Associate Professional in Human Resources - International 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년07월22일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 HRCI aPHRi 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 aPHRi 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 182개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
Air ventilation is an environmental factor crucial for a healthy workspace. Proper ventilation ensures air quality, reduces the risk of respiratory issues, and enhances overall employee well-being.
Why Air Ventilation (D) is Correct:
Air ventilation is an environmental factor critical to maintaining a healthy workspace. Proper ventilation ensures adequate air circulation, reduces the concentration of airborne contaminants, and helps prevent respiratory issues and the spread of illnesses. Good air quality directly impacts employee health, productivity, and overall well-being.
Reference: The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) highlights air ventilation as a key factor in workplace health standards (OSHA Standard 1910.94).
Why Not Weather Conditions (A):
Weather conditions are external factors and are not typically controlled by the organization. While they can indirectly affect the workspace (e.g., storms or extreme temperatures), they are not considered part of the internal environmental factors affecting workspace health.
Reference: SHRM's "Workplace Environmental Standards" (2022) distinguishes external weather conditions from controllable internal environmental factors.
Why Not Personal Hygiene (B):
Personal hygiene is an individual responsibility, not an environmental factor. While organizations can encourage hygiene through policies and resources, it does not constitute an environmental factor impacting workspace health.
Reference: World Health Organization (WHO), "Hygiene Practices in the Workplace" (2021).
Why Not Employee Morale (C):
Employee morale is a psychological and cultural factor rather than a physical or environmental factor. Although morale can influence productivity and engagement, it does not directly impact the physical health of the workspace.
Reference: Harvard Business Review, "Distinguishing Organizational Culture from Environmental Health" (2021).
Final Justification:
Air ventilation is a critical environmental factor for maintaining a healthy workspace by ensuring air quality and reducing health risks, making it the most appropriate answer.
Reference: Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), Standard 1910.94 (2022).
Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM), "Workplace Environmental Standards" (2022).
World Health Organization (WHO), "Hygiene Practices in the Workplace" (2021).
Harvard Business Review, "Distinguishing Organizational Culture from Environmental Health" (2021).
International Labour Organization (ILO), "Workplace Health and Safety Guidelines" (2023).
정답:
Explanation:
Attrition refers to the gradual reduction of a workforce due to employees leaving the organization without being replaced. This contrasts with turnover, which includes both departures and replacements. Attrition typically results from resignations, retirements, or other natural separations.
Explanation of Other Options:
A. Employees who have resigned: Resignations are a part of attrition but do not define it entirely.
B. Employees compensated to leave the organization: This describes severance agreements, not attrition.
C. Fired employees in a given time period: Involuntary terminations are not specific to attrition.
정답:
Explanation:
Definition of HRIS:
A Human Resource Information System (HRIS) is a software solution designed to manage and automate HR tasks such as record-keeping, payroll, benefits, and leave tracking.
Why These Options are Correct:
B. Employee data storage: HRIS stores and organizes employee information, ensuring secure and accessible data management.
D. Leave of absence tracking: HRIS simplifies leave management by tracking employee leave requests, balances, and approvals.
Eliminating Incorrect Options:
A. HR budget monitoring: Typically handled by financial systems, not HRIS.
C. Corporate social responsibility: Related to broader organizational initiatives, not HRIS functions.
E. Vision and mission communication: Not a function of HRIS but a part of leadership communication strategies.
International HR
Reference: ISO 30414: Encourages the use of HRIS for efficient data storage and tracking.
SHRM HR Technology Guidelines: Emphasizes HRIS benefits such as data storage and leave management.
정답:
Explanation:
Definition of a Matrix Reporting Structure:
A matrix structure combines functional and project-based reporting. Employees report to both a functional manager and a project leader.
Why Employees Assigned to a Project Leader is Correct:
In matrix structures, employees from different departments collaborate on projects under the leadership of a project manager, while maintaining their regular departmental roles.
Eliminating Incorrect Options:
A. Groups are networked based on job function: Describes a functional structure, not matrix.
B. Teams are accountable to manage themselves: Refers to self-managed teams, not matrix structures.
C. Managers oversee a small group for a short time: This relates to temporary supervisory arrangements, not matrix structures.
International HR
Reference: SHRM Organization Design Resources: Discusses matrix structures as multi-reporting systems.
정답:
Explanation:
Definition of Downward Communication:
Downward communication refers to information flow from higher levels of management to lower levels in an organization, such as instructions, policies, or announcements.
Why Bulletin Announcement is Correct:
A bulletin announcement is a direct example of downward communication, where information is passed from management to employees.
