Host: DNS
Domain Name System (DNS) services are essential for translating domain names into IP addresses, allowing users to log into the network. Replicating DNS services ensures that even if Site A is disrupted, users at Site B can still authenticate and access necessary resources. Replication to Site B for Finding 2:
Affected Host: Pumps
The operation of the pump room is crucial for maintaining various functions within the infrastructure. Replicating the control systems and configurations for the pumps at Site B ensures that operations can continue smoothly even if Site A is affected. Configuration Changes for Finding 3:
Affected Host: VPN Concentrator
Route flapping is a situation where routes become unstable, causing frequent changes in the best path for data to travel. This instability can be mitigated by modifying BGP configurations to ensure more stable routing. VPN concentrators, which manage connections between sites, are typically configured with BGP for optimal routing.
Reference: CompTIA Security+ Study Guide: This guide provides detailed information on disaster recovery and continuity of operations, emphasizing the importance of replicating critical services and making necessary configuration changes to ensure seamless operation during disruptions.
CompTIA Security+ Exam Objectives: These objectives highlight key areas in disaster recovery
planning, including the replication of critical services and network configuration adjustments. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity Planning (DRBCP): This resource outlines best practices for ensuring that operations can continue at an alternate site during a disaster, including the replication of essential services and network stability measures.
By ensuring that critical services like DNS and control systems for pumps are replicated at the alternate site, and by addressing network routing issues through proper BGP configuration, the organization can maintain operational continuity and minimize the impact of natural disasters on their operations.
