VMware NSX 4.x Professional 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년11월17일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 VMware 2V0-41.23 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 2V0-41.23 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 70개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
From the NSX UI the status of the VMware Identity Manager Integration must be “Enabled”. According to the VMware NSX Documentation1, after configuring VMware Identity Manager integration, you can validate the functionality by checking the status of the integration in the NSX UI. The status should be “Enabled” if the integration is successful. The other options are either incorrect or not relevant.
정답:
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX 4.x Professional documents and tutorials, BFD is a failover detection protocol that provides fast and reliable detection of link failures between two routing devices. BFD can be used with ECMP routing to monitor the health of the ECMP paths and trigger a route change in case of a failure12. BFD is supported by both BGP and OSPF routing protocols in NSX-T3. BFD can also be configured with different timers to achieve different detection times3.
정답:
Explanation:
According to the web search results, the command that is used to verify the Local Control Plane (LCP) connectivity with Central Control Plane (CCP) on ESXi is get control-cluster status. This command displays the status of the LCP and CCP components on the ESXi host, such as the LCP agent, CCP client, CCP server, and CCP connection. It also shows the IP address and port number of the CCP server that the LCP agent is connected to. If the LCP agent or CCP client are not running or not connected, it means that there is a problem with the LCP connectivity.
정답:
Explanation:
esxcfg-nics -l and esxcli network nic list are two CLI commands that can be used to see the vmnic link status on an ESXi host. Both commands display information such as the vmnic name, driver, link state, speed, and duplex mode. The link state can be either Up or Down, indicating whether the vmnic is connected or not.
For example, the output of esxcfg-nics -l can look like this:
Name PCI Driver Link Speed Duplex MAC Address MTU Description
vmnic0 0000:02:00.0 igbn Up 1000Mbps Full 00:50:56:01:2a:3b 1500 Intel Corporation I350 Gigabit Network Connection
vmnic1 0000:02:00.1 igbn Down 0Mbps Half 00:50:56:01:2a:3c 1500 Intel Corporation I350 Gigabit Network Connection
정답:
Explanation:
L2 VPN is a feature of NSX that allows extending Layer 2 networks across different sites or clouds over an IPsec tunnel. L2 VPN has an advantage of enabling VM mobility with re-IP, which means that VMs can be moved from one site to another without changing their IP addresses or network configurations. This is possible because L2 VPN allows both sites to use the same broadcast domain, which means that they share the same subnet and VLAN.
정답:
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation, these are two of the features that are supported for the Standard NSX Application Platform Deployment:
- NSX Network Detection and Response: This feature provides advanced threat detection and response capabilities for network and application security. It includes features such as Distributed Intrusion Detection and Prevention (IDS/IPS), Web Reputation Analysis, File and Process Analysis, and NSX Advanced Threat Prevention.
- NSX Intrinsic Security: This feature provides built-in security for applications and workloads across clouds. It includes features such as Distributed Firewall, Identity Firewall, Service Insertion, Micro-segmentation, and Policy-based Automation.
정답:
Explanation:
According to the web search results, the command that is used to test management connectivity from a transport node to NSX Manager is get managers. This command displays the status, IP address, and thumbprint of the NSX Manager that the transport node is connected to. It also shows the connection state, which can be UP or DOWN. If the connection state is DOWN, it means that there is a problem with the management connectivity.
정답:
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX 4.x Professional documents and tutorials, NSX-T has two logical router components, namely the Services Router (SR) and the Distributed Router (DR). As the names imply, SR is where centralized services are provisioned such as NAT, DHCP, VPN, Perimeter Firewall, Load Balancing, etc., and DR performs distributed routing across all hosts participating in a given transport zone3. The DR component is present in both Tier-0 and Tier-1 logical routers, while the SR component is only present in Tier-1 logical routers or in active-standby mode of Tier-0 logical routers4. Therefore, the logical router components that span across all transport nodes are TIER0_DISTRIBUTED_ROUTER and DISTRIBUTED_ROUTER_TIER1.
정답:
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation1, TraceFlow supports four types of traffic: Unicast, Broadcast, Multicast, and Anycast. Unicast traffic is sent to a specific destination IP address. Broadcast traffic is sent to all hosts on a network segment. Multicast traffic is sent to a group of hosts that have joined a multicast group. Anycast traffic is sent to the nearest or best destination among a group of hosts that share the same IP address.
Anycast traffic is useful for validating connectivity between virtual machines that reside on different segments, because it can test the routing and firewall rules that apply to the traffic. Anycast traffic can also help identify the optimal path for the traffic based on factors such as latency, bandwidth, and load balancing.