Eliminating Incorrect Options:
A. Satisfaction survey: Reflects upward communication (feedback from employees).
B. Grievance procedure: Typically an upward or lateral communication process.
C. Suggestion box: Represents upward communication (employee suggestions).
International HR
Reference: SHRM Organizational Communication Resources: Highlights downward communication tools such as announcements.
정답:
Explanation:
Definition of Planned Absence:
Planned absences are pre-approved leaves of absence that are scheduled in advance and often legally protected or policy-based.
Why Maternity or Paternity Leave is Correct:
Maternity or paternity leave is a planned, legally protected leave granted to employees for childbirth or adoption. These leaves are communicated and approved ahead of time.
Eliminating Incorrect Options:
A. Compassionate time-off: Usually unplanned and occurs during emergencies.
C. Discipline resulting in suspension: Is not considered an absence but rather a disciplinary measure.
D. Time-off to recover from an accident: Generally unplanned and depends on medical emergencies.
International HR
Reference: FMLA (U.S.): Covers planned absences like maternity/paternity leave.
ILO Maternity Protection Convention: Promotes maternity leave as a planned absence.
정답:
Explanation:
they provide access to networks of industry professionals who may not be actively job-hunting but are engaged in their fields.
This repeats Question No. 63, and the same reasoning applies.
Reference: SHRM - Performance Appraisal Biases
WorldatWork - Short-term vs. Long-term Incentive Plans Harvard Business Review - Sourcing Passive Talent Strategies
정답:
Explanation:
Professional associations are one of the most common ways to source passive job candidates, as they often house directories, forums, and networking opportunities for experienced professionals who are not actively seeking jobs but are open to discussions.
Why Professional Associations (A) is Correct:
Professional associations are one of the most effective ways to source passive candidates, as they are typically composed of individuals who are already employed and engaged in their respective industries or professions. These associations provide networking opportunities, industry events, and specialized job boards where recruiters can identify and connect with high-caliber talent who may not be actively looking for new roles.
Reference: According to SHRM's "Guide to Passive Candidate Recruitment" (2022), professional associations are cited as a leading source for engaging passive talent.
Why Not Job Fair (B):
Job fairs primarily target active job seekers, such as recent graduates or individuals actively looking for new opportunities. Passive candidates typically do not attend job fairs.
Reference: CIPD, "Recruitment Strategies for Active vs Passive Talent" (2023).
Why Not Internal Posting (C):
Internal postings are aimed at existing employees within the organization, not passive candidates who are external to the company. While useful for internal mobility, they do not address external talent sourcing.
Reference: Harvard Business Review, "Internal vs External Recruitment" (2021).
Why Not Radio Advertisement (D):
Radio advertisements are generally broad and target a mass audience, making them less effective for reaching the skilled and selective passive job candidate pool.
Reference: SHRM, "Effectiveness of Recruitment Media Channels" (2022).
Final Justification:
Professional associations are a targeted and industry-specific method for sourcing passive candidates, making them the most effective option in this scenario.
Reference: Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM), "Guide to Passive Candidate Recruitment" (2022).
Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD), "Recruitment Strategies for Active vs Passive Talent" (2023).
Harvard Business Review, "Internal vs External Recruitment" (2021).
SHRM, "Effectiveness of Recruitment Media Channels" (2022).
WorldatWork, "Best Practices in Talent Sourcing" (2021).
정답: 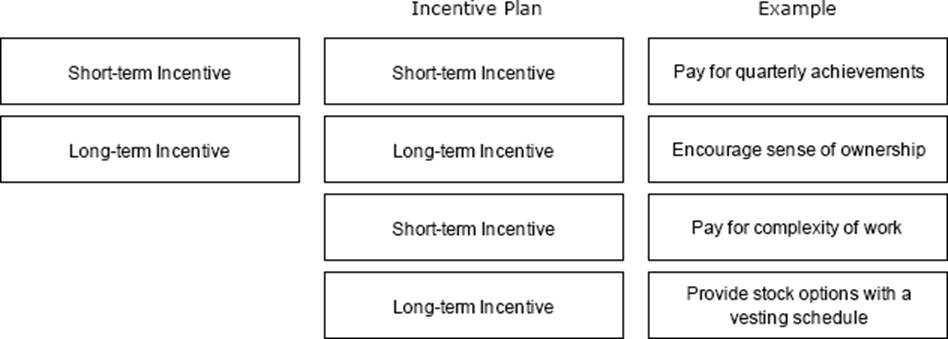
Explanation:
Short-term Incentive → Pay for quarterly achievements
These rewards are tied to short-term goals and frequent performance evaluations.