정답: 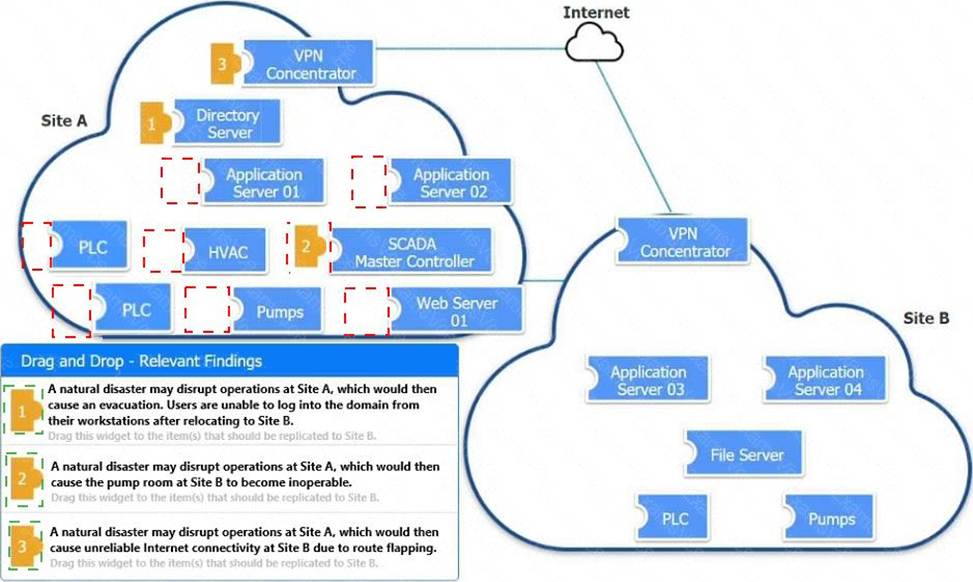
Explanation:
A computer screen shot of a diagram Description automatically generated
A screenshot of a computer
error Description automatically generated
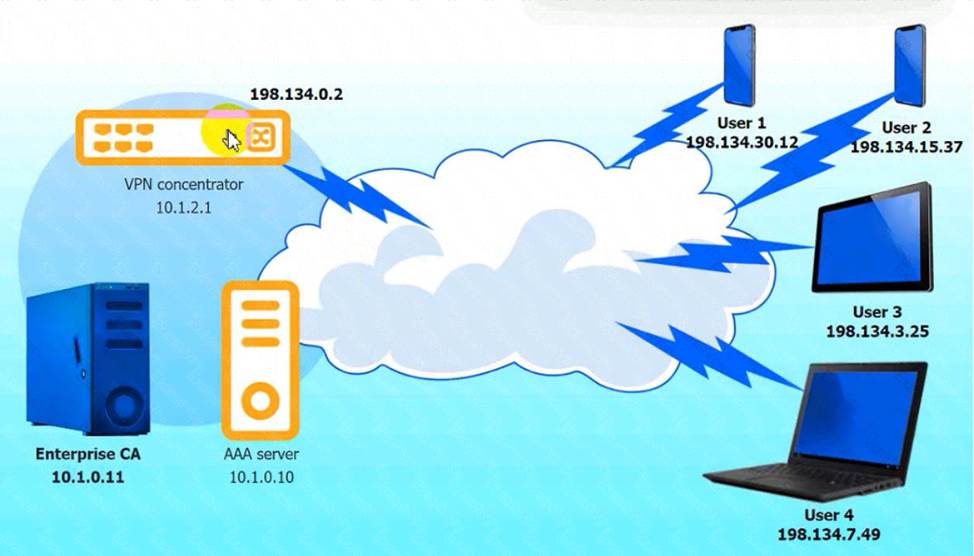
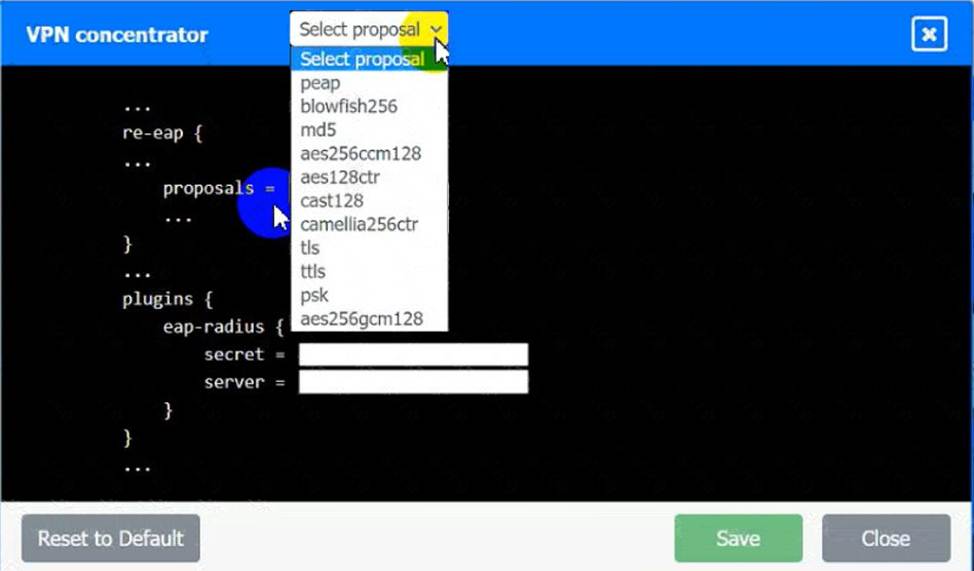
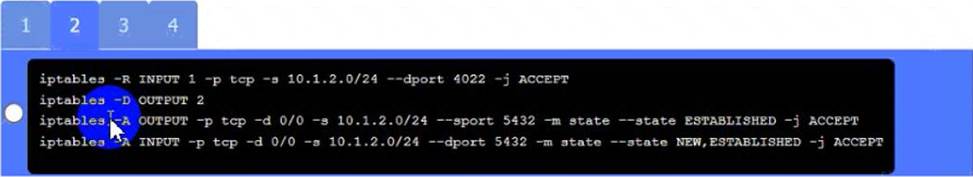
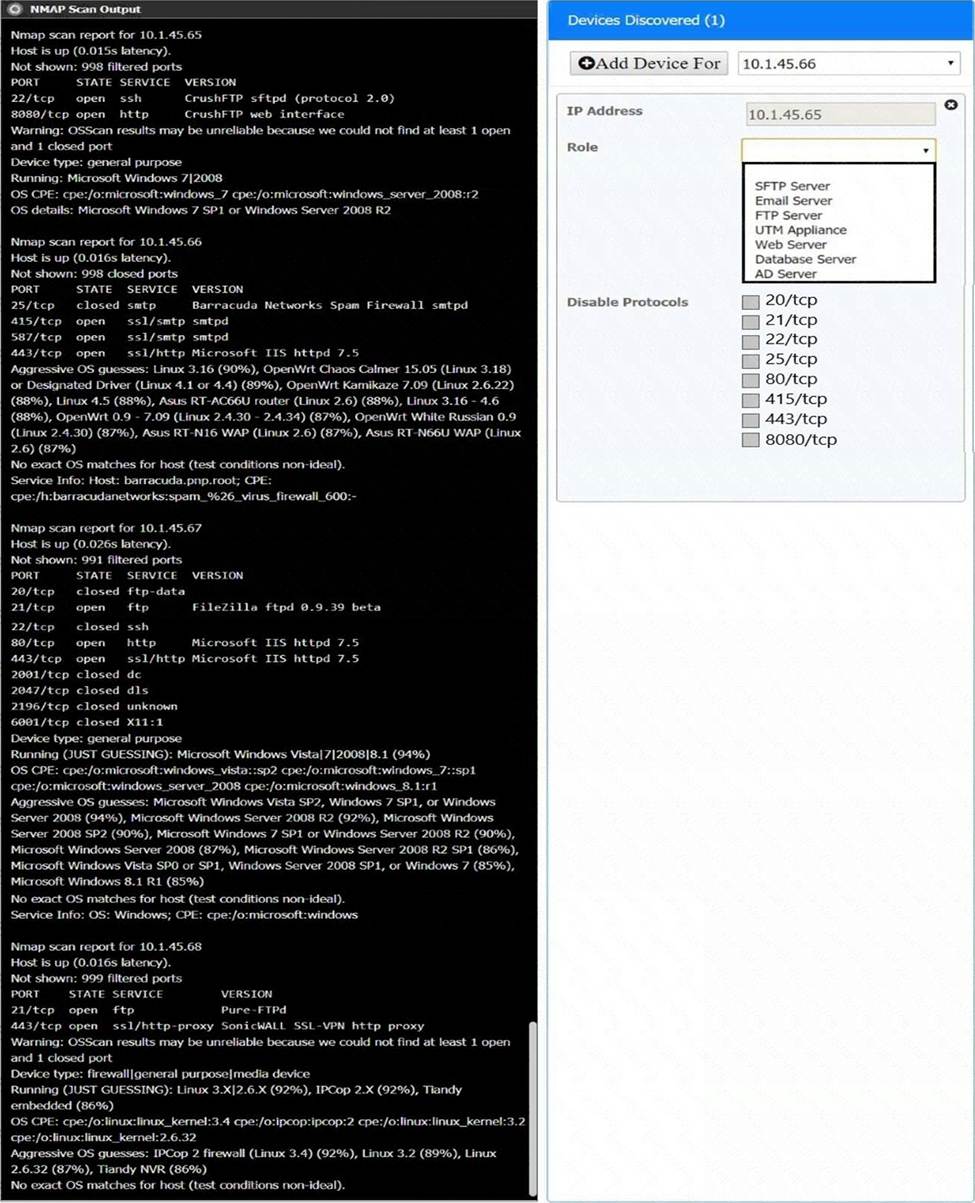
정답: VPN Concentrator:
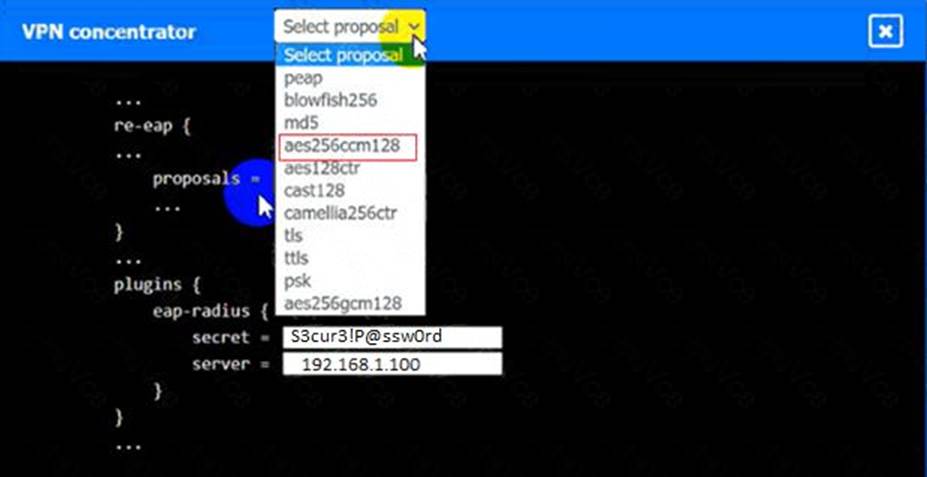
A screenshot of a computer Description automatically generated
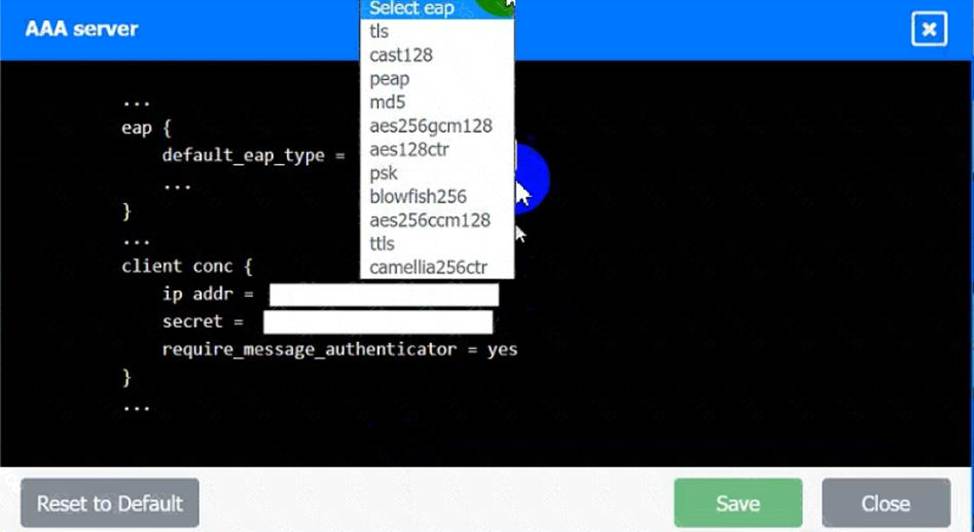
AAA Server:
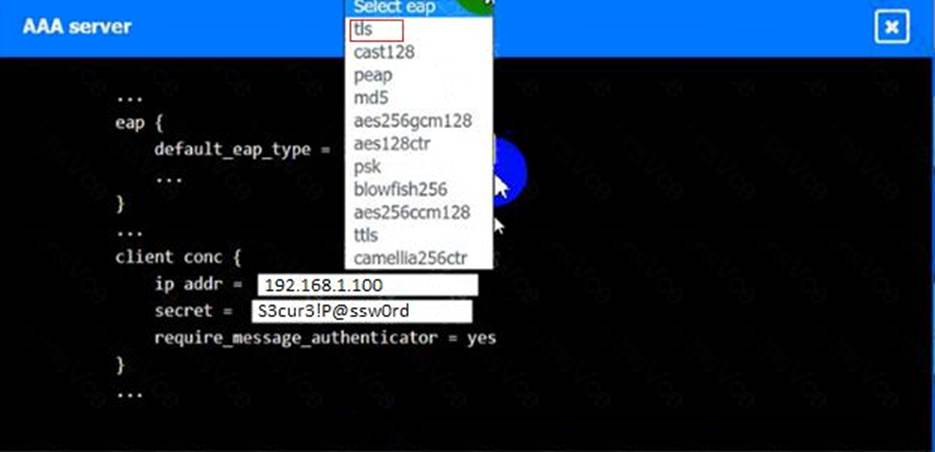
A screenshot of a computer Description automatically generated
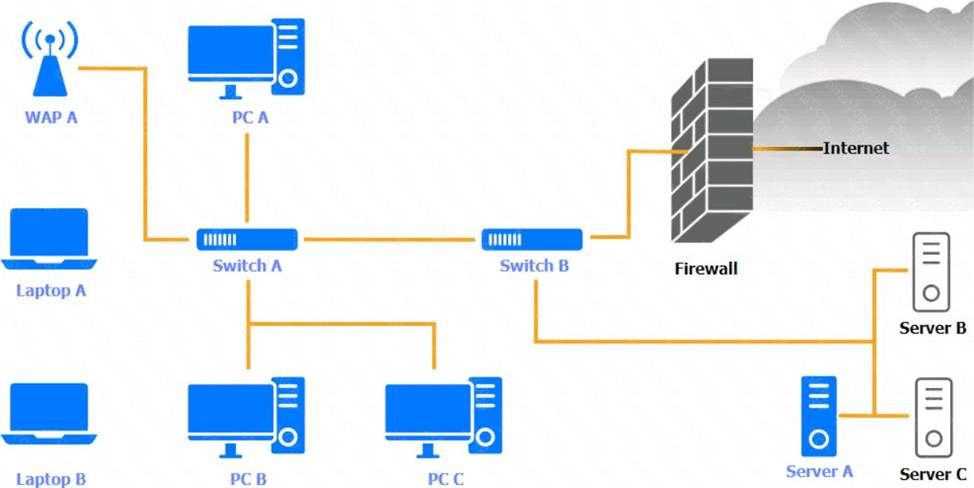
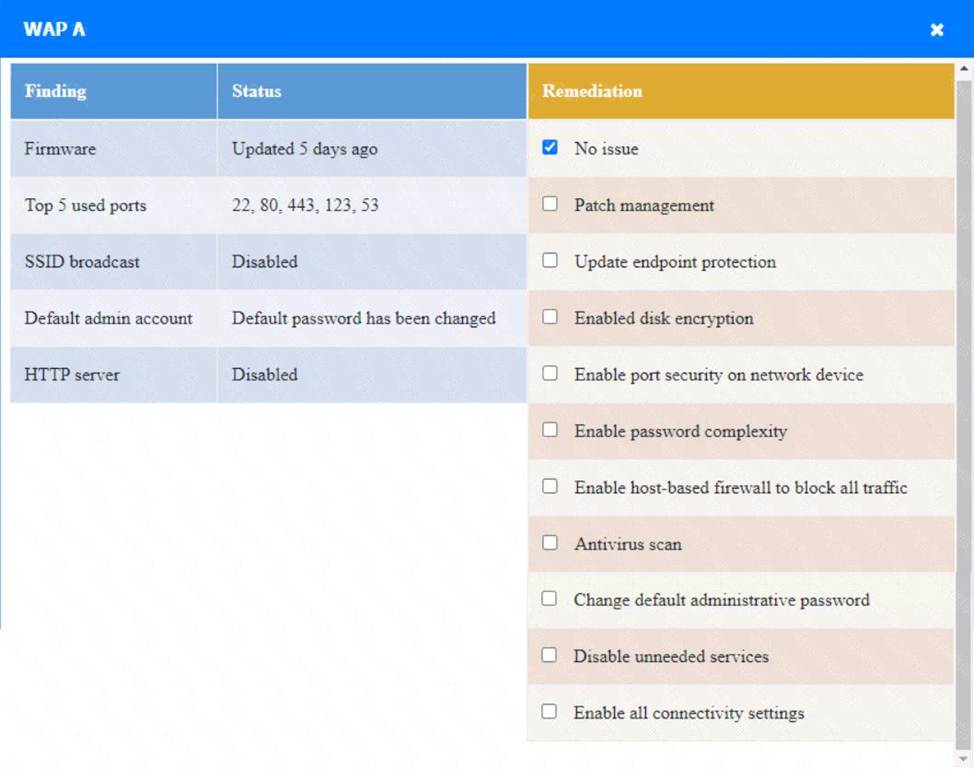
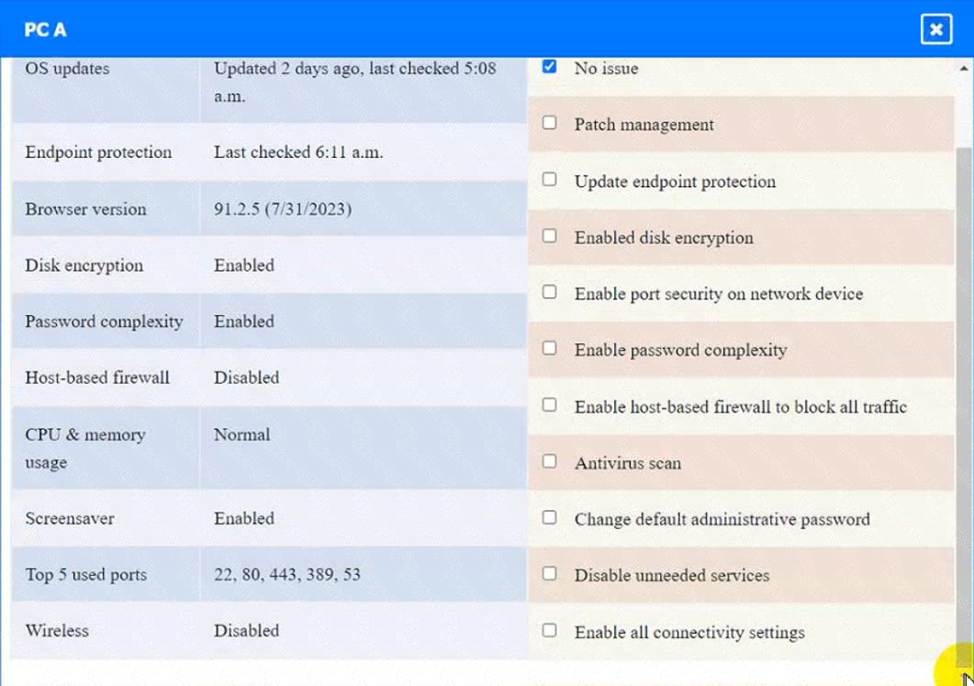
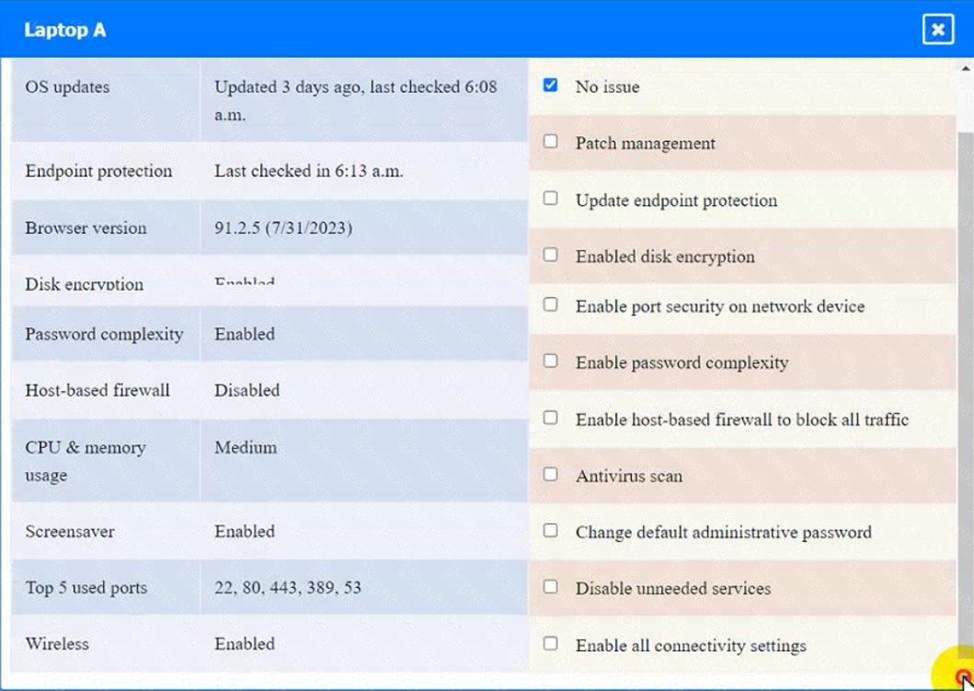