정답: The correct order of the rule processing steps of the Distributed Firewall is as follows:
- Packet arrives at vfilter connection table. If matching entry in the table, process the packet.
- If connection table has no match, compare the packet to the rule table.
- If the packet matches source, destination, service, profile and applied to fields, apply the action defined.
- If the rule table action is allow, create an entry in the connection table and forward the packet.
- If the rule table action is reject or deny, take that action.
This order is based on the description of how the Distributed Firewall works in the web search results1. The first step is to check if there is an existing connection entry for the packet in the vfilter connection table, which is a cache of flow entries for rules with an allow action. If there is a match, the packet is processed according to the connection entry. If there is no match, the packet is compared to the rule table, which contains all the security policy rules. The rules are evaluated from top to bottom until a match is found. The match criteria include source, destination, service, profile and applied to fields. The action defined by the matching rule is applied to the packet. The action can be allow, reject or deny. If the action is allow, a new connection entry is created for the packet and the packet is forwarded to its destination. If the action is reject or deny, the packet is dropped and an ICMP message or a TCP reset message is sent back to the source.
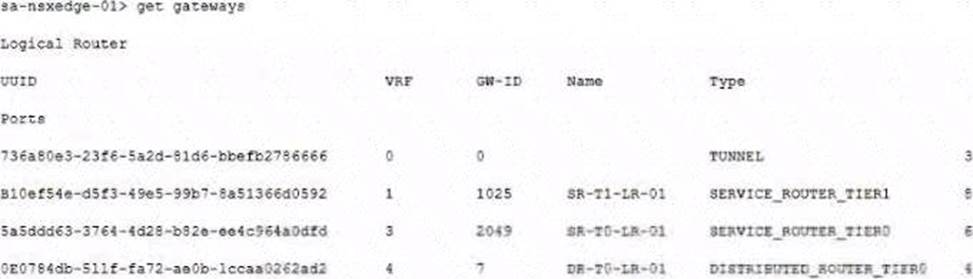
정답:
Explanation:
According to the image that you sent, the BGP neighbor is configured on the tier-0 gateway with the UUID 9f8e3a7c-5f9c-4d1a-bb6f-9c7f3d6f3d63 and the VRF ID 4. Therefore, to check the BGP neighbor status, you need to enter the VRF context of 4 and execute the get bgp neighbor command on the tier-0 service router (SR) node.
The other options are either incorrect or not applicable for this scenario. vrf 1, vrf 3, and sa-nexedge-01(tier1_dr)> get bgp neighbor are not related to the BGP neighbor configuration on the tier-0 gateway. sa-nexedge-01(tier1_sr> get bgp neighbor is also not relevant, as there is no BGP neighbor configured on the tier-1 gateway.
정답:
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation, a non-preemptive failover policy means that the original failed node will not become the active node upon recovery, unless the current active node fails again. This policy can help avoid unnecessary failovers and ensure stability.
The other options are either incorrect or not available for this configuration. Preemptive is the opposite of non-preemptive, meaning that the original failed node will become the active node upon recovery, if it has a higher priority than the current active node. Enable Preemptive and Disable Preemptive are not valid options for the failover policy, as the failover policy is a drop-down menu that only has two choices: Preemptive and Non-Preemptive.
정답:
Explanation:
- AS-Path Prepend: This attribute allows you to prepend one or more AS numbers to the AS path of a route, making it appear longer and less preferable to other BGP routers. You can use this attribute to manipulate the inbound traffic from your BGP peers by advertising a longer AS path for some routes and a shorter AS path for others.
- MED: This attribute stands for Multi-Exit Discriminator and allows you to specify a preference value for a route among multiple exit points from an AS. You can use this attribute to manipulate the outbound traffic to your BGP peers by advertising a lower MED value for some routes and a higher MED value for others.
정답:
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation1, core files and audit logs can contain sensitive information and should be excluded from the support bundle unless requested by VMware technical support. Controller files and management files are not mentioned as containing sensitive information.
정답:
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation1, NSX-T Data Center supports the following types of DHCP configuration on a segment:
- Local DHCP server: This option creates a local DHCP server that has an IP address on the segment and provides dynamic IP assignment service only to the VMs that are attached to the segment.
- Gateway DHCP server: This option is attached to a tier-0 or tier-1 gateway and provides DHCP service to the networks (overlay segments) that are directly connected to the gateway and configured to use a gateway DHCP server.
- DHCP Relay: This option relays the DHCP client requests to the external DHCP servers that can be in any subnet, outside the SDDC, or in the physical network.