Long-term Incentive → Encourage sense of ownership
Long-term incentives like profit-sharing or equity grants create a connection to the organization's success over time.
Short-term Incentive → Pay for complexity of work These are immediate rewards based on task difficulty.
Long-term Incentive → Provide stock options with a vesting schedule
Vesting schedules reward employees for staying with the company long-term while aligning with corporate success.
Reference: Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM), "Incentive Compensation: Short-term vs Long-term" (2022).
WorldatWork, "Equity Compensation and Long-term Incentives" (2021).
Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development (CIPD), "Performance-based Compensation" (2023).
SHRM, "Guide to Stock Option Plans" (2022).
International Labour Organization (ILO), "Compensation Structures and Strategies" (2022).
정답:
Explanation:
The halo effect occurs when a manager gives an employee an overall performance rating based on one positive trait (e.g., interpersonal skills) while ignoring other areas (e.g., technical skills). This cognitive bias skews the evaluation toward one aspect of the employee's performance.
Explanation of Other Options:
B. A contrast error: Happens when an employee is compared to others rather than an objective standard.
C. A strictness error: Refers to consistently rating employees lower than deserved.
정답:
Explanation:
Job Satisfaction and Task Variety:
Task variety involves diverse and engaging responsibilities, reducing monotony and increasing job fulfillment.
Why Task Variety is Correct:
Employees are more satisfied when their roles challenge them and provide opportunities for skill application and development.
Eliminating Incorrect Options:
B. Management duties: Only relevant for leadership roles, not universally satisfying.
C. Repetitive assignments: Often lead to boredom and dissatisfaction.
D. Delegation of authority: May not appeal to all employees or impact satisfaction significantly.
International HR
Reference: Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory: Task variety contributes to job satisfaction.
정답:
Explanation:
Monitoring Internal Social Platforms:
Internal social platforms provide insights into employee interactions, concerns, and overall sentiment, offering a pulse on workplace morale.
Why Gauging Employee Morale is Correct:
Monitoring these platforms helps HR identify issues, improve engagement, and address challenges affecting employee satisfaction and productivity.
Eliminating Incorrect Options:
A. To encourage self-management: Internal platforms are not focused on self-management practices.
B. To encourage social behaviors: Encouraging behavior is secondary to understanding morale.
C. To gauge employee absenteeism: Absenteeism is tracked through attendance systems, not social platforms.
International HR
Reference: Gallup Employee Engagement Reports: Highlights monitoring tools for assessing morale.
정답:
Explanation:
Work-Life Balance Initiatives:
Flex-time allows employees to choose start and end times within core working hours, offering flexibility to accommodate personal needs.
A compressed schedule allows employees to work longer hours over fewer days, providing additional days off.
Why These Options are Correct:
Both arrangements reduce stress and improve work-life integration, enhancing overall job satisfaction and retention.
Eliminating Incorrect Options:
C. Training schedule: Training is unrelated to work-life balance.
D. Internal transfers: Focuses on career progression, not work-life integration.
E. Use of temporary employees: Addresses staffing flexibility but not employee work-life balance directly.
International HR
Reference: SHRM Guidelines on Work-Life Balance: Highlights flex-time and compressed schedules as key practices.
정답:
Explanation:
Definition of Contingent Employees:
Contingent employees include temporary workers, independent contractors, and on-call workers who are not part of an organization’s permanent workforce.
Why Contingent Employees is Correct:
These workers are hired to address short-term or specific needs and often lack traditional employment benefits such as healthcare or job security.
Eliminating Incorrect Options:
A. Diversity management: Focuses on fostering inclusivity and equity, not employment types.
C. Flexible work programs: Refers to alternative work arrangements (e.g., telecommuting, flex-time).
D. Part-time employment: Part-time workers are a subset of employees, not synonymous with contingent employees.
International HR
Reference: ILO Non-Standard Employment Reports: Addresses contingent workforce practices.
정답:
Explanation:
When an employee willingly leaves an organization, it is referred to as a resignation. The employee voluntarily informs the organization of their intent to leave, typically providing a notice period.
Explanation of Other Options:
A. Layout: Incorrect term, likely a typo for "layoff," which is involuntary.
C. Separation: A broader term that can include voluntary and involuntary departures.
D. Termination: Implies the organization initiated the employee's departure.
Reference: SHRM - Candidate Selection Guidelines
CIPD - Stakeholder Analysis and Definitions
ILO - Job Competencies Framework
Harvard Business Review - Resignation Best Practices and Management