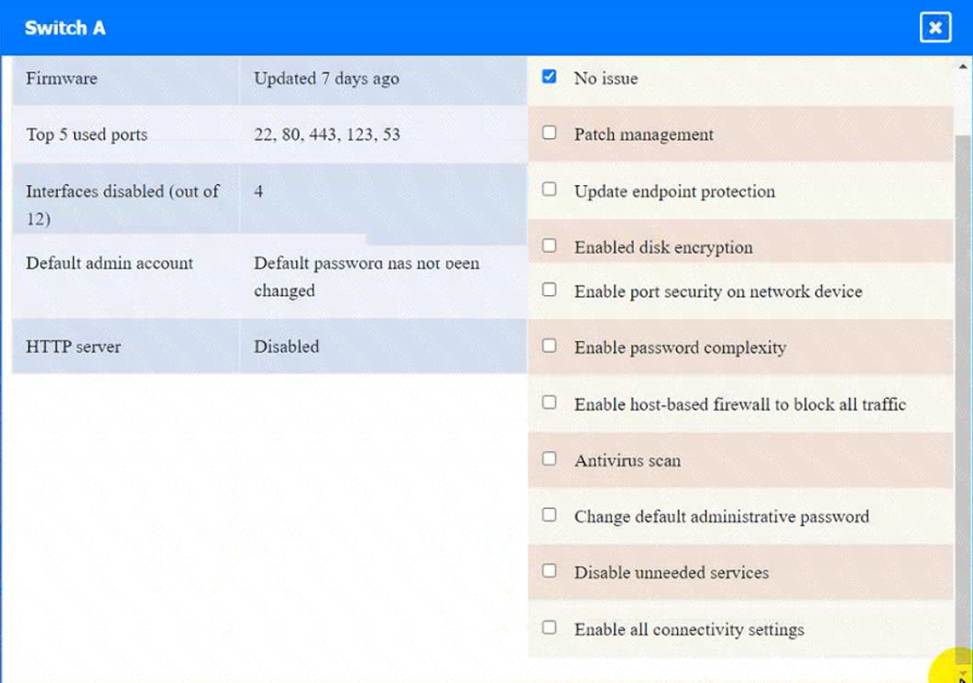
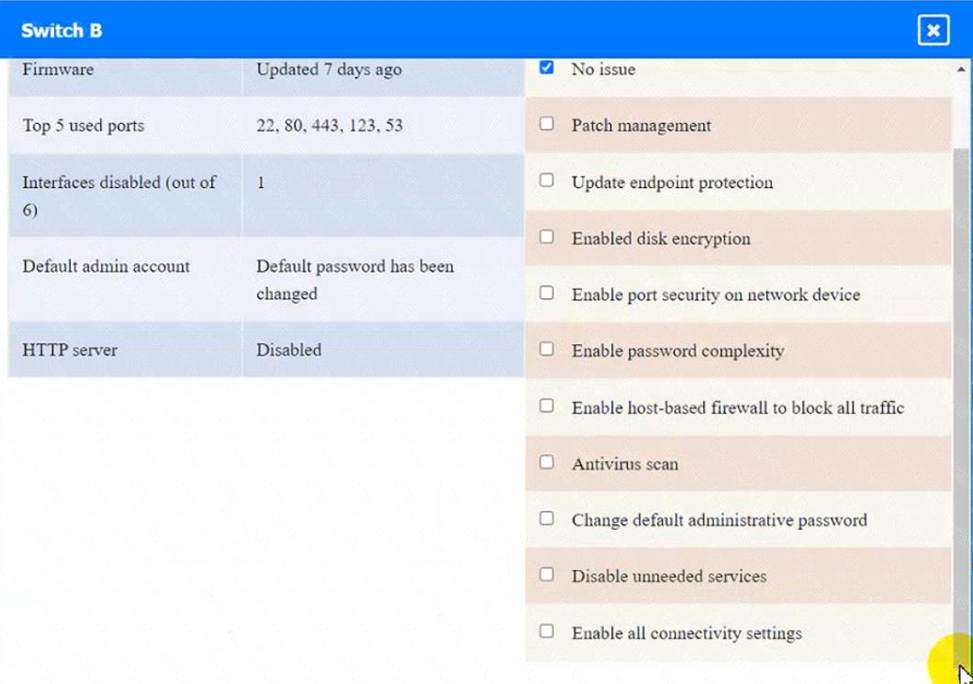
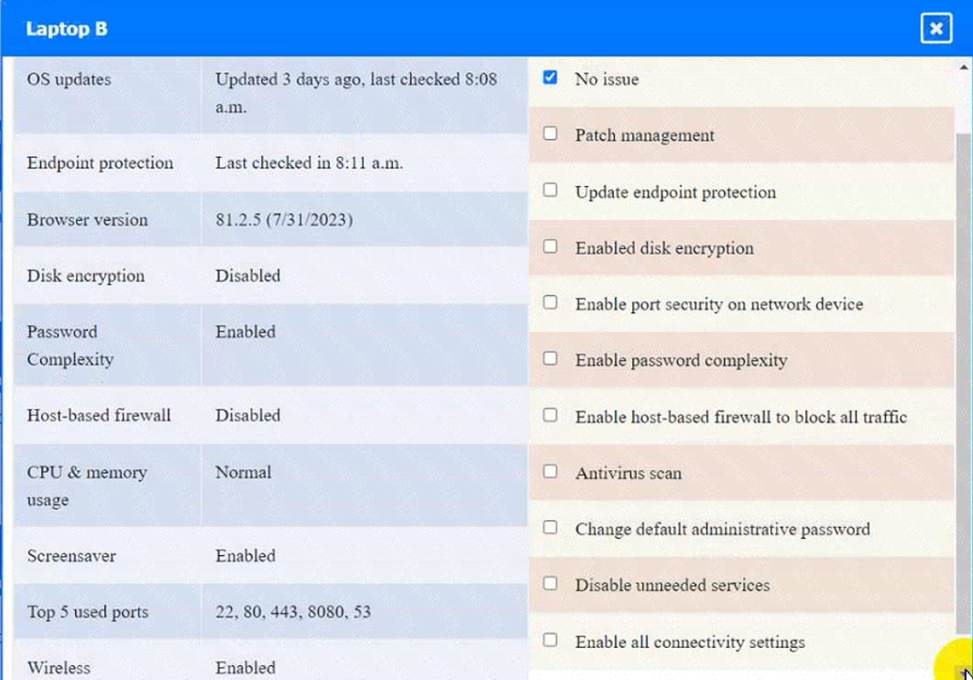
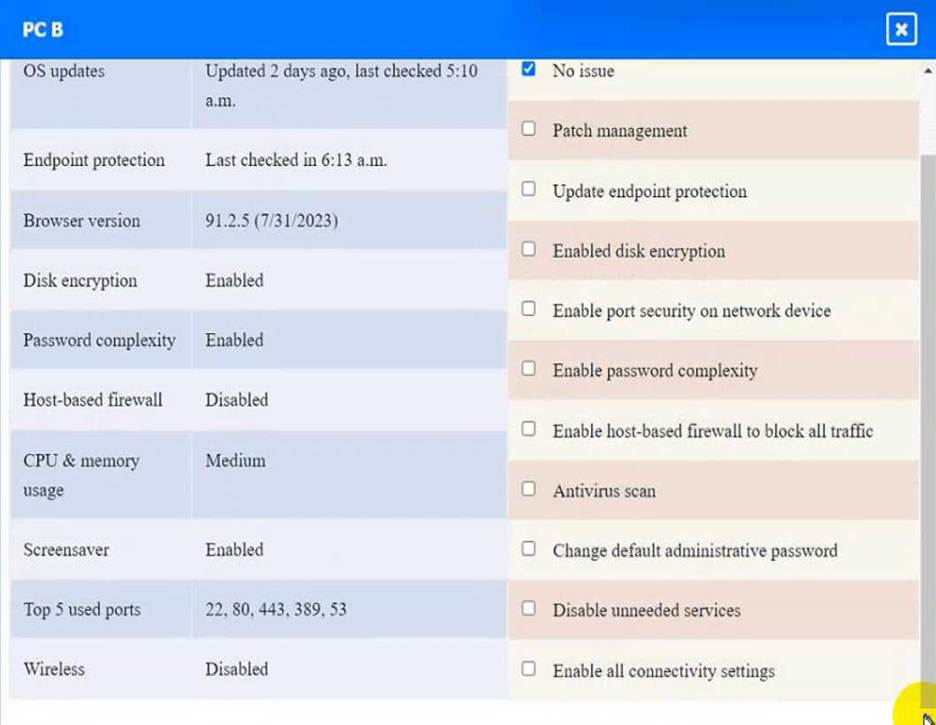
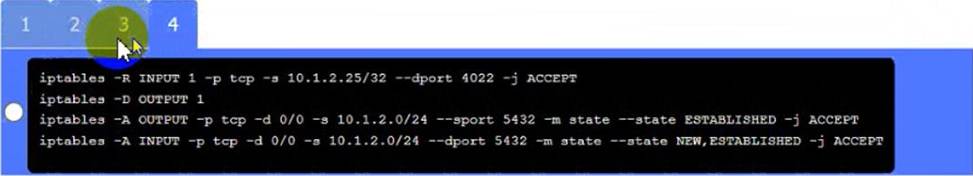
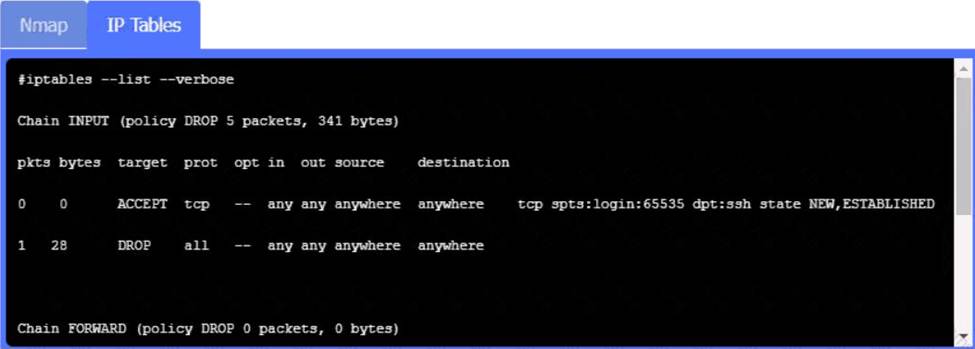
정답: WAP A: No issue found. The WAP A is configured correctly and meets the requirements.
PC A = Enable host-based firewall to block all traffic
This option will turn off the host-based firewall and allow all traffic to pass through. This will comply with the requirement and also improve the connectivity of PC A to other devices on the network. However, this option will also reduce the security of PC A and make it more vulnerable to attacks. Therefore, it is recommended to use other security measures, such as antivirus, encryption, and password complexity, to protect PC A from potential threats.
Laptop A: Patch management
This option will install the updates that are available for Laptop A and ensure that it has the most recent security patches and bug fixes. This will comply with the requirement and also improve the performance and stability of Laptop
A. However, this option may also require a reboot of Laptop A and some downtime during the update process. Therefore, it is recommended to backup any important data and close any open applications before applying the updates.
Switch A: No issue found. The Switch A is configured correctly and meets the requirements.
Switch B: No issue found. The Switch B is configured correctly and meets the requirements.
Laptop B: Disable unneeded services
This option will stop and disable the telnet service that is using port 23 on Laptop
B. Telnet is a cleartext service that transmits data in plain text over the network, which exposes it to eavesdropping, interception, and modification by attackers. By disabling the telnet service, you will comply with the requirement and also improve the security of Laptop
B. However, this option may also affect the functionality of Laptop B if it needs to use telnet for remote administration or other purposes. Therefore, it is recommended to use a secure alternative to telnet, such as SSH or HTTPS, that encrypts the data in transit.
PC B: Enable disk encryption
This option will encrypt the HDD of PC B using a tool such as BitLocker or VeraCrypt. Disk encryption is a technique that protects data at rest by converting it into an unreadable format that can only be decrypted with a valid key or password. By enabling disk encryption, you will comply with the requirement and also improve the confidentiality and integrity of PC B’s data. However, this option may also affect the performance and usability of PC B, as it requires additional processing time and user authentication to access the encrypted data. Therefore, it is recommended to backup any important data and choose a strong key or password before encrypting the disk.
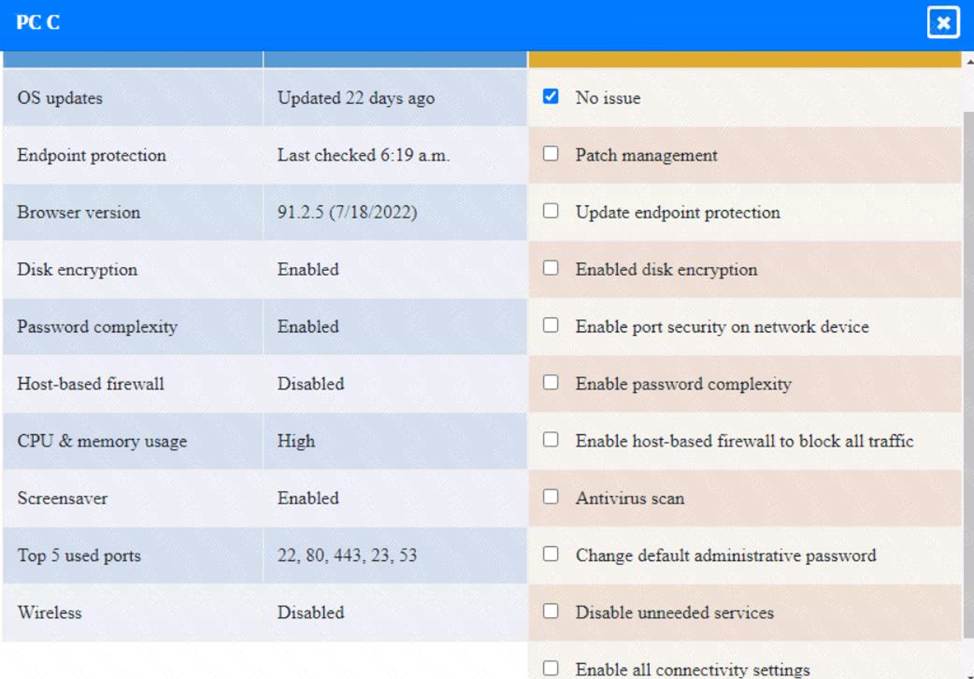
PC C: Disable unneeded services
This option will stop and disable the SSH daemon that is using port 22 on PC
C. SSH is a secure service that allows remote access and command execution over an encrypted channel. However, port 22 is the default and well-known port for SSH, which makes it a common target for brute-force attacks and port scanning. By disabling the SSH daemon on port 22, you will comply with the requirement and also improve the security of PC
C. However, this option may also affect the functionality of PC C if it needs to use SSH for remote administration or other purposes. Therefore, it is recommended to enable the SSH daemon on a different port, such as 4022, by editing the configuration file using the following command:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
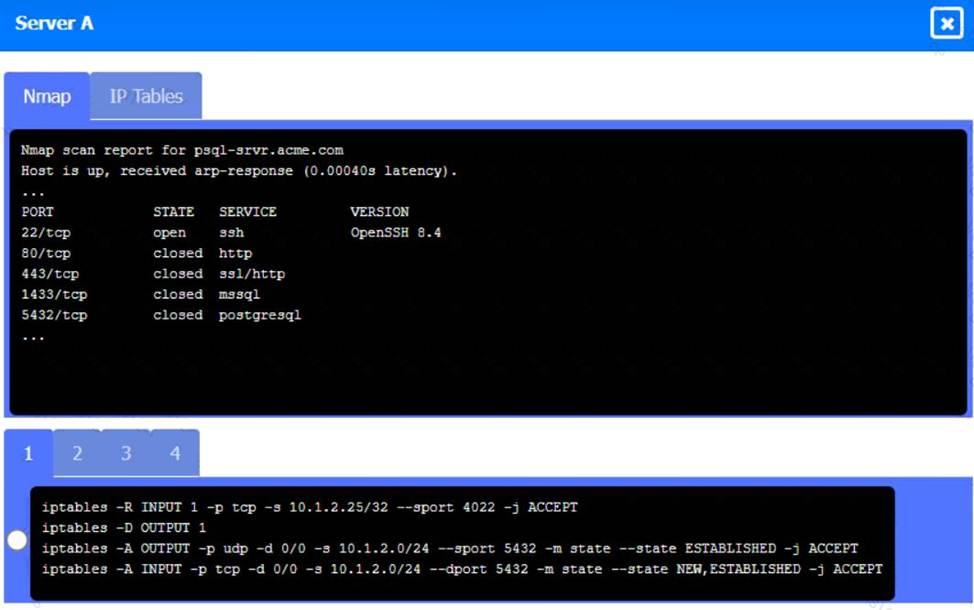
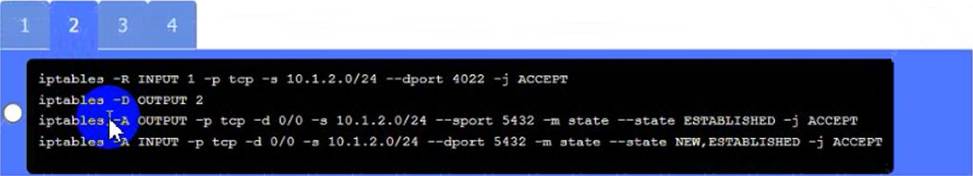
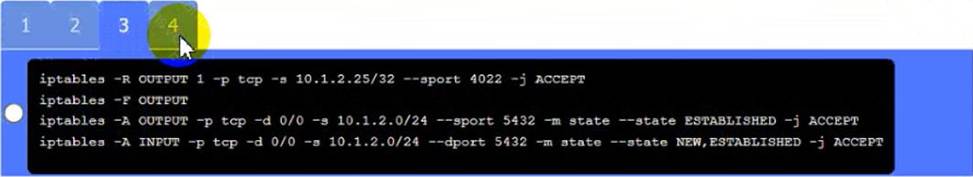
Server
A. Need to select the following:
A black and white screen with white text Description automatically generated
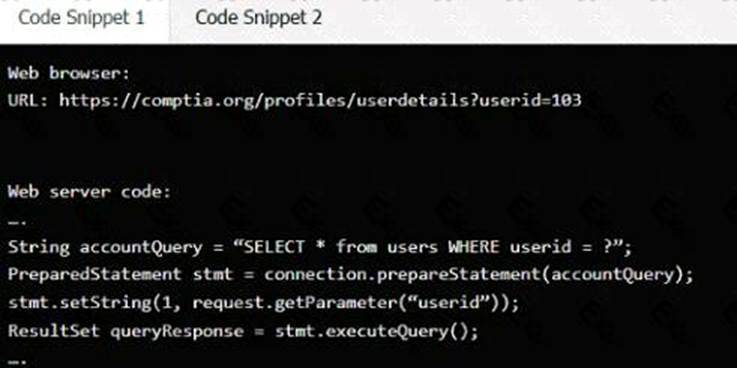
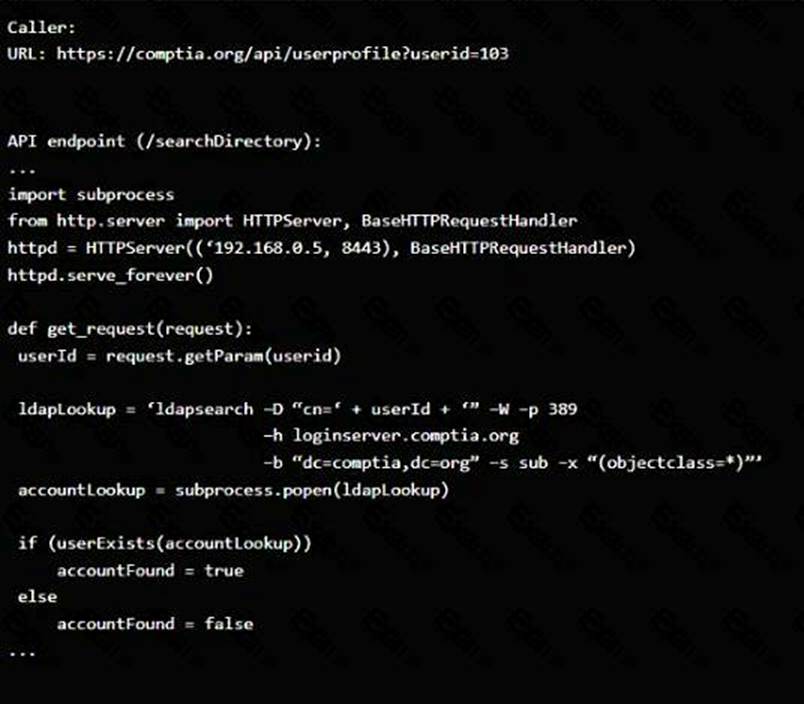
정답: Code Snippet 1
Vulnerability 1: SQL injection
SQL injection is a type of attack that exploits a vulnerability in the code that interacts with a database. An attacker can inject malicious SQL commands into the input fields, such as username or password, and execute them on the database server. This can result in data theft, data corruption, or unauthorized access.
Fix 1: Perform input sanitization of the use rid field.
Input sanitization is a technique that prevents SQL injection by validating and filtering the user input values before passing them to the database. The input sanitization should remove any special characters, such as quotes, semicolons, or dashes, that can alter the intended SQL query. Alternatively, the input sanitization can use a whitelist of allowed values and reject any other values.
Code Snippet 2
Vulnerability 2: Cross-site request forgery
Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) is a type of attack that exploits a vulnerability in the code that handles web requests. An attacker can trick a user into sending a malicious web request to a server that performs an action on behalf of the user, such as changing their password, transferring funds, or deleting data. This can result in unauthorized actions, data loss, or account compromise.
Fix 2: Implement anti-forgery tokens.
Anti-forgery tokens are techniques that prevent CSRF by adding a unique and secret value to each web request that is generated by the server and verified by the server before performing the action.
The anti-forgery token should be different for each user and each session, and should not be predictable or reusable by an attacker. This way, only legitimate web requests from the user’s browser can be accepted by the server.
정답:
정답:
Explanation:
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) is the best solution to help the company overcome challenges associated with suspicious activity that cannot be categorized by traditional detection tools. UEBA uses advanced analytics to establish baselines of normal behavior for users and entities within the network. It then identifies deviations from these baselines, which may indicate malicious activity. This approach is particularly effective for detecting unknown threats and sophisticated attacks that do not match known indicators of compromise (IoCs).
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX Study Guide, Chapter on Advanced Threat Detection and Mitigation, Section on User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA).
정답:
Explanation:
Microsegmentation is a critical strategy within Zero Trust architecture that enhances context-aware access systems by dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments. This reduces the attack surface and limits lateral movement of attackers within the network. It ensures that even if one segment is compromised, the attacker cannot easily access other segments. This granular approach to network security is essential for enforcing strict access controls and monitoring within Zero Trust environments.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX Study Guide, Chapter on Zero Trust Security, Section on Microsegmentation and Network Segmentation.
정답:
Explanation:
The code function provided in the question seems tobe designed to parse JSON formatted logs to check for an alarm state.
Option A is a JSON format that matches the structure likely expected by the code. The presence of the "error_log" and "InAlarmState" keys suggests that this is the correct input format.
Reference: CompTIA SecurityX Study Guide, Chapter on Log Management and Automation, Section on Parsing Structured Logs.
정답:
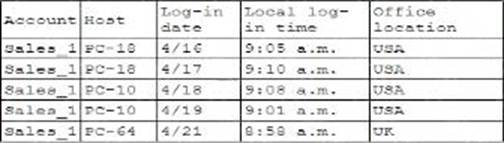
Explanation:
In the given scenario, the security engineer is likely examining login activities and their associated geolocations. This type of analysis is aimed at identifying unusual login patterns that might indicate an impossible travel scenario. An impossible travel scenario is when a single user account logs in from geographically distant locations in a short time, which is physically impossible. By assessing login activities using geolocation, the engineer can tune alerts to identify and respond to potential security breaches more effectively.